F2 F2 Fig. Q1.a. Complete 3D view Fig. Q1.b. Front view Fig. Q1.c. Cross section Point P is on the inclined plane (i.e., shaded plane) and on the front surface of the beam, which is subjected to external force F. (Fig. Q1.a.). The shaded plane is inclined by angle 0 with respect to negative Z axis (Fig. Q1.b.). The point P is in-plane stress state - stresses in X axis are zero - since point P is on the beam surface. At the point P, a normal vector of the cross-section, of which angle with Z axis is zero, is in parallel with Z axis. The cross-section dimension is shown in Fig. Q1.c. Assumption: Disregard Poisson's effect. Given: F= 50 N; h = 220 mm; w = 900 mm 1. Draw a 2D Mohr's circle (M.C.) - present explicitly radius, center, and principal stresses in the M.C. - by considering only stress components in Y-Z space at point P in Fig. Q1.b. 2. For a case when 0 is 35°, please calculate a normal stress and a shear stress, which occur the shaded plane, at point P. Also, draw the stress states with a square element that has sides in parallel with the inclined plane (Fig. Q1.b.) when 0 is 35° 3. Calculate maximum shear stress at point P using the M.C. drawn in 1); and find an angle 0 of the inclined plane (Fig. Q1.b.) where maximum shear stress occurs
F2 F2 Fig. Q1.a. Complete 3D view Fig. Q1.b. Front view Fig. Q1.c. Cross section Point P is on the inclined plane (i.e., shaded plane) and on the front surface of the beam, which is subjected to external force F. (Fig. Q1.a.). The shaded plane is inclined by angle 0 with respect to negative Z axis (Fig. Q1.b.). The point P is in-plane stress state - stresses in X axis are zero - since point P is on the beam surface. At the point P, a normal vector of the cross-section, of which angle with Z axis is zero, is in parallel with Z axis. The cross-section dimension is shown in Fig. Q1.c. Assumption: Disregard Poisson's effect. Given: F= 50 N; h = 220 mm; w = 900 mm 1. Draw a 2D Mohr's circle (M.C.) - present explicitly radius, center, and principal stresses in the M.C. - by considering only stress components in Y-Z space at point P in Fig. Q1.b. 2. For a case when 0 is 35°, please calculate a normal stress and a shear stress, which occur the shaded plane, at point P. Also, draw the stress states with a square element that has sides in parallel with the inclined plane (Fig. Q1.b.) when 0 is 35° 3. Calculate maximum shear stress at point P using the M.C. drawn in 1); and find an angle 0 of the inclined plane (Fig. Q1.b.) where maximum shear stress occurs
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305578296
Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Chapter33: Hydronic Heat
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 28RQ: The varying intensity of the sun's energy that reaches the earth is due in part to the A. solar...
Related questions
Question
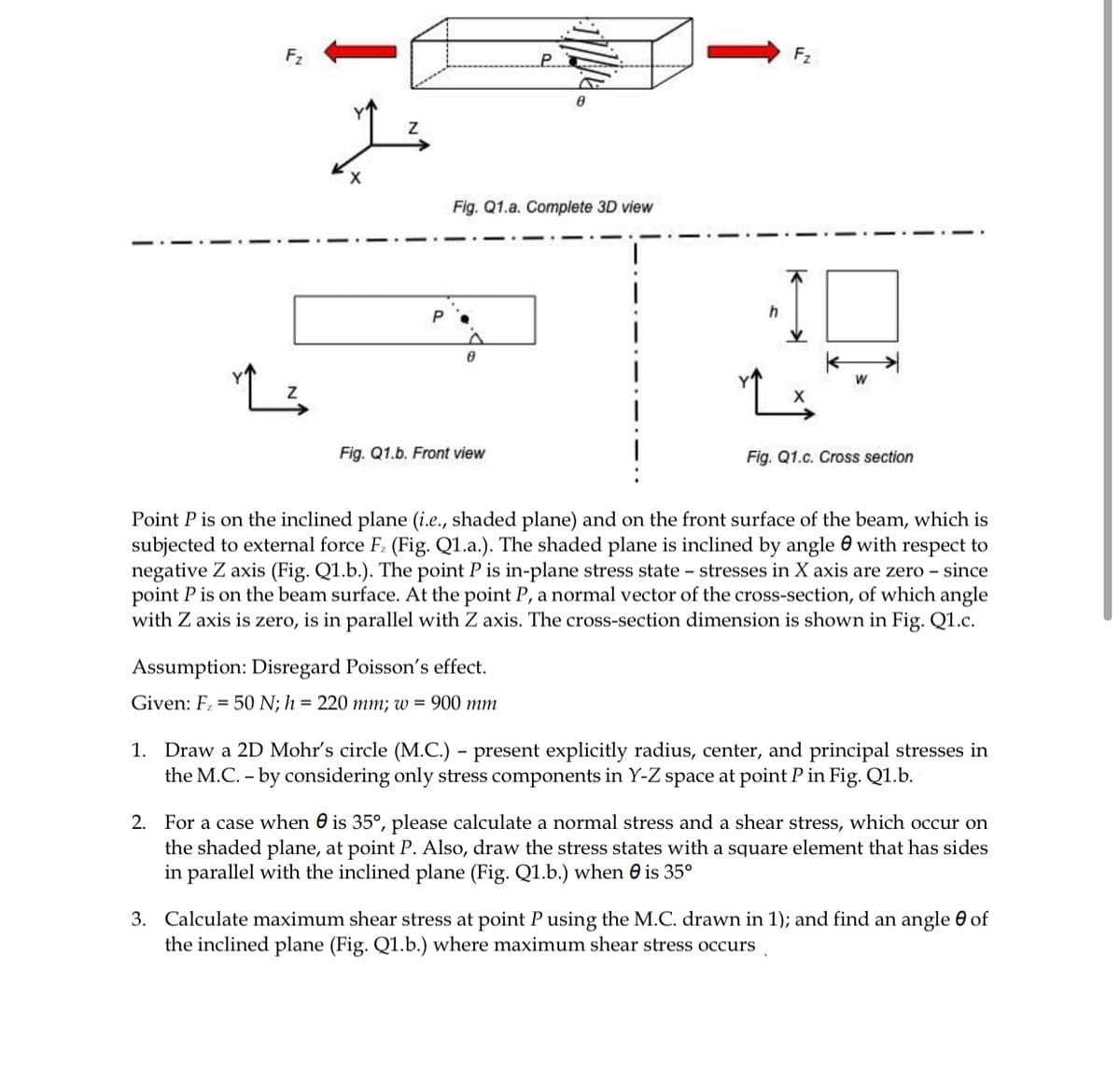
Transcribed Image Text:F2
F2
Fig. Q1.a. Complete 3D view
Fig. Q1.b. Front view
Fig. Q1.c. Cross section
Point P is on the inclined plane (i.e., shaded plane) and on the front surface of the beam, which is
subjected to external force F: (Fig. Q1.a.). The shaded plane is inclined by angle e with respect to
negative Z axis (Fig. Q1.b.). The point P is in-plane stress state – stresses in X axis are zero - since
point P is on the beam surface. At the point P, a normal vector of the cross-section, of which angle
with Z axis is zero, is in parallel with Z axis. The cross-section dimension is shown in Fig. Q1.c.
Assumption: Disregard Poisson's effect.
Given: F = 50 N; h = 220 mm; w = 900 mm
1. Draw a 2D Mohr's circle (M.C.) – present explicitly radius, center, and principal stresses in
the M.C. - by considering only stress components in Y-Z space at point P in Fig. Q1.b.
-
2. For a case when 0 is 35°, please calculate a normal stress and a shear stress, which occur on
the shaded plane, at point P. Also, draw the stress states with a square element that has sides
in parallel with the inclined plane (Fig. Q1.b.) when e is 35°
3. Calculate maximum shear stress at point P using the M.C. drawn in 1); and find an angle 0 of
the inclined plane (Fig. Q1.b.) where maximum shear stress occurs
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning