Figure 6 (a) shows the circuit diagram for a differential amplifier. You may assume that M and M2 have identical parameters. Referring to Figure 6 (a): (a) What kind of amplifier is it? What is its role in a three-stage op amp? Draw the small signal equivalent circuit and derive the differential voltage gain Adiff. For the analysis consider RD1 = RD2 RD, gml gm2 = gm, and rol = ro2 = r >Rp. State any assumption. (b) What is the new Adiff in the circuit of Figure 6 (b), where a PMOS current source has replaced the two drain resistors RpI = RD2 = RD and a NMOS current sink has replaced the source resistor Rs? (c) What are the advantages in using the circuit of Figure 6 (b) instead of Figure 6 (a) to realize an op amp? (d)
Figure 6 (a) shows the circuit diagram for a differential amplifier. You may assume that M and M2 have identical parameters. Referring to Figure 6 (a): (a) What kind of amplifier is it? What is its role in a three-stage op amp? Draw the small signal equivalent circuit and derive the differential voltage gain Adiff. For the analysis consider RD1 = RD2 RD, gml gm2 = gm, and rol = ro2 = r >Rp. State any assumption. (b) What is the new Adiff in the circuit of Figure 6 (b), where a PMOS current source has replaced the two drain resistors RpI = RD2 = RD and a NMOS current sink has replaced the source resistor Rs? (c) What are the advantages in using the circuit of Figure 6 (b) instead of Figure 6 (a) to realize an op amp? (d)
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Stephen L. Herman
Chapter18: Resistive-inductive Parallel Circuits
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13PP: In an R-L parallel circuit, IT=1.25 amps, R=1.2k, and XL=1k. Find IR
Related questions
Question
100%
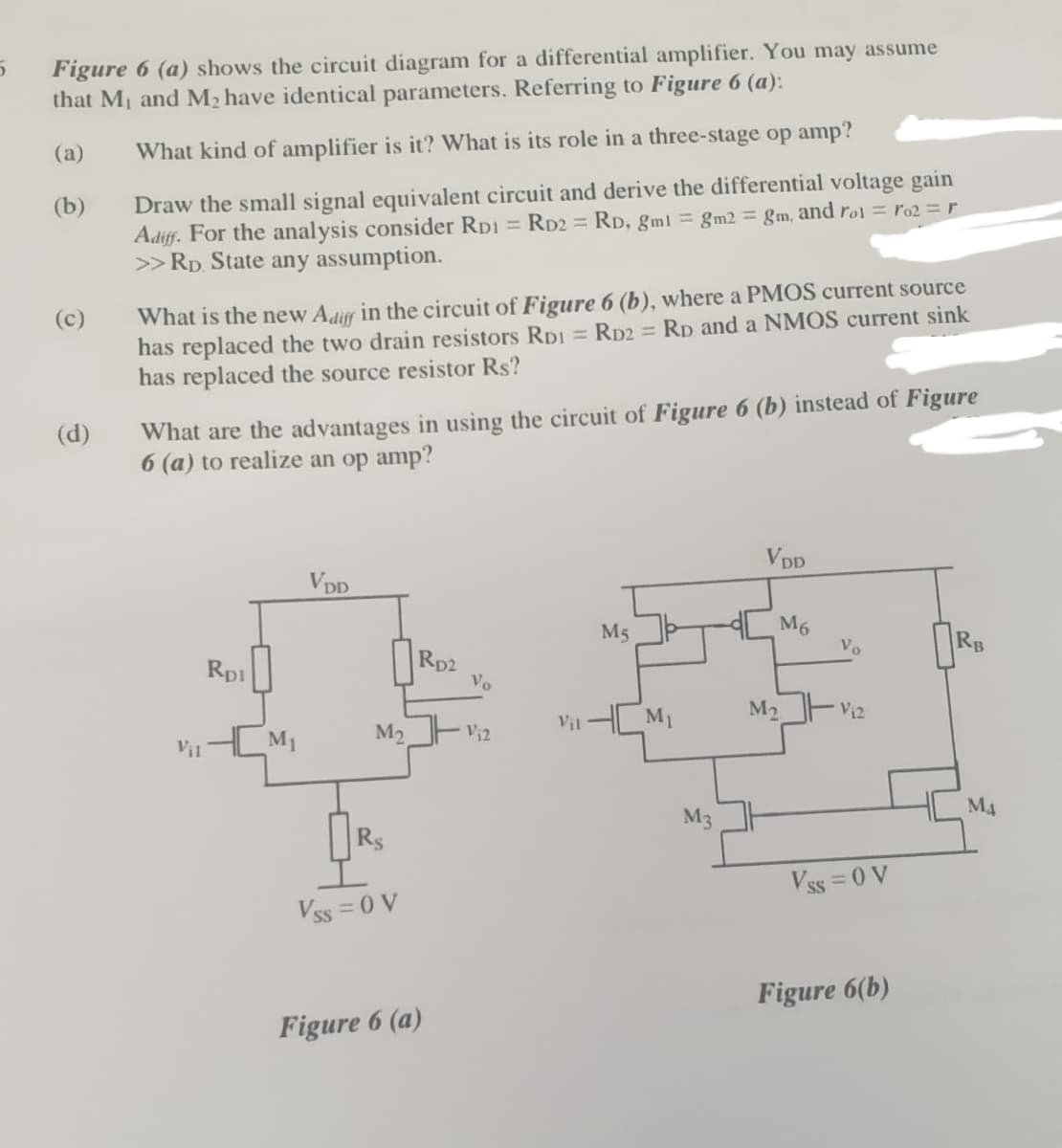
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 6 (a) shows the circuit diagram for a differential amplifier. You may assume
that M1 and M2 have identical parameters. Referring to Figure 6 (a):
(а)
What kind of amplifier is it? What is its role in a three-stage op amp?
Draw the small signal equivalent circuit and derive the differential voltage gain
Adiff. For the analysis consider RD1 = RD2 = RD, gml = gm2 gm, and rol = ro2 =r
>>Rp. State any assumption.
(b)
What is the new Adiff in the circuit of Figure 6 (b), where a PMOS current source
has replaced the two drain resistors RpI = RD2 = RD and a NMOS current sink
has replaced the source resistor Rs?
(c)
What are the advantages in using the circuit of Figure 6 (b) instead of Figure
6 (a) to realize an op amp?
(d)
VDD
VDD
M6
Vo
M5
RB
Rp1
Rp2
Vo
M1
M2
V12
Vil
M1
M2
Vi2
Vi1
M4
M3
Rs
Vss = 0 V
%3D
Vss = 0 V
Figure 6(b)
Figure 6 (a)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning