Figure.2 shows the heat transfer rate per unit width (normal to the page) from a longitudinal section, x2-x₁, can be expressed as 912 = h₁2(x2-x1)(Ts - T∞), where h₁₂ is the average coefficient for the section of length (x2-x1). Consider laminar flow over a flat plate with a uniform temperature Ts. The spatial variation of the local convection coefficient is of the form hx =Cx², where C is a const To loo x2 dx 912 TSK Fig.2. A heat transfer of a longitudinal plate (a) Beginning with the convection rate equation in the form dq' = hxdx(Ts - T∞), derive an expression for h₁₂ in terms of C, x₁, andx2. (b) Derive an expression for h₁₂ in terms of x1, x2, and the average coefficients and h₂, corresponding to lengths x₁, andx2., respectively.
Figure.2 shows the heat transfer rate per unit width (normal to the page) from a longitudinal section, x2-x₁, can be expressed as 912 = h₁2(x2-x1)(Ts - T∞), where h₁₂ is the average coefficient for the section of length (x2-x1). Consider laminar flow over a flat plate with a uniform temperature Ts. The spatial variation of the local convection coefficient is of the form hx =Cx², where C is a const To loo x2 dx 912 TSK Fig.2. A heat transfer of a longitudinal plate (a) Beginning with the convection rate equation in the form dq' = hxdx(Ts - T∞), derive an expression for h₁₂ in terms of C, x₁, andx2. (b) Derive an expression for h₁₂ in terms of x1, x2, and the average coefficients and h₂, corresponding to lengths x₁, andx2., respectively.
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter8: Natural Convection
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8.54P
Related questions
Question
Hello, I am a
Thank you very much
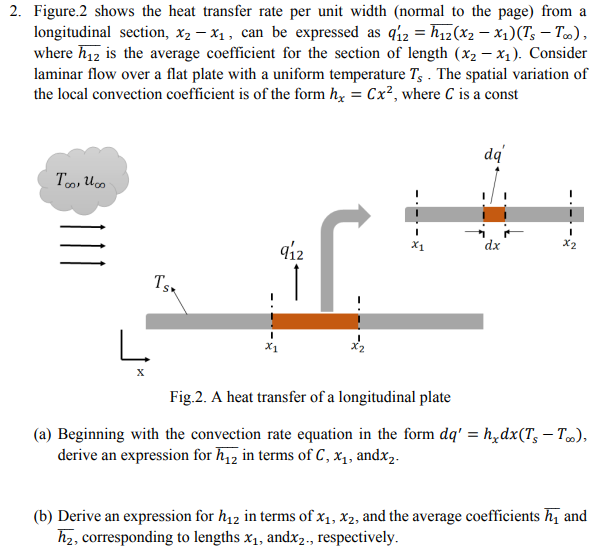
Transcribed Image Text:2. Figure 2 shows the heat transfer rate per unit width (normal to the page) from a
longitudinal section, x₂ - x₁, can be expressed as q12 = h₁2(x2 − x₁)(Ts - Too),
where h₁2 is the average coefficient for the section of length (x₂-x₁). Consider
laminar flow over a flat plate with a uniform temperature T. The spatial variation of
the local convection coefficient is of the form hx = Cx², where C is a const
Too, Uco
111
TSK
L
X
912
X1
I
x2
I
X1
dq
dx
I
X2
Fig.2. A heat transfer of a longitudinal plate
(a) Beginning with the convection rate equation in the form dq' =h_dx(T, -T),
derive an expression for h₁2 in terms of C, x₁, andx₂.
(b) Derive an expression for h₁2 in terms of x₁, x2, and the average coefficients h₁ and
h₂, corresponding to lengths x₁, andx₂., respectively.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning