Find the determinant. x² -Ed 2x 5x4 W(x5, x²) = = (x²)(5x4) - (2x)(x5) The Wronskian ---Select--- equal to 0 for every x in the interval (0, ∞o), therefore the set of solutions ---Select--- linearly independent. Submit Skip (you cannot come back)
Find the determinant. x² -Ed 2x 5x4 W(x5, x²) = = (x²)(5x4) - (2x)(x5) The Wronskian ---Select--- equal to 0 for every x in the interval (0, ∞o), therefore the set of solutions ---Select--- linearly independent. Submit Skip (you cannot come back)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:James Stewart
Chapter1: Functions And Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Question
100%
Transcribed Image Text:N?
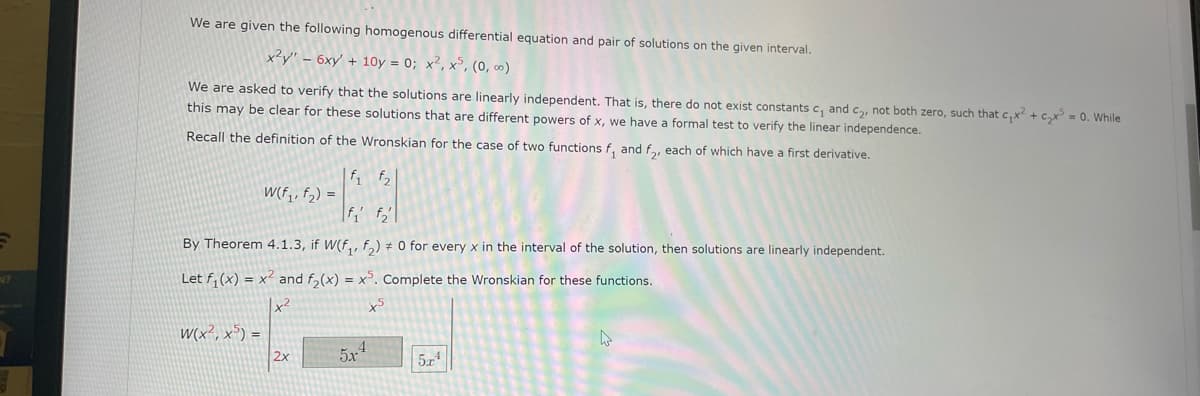
We are given the following homogenous differential equation and pair of solutions on the given interval.
x²y" - 6xy' +10y = 0; x², x5, (0,00)
We are asked to verify that the solutions are linearly independent. That is, there do not exist constants c₁ and c₂, not both zero, such that c₁x² + ₂x³ = 0. While
this may be clear for these solutions that are different powers of x, we have a formal test to verify the linear independence.
Recall the definition of the Wronskian for the case of two functions f, and f₂, each of which have a first derivative.
W(f₁, f₂) =
W(x², x5)=
By Theorem 4.1.3, if W(f₁, f₂) = 0 for every x in the interval of the solution, then solutions are linearly independent.
Let f₁(x) = x² and f₂(x) = x³. Complete the Wronskian for these functions.
f₁ f₂
2x
5x4
5.4
Transcribed Image Text:ON?
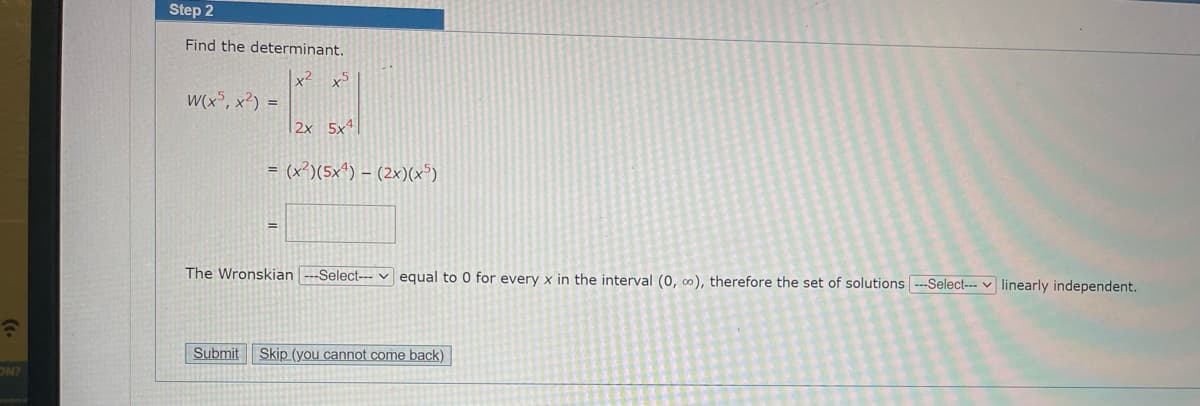
Step 2
Find the determinant.
W(x5, x²) =
x5
2
2x 5x4
= (x²)(5x4) (2x)(x5)
The Wronskian ---Select--- equal to 0 for every x in the interval (0, ∞o), therefore the set of solutions ---Select--- linearly independent.
Submit Skip (you cannot come back)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781319050740
Author:
Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:
9781337552516
Author:
Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:
Cengage Learning