Fluid Mechanics
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
Fluid
Transcribed Image Text:Faculty of Engineering
Department: - Civil Engineering
UNIVERSITY or BISA
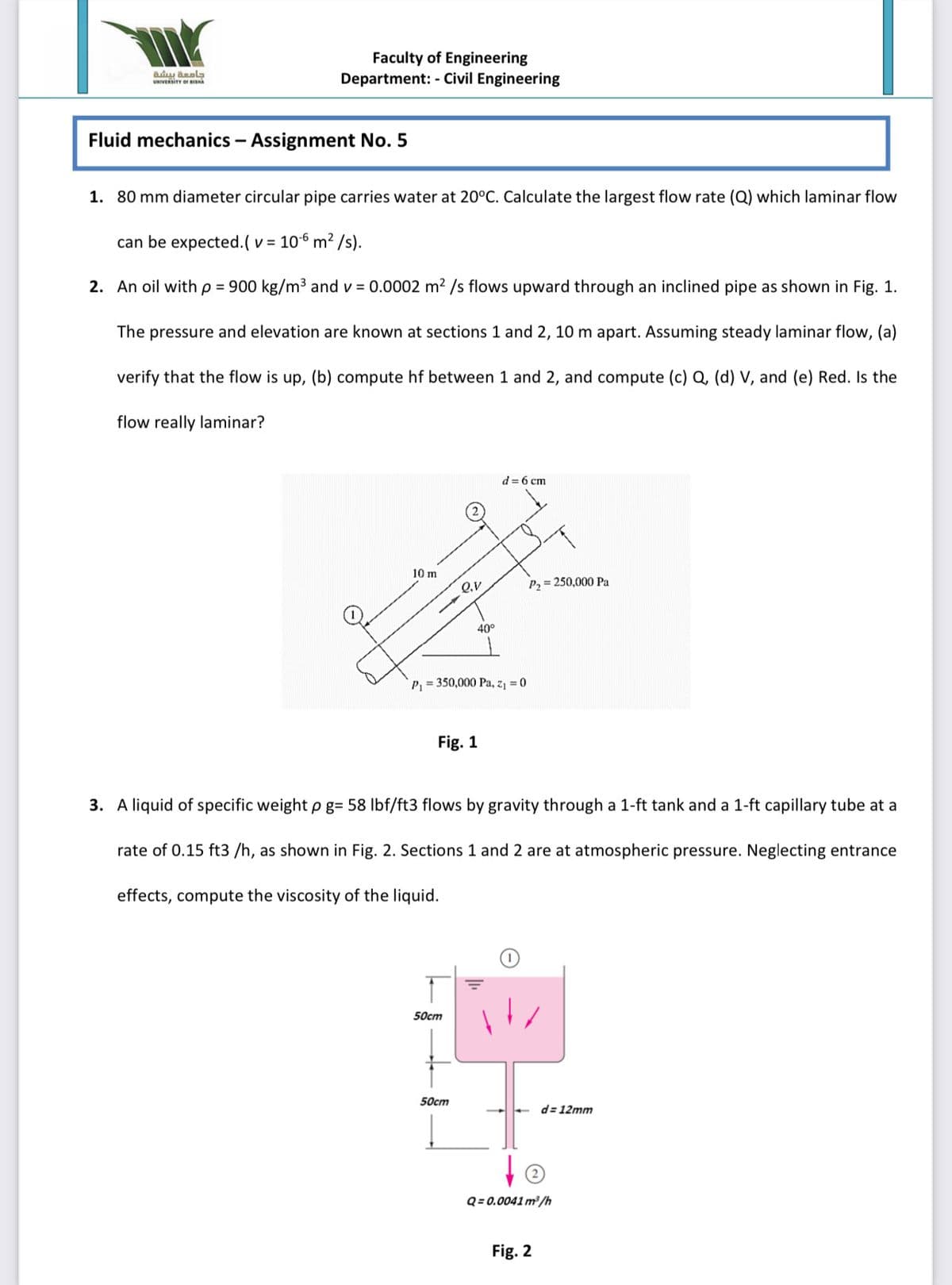
Fluid mechanics - Assignment No. 5
1. 80 mm diameter circular pipe carries water at 20°C. Calculate the largest flow rate (Q) which laminar flow
can be expected.( v = 106 m² /s).
2. An oil with p = 900 kg/m³ and v = 0.0002 m2 /s flows upward through an inclined pipe as shown in Fig. 1.
The pressure and elevation are known at sections 1 and 2, 10 m apart. ASsuming steady laminar flow, (a)
verify that the flow is up, (b) compute hf between 1 and 2, and compute (c) Q, (d) V, and (e) Red. Is the
flow really laminar?
d= 6 cm
10 m
Q.V
P2 = 250,000 Pa
40°
P, = 350,000 Pa, z = 0
Fig. 1
3. A liquid of specific weight p g= 58 lbf/ft3 flows by gravity through a 1-ft tank and a 1-ft capillary tube at a
rate of 0.15 ft3 /h, as shown in Fig. 2. Sections 1 and 2 are at atmospheric pressure. Neglecting entrance
effects, compute the viscosity of the liquid.
50cm
50cm
d= 12mm
Q = 0.0041 m³/h
Fig. 2
Transcribed Image Text:Faculty of Engineering
Department: - Civil Engineering
UNIVERSITY or BISA
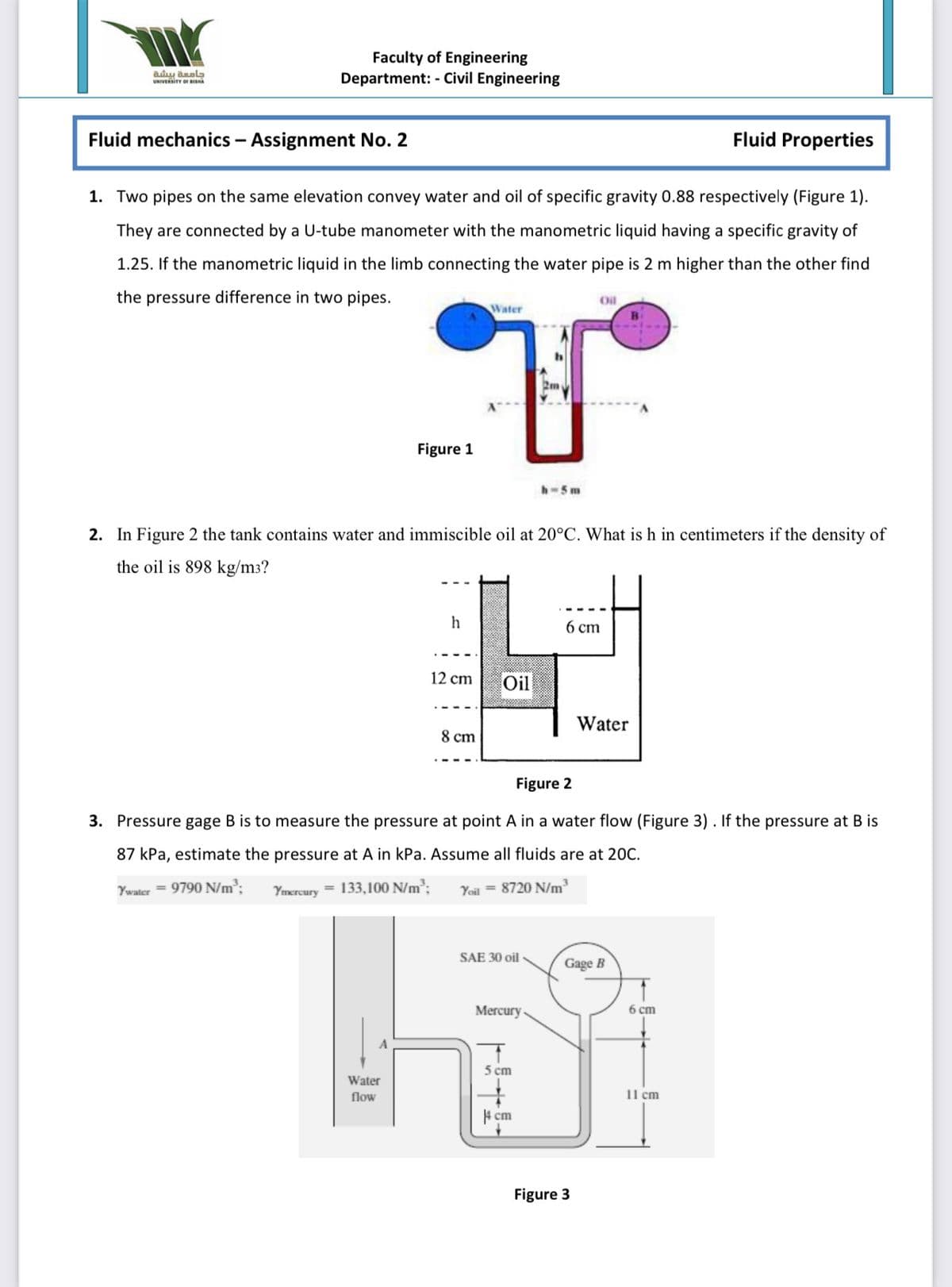
Fluid mechanics - Assignment No. 2
Fluid Properties
1. Two pipes on the same elevation convey water and oil of specific gravity 0.88 respectively (Figure 1).
They are connected by a U-tube manometer with the manometric liquid having a specific gravity of
1.25. If the manometric liquid in the limb connecting the water pipe is 2 m higher than the other find
the pressure difference in two pipes.
Oil
Water
B.
Figure 1
h-5m
2. In Figure 2 the tank contains water and immiscible oil at 20°C. What is h in centimeters if the density of
the oil is 898 kg/m3?
h
6 ст
12 cm
Oil
Water
8 cm
Figure 2
3. Pressure gage B is to measure the pressure at point A in a water flow (Figure 3). If the pressure at B is
87 kPa, estimate the pressure at A in kPa. Assume all fluids are at 20C.
Ywater = 9790 N/m³:
Ymercury = 133,100 N/m³;
Yoil = 8720 N/m³
SAE 30 oil
Gage B
Mercury
6 cm
5 cm
Water
flow
11 cm
4 cm
Figure 3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning