For all sets A, B,C.Then: (AUB) – (C – A) = AU(B The following algebraic proof is almost finished. You must provide a reason for every step that exactly justifies what was done in the step. (Fill the number into the box) As a reminder the 12 rules are: 1. Commutative Law 2. Associative Law 3. Distributive Law 4. Identity Law 5. Complement Law 6. Double Complement Law 7. Idempotent Law 8. Universal Bound Law 9. De Morgan's Law 10. Absorption Law 11. Complements of U and Empty Set 12. Set Difference Law Proof: Let A, B,C be any sets. Then: by LHS = (AUB) - (C – A) = (AU B) - (CN A°) by = (AUB)n (CN A^)° by = (AU B) N (C° U(A°)*) by = (AU B)n (CUA)
For all sets A, B,C.Then: (AUB) – (C – A) = AU(B The following algebraic proof is almost finished. You must provide a reason for every step that exactly justifies what was done in the step. (Fill the number into the box) As a reminder the 12 rules are: 1. Commutative Law 2. Associative Law 3. Distributive Law 4. Identity Law 5. Complement Law 6. Double Complement Law 7. Idempotent Law 8. Universal Bound Law 9. De Morgan's Law 10. Absorption Law 11. Complements of U and Empty Set 12. Set Difference Law Proof: Let A, B,C be any sets. Then: by LHS = (AUB) - (C – A) = (AU B) - (CN A°) by = (AUB)n (CN A^)° by = (AU B) N (C° U(A°)*) by = (AU B)n (CUA)
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Chapter1: Line And Angle Relationships
Section1.3: Introduction To Geometric Proof
Problem 23E: In Exercises 23 to 24, fill in the missing reasons for the algebraic proof. Given: 3(x5)=21 Prove:...
Related questions
Question
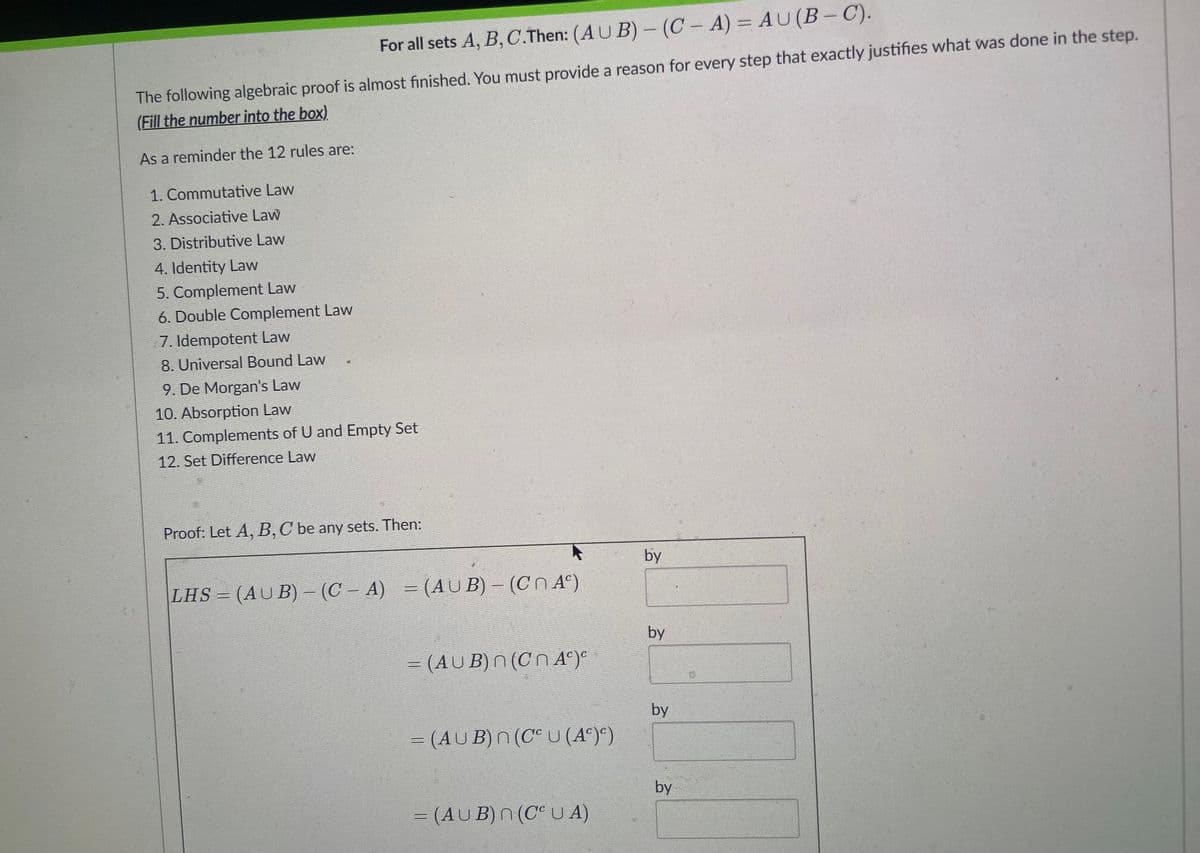
Transcribed Image Text:For all sets A, B, C.Then: (AU B)- (C - A) = AU(B – C).
The following algebraic proof is almost finished. You must provide a reason for every step that exactly justifies what was done in the step.
(Fill the number into the box)
As a reminder the 12 rules are:
1. Commutative Law
2. Associative Law
3. Distributive Law
4. Identity Law
5. Complement Law
6. Double Complement Law
7. Idempotent Law
8. Universal Bound Law
9. De Morgan's Law
10. Absorption Law
11. Complements of U and Empty Set
12. Set Difference Law
Proof: Let A, B,C be any sets. Then:
by
LHS = (AU B) - (C – A) = (AUB) - (Cn A°)
by
= (AUB)n (Cn A°)°
%3D
by
= (AU B)n(Ce U (A°))
by
= (AUB)n (C U A)

Transcribed Image Text:Is the following proposition true or false?
For all sets A and B :
A x (B – A) = A x B.
(Select all the choices that apply)
No, and I can disprove it by finding a counterexample.
O Yes, and I can prove it using the element method.
O Yes, and I can prove it using the algebraic method.
| cannot tell with the given information.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage