For any two sets A and B, if m* (A) = 0, then m* (AUB) = m* (B). In particular, if BCA, then m* (B) = 0.
For any two sets A and B, if m* (A) = 0, then m* (AUB) = m* (B). In particular, if BCA, then m* (B) = 0.
Chapter9: Sequences, Probability And Counting Theory
Section9.5: Counting Principles
Problem 38SE: Suppose a set A has 2,048 subsets. How many distinct objects are contained in A?
Related questions
Question
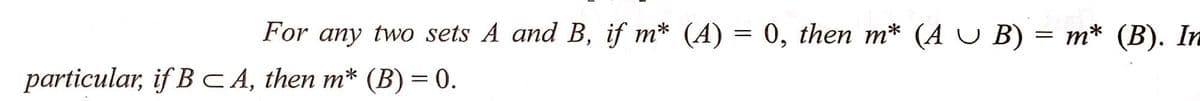
Transcribed Image Text:For any two sets A and B, if m* (A) = 0, then m* (AUB) = m* (B). In
particular, if BCA, then m* (B) = 0.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

