An air stream is contaminated by 100 ppm (on a molar basis) of compound X. You wish to remove compound X from the air by condensation. 100 ppm (parts per million) = 0.01 mol% = 10-4 mol fraction. Please mark answers on graph when applicable
An air stream is contaminated by 100 ppm (on a molar basis) of compound X. You wish to remove compound X from the air by condensation. 100 ppm (parts per million) = 0.01 mol% = 10-4 mol fraction.
Please mark answers on graph when applicable
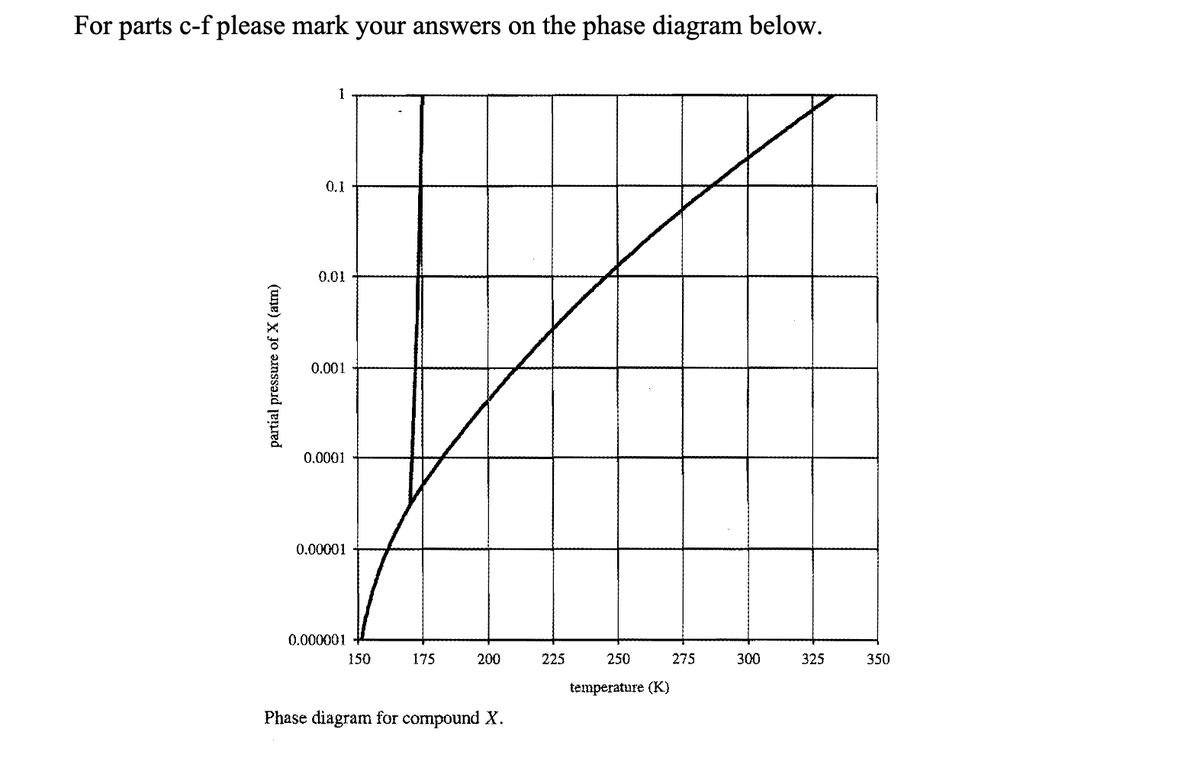
c) Consider the phase diagram of compound X shown above. Locate the point on the
graph that corresponds to 100 molar ppm of compound X in air at 300 K and 1 atm.
d) If the contaminated air is cooled at constant pressure (1 atm), at what temperature
will compound X start to condense?
e) To what temperature must you cool the air (at total pressure of 1 atm) to reduce the
contamination level to 10 ppm?
f) If the contaminated air is compressed at constant temperature (300 K), at what
pressure will compound X start to condense?
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

for question C, why is the dot at when the atm is 1 rather than 0.0001?








