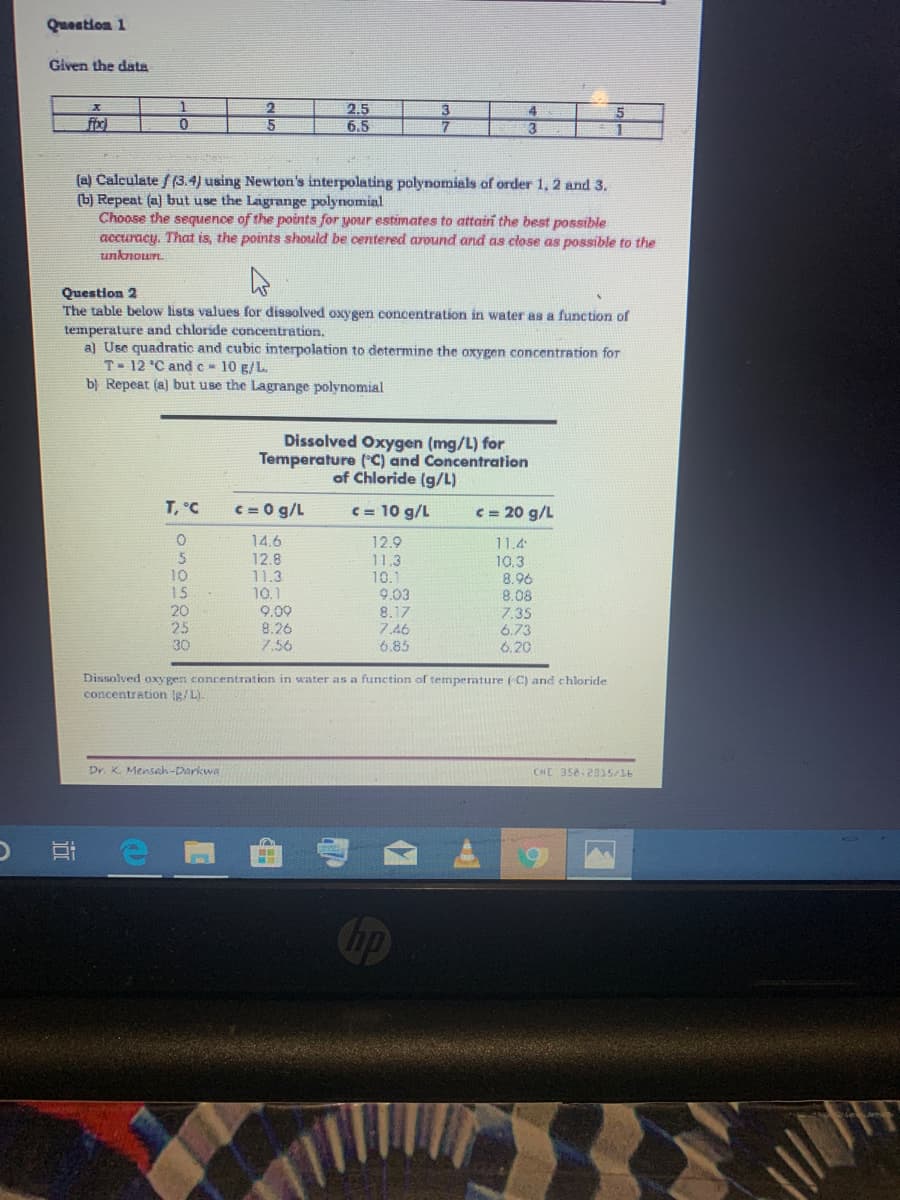
Given the data X 1 0 5 2.5 6.5 3 7 (a) Calculate / (3.4) using Newton's interpolating polynomials of order 1, 2 and 3. [b] Repeat (a) but use the Lagrange polynomial Choose the sequence of the points for your estimates to attain the best possibla 5 1
Given the data X 1 0 5 2.5 6.5 3 7 (a) Calculate / (3.4) using Newton's interpolating polynomials of order 1, 2 and 3. [b] Repeat (a) but use the Lagrange polynomial Choose the sequence of the points for your estimates to attain the best possibla 5 1
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter7: Analytic Trigonometry
Section7.3: The Addition And Subtraction Formulas
Problem 76E
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:D
Question 1
Given the data
x
fibx)
1
0
T, °C
6505228
10
(a) Calculate / (3.4) using Newton's interpolating polynomials of order 1, 2 and 3.
(b) Repeat (a) but use the Lagrange polynomial
Choose the sequence of the points for your estimates to attain the best possible
accuracy. That is, the points should be centered around and as close as possible to the
unknown.
15
2
5
Question 2
The table below lists values for dissolved oxygen concentration in water as a function of
temperature and chloride concentration.
a) Use quadratic and cubic interpolation to determine the oxygen concentration for
T 12 °C and c= 10 g/L.
b) Repeat (a) but use the Lagrange polynomial
30
Dr. K. Mensah-Darkwa
2.5
6.5
c=0 g/L
14.6
12.8
11.3
10.1
Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L) for
Temperature (°C) and Concentration
of Chloride (g/L)
c = 10 g/L
12.9
11.3
10.1
9.09
8.26
7.56
3
7
CH
9.03
8.17
7.46
6.85
4
hp
c = 20 g/L
11.4
10.3
Dissolved oxygen concentration in water as a function of temperature (C) and chloride
concentration (g/L).
8.96
8.08
5
1
7.35
6.73
6.20
CHE 358-2015/16
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage