Graph x - 3y = 6 by finding the y- and x-intercepts. We will let x = 0 to find the y-intercept of the graph. We will then let y = 0 to find the x-intercept. Since two points determine a line, the y-intercept and x-intercept are enough information to graph this linear equation. x-intercept:y = 0 x - 3y = 6 y-intercept:x = 0 x - 3y = 6. Substitute Substitute - 3y 6. X - 3( = 6 O for x. O for y. -3y = X - To isolate X = y, divide both sides y = The x-intercept is (6, 0). by -3. The y-intercept is (0, -2). Since each intercept of the graph is a solution of the equation, we enter the intercepts in a table of solutions below. As a check, we find one more point on the line. We select a convenient value for x, say, 3, and find the corresponding value of y. х — Зу %3D 6 - 3y = 6 Substitute 3 for x. - Зу %3 To isolate the variable term, -3y, subtract 3 from both sides. y = To isolate y, divide both sides by -3. Therefore, (3, -1) is a solution. It is also entered in the table. We plot the intercepts and the check point, draw a straight line through them, and label the line as х— Зу %3D 6. x - 3y = 6 y (х, у) x – 3y = 6 0 -2 (,-2) + y-intercept (6, 0)
Graph x - 3y = 6 by finding the y- and x-intercepts. We will let x = 0 to find the y-intercept of the graph. We will then let y = 0 to find the x-intercept. Since two points determine a line, the y-intercept and x-intercept are enough information to graph this linear equation. x-intercept:y = 0 x - 3y = 6 y-intercept:x = 0 x - 3y = 6. Substitute Substitute - 3y 6. X - 3( = 6 O for x. O for y. -3y = X - To isolate X = y, divide both sides y = The x-intercept is (6, 0). by -3. The y-intercept is (0, -2). Since each intercept of the graph is a solution of the equation, we enter the intercepts in a table of solutions below. As a check, we find one more point on the line. We select a convenient value for x, say, 3, and find the corresponding value of y. х — Зу %3D 6 - 3y = 6 Substitute 3 for x. - Зу %3 To isolate the variable term, -3y, subtract 3 from both sides. y = To isolate y, divide both sides by -3. Therefore, (3, -1) is a solution. It is also entered in the table. We plot the intercepts and the check point, draw a straight line through them, and label the line as х— Зу %3D 6. x - 3y = 6 y (х, у) x – 3y = 6 0 -2 (,-2) + y-intercept (6, 0)
Intermediate Algebra
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285195728
Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Chapter7: Equations And Inequalities In Two Variables
Section7.1: Rectangular Coordinate System And Linear Equations
Problem 43PS
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
100%
Help me with all of them please.
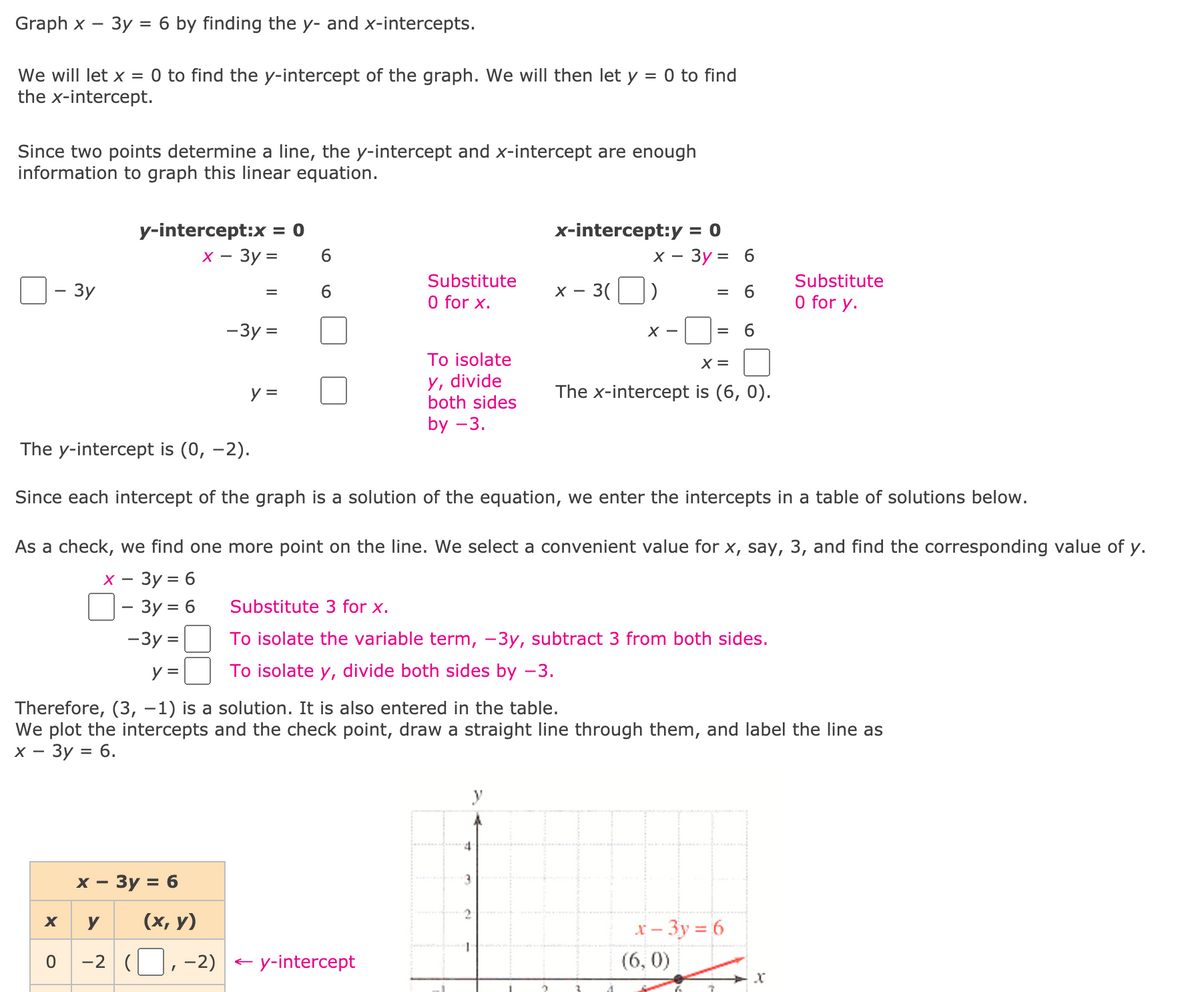
Transcribed Image Text:Graph x – 3y = 6 by finding the y- and x-intercepts.
%D
We will let x
0 to find the y-intercept of the graph. We will then let y
0 to find
the x-intercept.
Since two points determine a line, the y-intercept and x-intercept are enough
information to graph this linear equation.
y-intercept:x
= 0
x-intercept:y = 0
х — Зу 3
6.
х —
— Зу %3D 6
Substitute
Substitute
- Зу
х — 3(
6.
-
%D
O for x.
O for y.
-3y =
X -
To isolate
X =
Y, divide
both sides
y =
The x-intercept is (6, 0).
by -3.
The y-intercept is (0, –2).
Since each intercept of the graph is a solution of the equation, we enter the intercepts in a table of solutions below.
As a check, we find one more point on the line. We select a convenient value for x, say, 3, and find the corresponding value of y.
X -
3y = 6
- 3y = 6
Substitute 3 for x.
— Зу %3
To isolate the variable term, –3y, subtract 3 from both sides.
y =
To isolate y, divide both sides by -3.
Therefore, (3, -1) is a solution. It is also entered in the table.
We plot the intercepts and the check point, draw a straight line through them, and label the line as
х — Зу %3D 6.
y
х — Зу %3D 6
y
(х, у)
x – 3y = 6
-2 (,-2) + y-intercept
(6, 0)
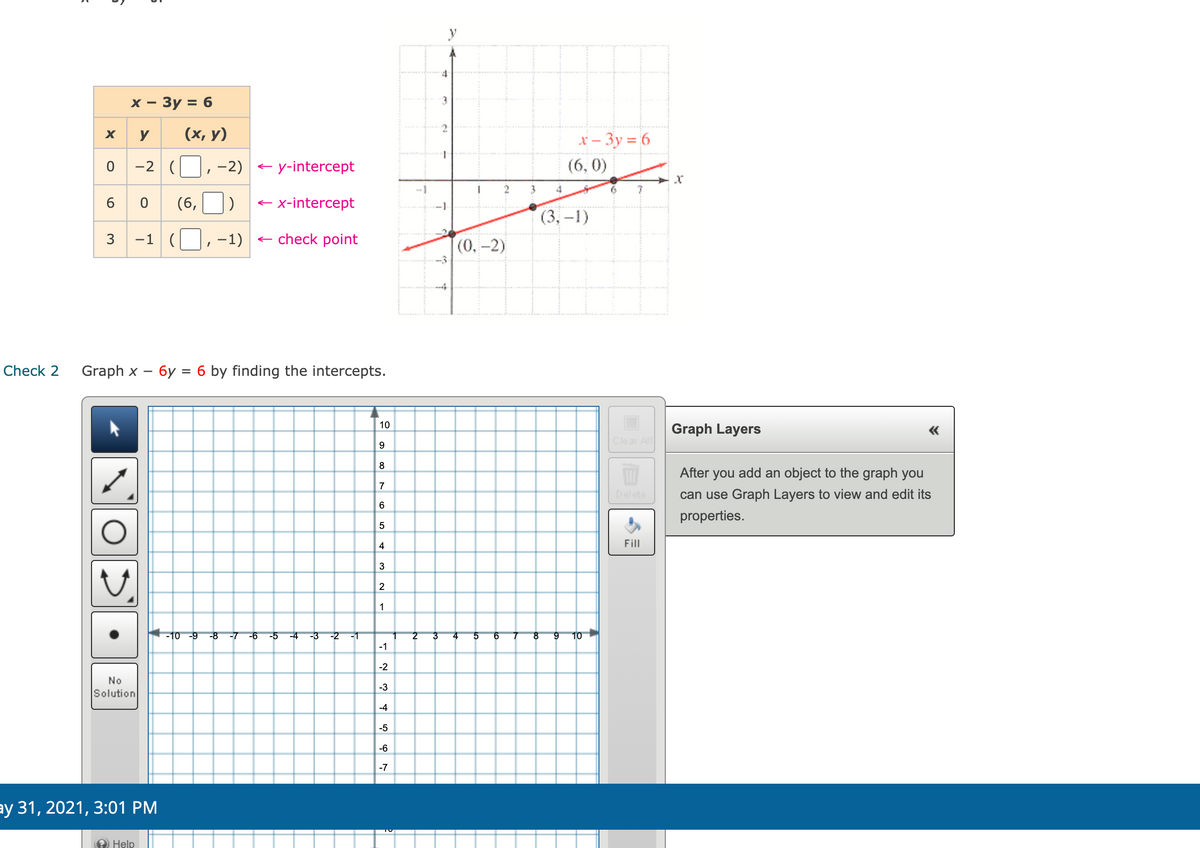
Transcribed Image Text:4
х — Зу %3D 6
3
X
y
(х, у)
X – 3y = 6
-2
--2) - y-intercept
(6, 0)
3
4
6.
6
(6,
e x-intercept
(3, –1)
3
-1
-1)
e check point
(0,-2)
--4
Check 2
Graph x – 6y = 6 by finding the intercepts.
10
Graph Layers
Clear All
9
8
After you add an object to the graph you
7
Delete
can use Graph Layers to view and edit its
6
properties.
4
Fill
3
2
1
-10 -9
-8
-7
-9
-5
-3
-2
-1
2
3
4
5
6
8.
10
-1
-2
No
-3
Solution
-4
-5
-6
-7
ay 31, 2021, 3:01 PM
2 Help
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, algebra and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Intermediate Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195728
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195728
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Elementary Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9780998625713
Author:
Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-Smith
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University