Greenville Cabinets received a contract to produce cabinets for a major furniture distributor. The contract calls for the production of 3,300 small cabinets and 4,100 large over the next two months, with the following delivery schedule Model Month 1 Month 2 Small 2,100 1,200 Large 1,500 2,600 Greenville estimates that the production time for each small cabinet is 0.7 hours and the production time for each large cabinet is 1 hour. The raw material costs are $10 for each small cabinet and $12 for each large cabinet. Labor costs are $22 per hour using regular production time and $33 using overtime. Greenville has up to 2,400 hours of regular production time available each month and up to 1,000 additional hours of overtime available each month. If production for either cabinet exceeds demand in month 1, the cabinets can be stored at a cost of $5 per cabinet. For each product, determine the number of units that should be manufactured each month on regular time and on overtime to minimize total production and storage costs. (Round your answers to the nearest integer. Let SaR = regular small cabinets for month 1, SbR = regular small cabinets for month 2, LaR = regular large cabinets for month 1, LbR = regular large cabinets for month 2, SaO = overtime small cabinets for month 1, SbO = overtime small cabinets for month 2, LaO = overtime large cabinets for month 1, and LbO = overtime large cabinets for month 2) (SaR, SbR, LaR, LbR, SaO, SbO, LaO, LbO)= Total Production Cost=$
Greenville Cabinets received a contract to produce cabinets for a major furniture distributor. The contract calls for the production of 3,300 small cabinets and 4,100 large over the next two months, with the following delivery schedule Model Month 1 Month 2 Small 2,100 1,200 Large 1,500 2,600 Greenville estimates that the production time for each small cabinet is 0.7 hours and the production time for each large cabinet is 1 hour. The raw material costs are $10 for each small cabinet and $12 for each large cabinet. Labor costs are $22 per hour using regular production time and $33 using overtime. Greenville has up to 2,400 hours of regular production time available each month and up to 1,000 additional hours of overtime available each month. If production for either cabinet exceeds demand in month 1, the cabinets can be stored at a cost of $5 per cabinet. For each product, determine the number of units that should be manufactured each month on regular time and on overtime to minimize total production and storage costs. (Round your answers to the nearest integer. Let SaR = regular small cabinets for month 1, SbR = regular small cabinets for month 2, LaR = regular large cabinets for month 1, LbR = regular large cabinets for month 2, SaO = overtime small cabinets for month 1, SbO = overtime small cabinets for month 2, LaO = overtime large cabinets for month 1, and LbO = overtime large cabinets for month 2) (SaR, SbR, LaR, LbR, SaO, SbO, LaO, LbO)= Total Production Cost=$
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter2: Introduction To Spreadsheet Modeling
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20P: Julie James is opening a lemonade stand. She believes the fixed cost per week of running the stand...
Related questions
Question
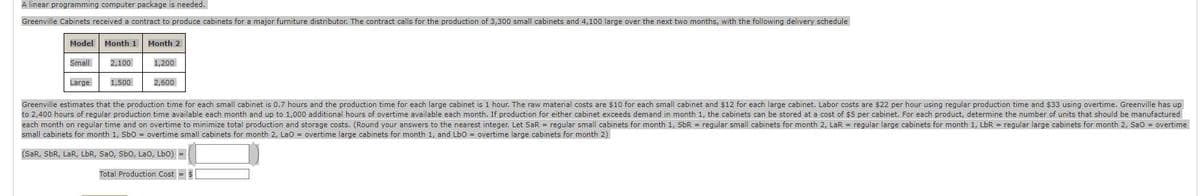
A linear programming computer package is needed.
Greenville Cabinets received a contract to produce cabinets for a major furniture distributor. The contract calls for the production of 3,300 small cabinets and 4,100 large over the next two months, with the following delivery schedule
| Model | Month 1 | Month 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Small | 2,100 | 1,200 |
| Large | 1,500 | 2,600 |
Greenville estimates that the production time for each small cabinet is 0.7 hours and the production time for each large cabinet is 1 hour. The raw material costs are $10 for each small cabinet and $12 for each large cabinet. Labor costs are $22 per hour using regular production time and $33 using overtime. Greenville has up to 2,400 hours of regular production time available each month and up to 1,000 additional hours of overtime available each month. If production for either cabinet exceeds demand in month 1, the cabinets can be stored at a cost of $5 per cabinet. For each product, determine the number of units that should be manufactured each month on regular time and on overtime to minimize total production and storage costs. (Round your answers to the nearest integer. Let SaR = regular small cabinets for month 1, SbR = regular small cabinets for month 2, LaR = regular large cabinets for month 1, LbR = regular large cabinets for month 2, SaO = overtime small cabinets for month 1, SbO = overtime small cabinets for month 2, LaO = overtime large cabinets for month 1, and LbO = overtime large cabinets for month 2)
(SaR, SbR, LaR, LbR, SaO, SbO, LaO, LbO)=
Total Production Cost=$
Transcribed Image Text:A linear programming computer package is needed.
Greenville Cabinets received a contract to produce cabinets for a major furniture distributor. The contract calls for the production of 3,300 small cabinets and 4,100 large over the next two months, with the following delivery schedule
Model Month 1 Month 2
Small 2,100
Large
1,500
1,200
2,600
Greenville estimates that the production time for each small cabinet is 0.7 hours and the production time for each large cabinet is 1 hour. The raw material costs are $10 for each small cabinet and $12 for each large cabinet. Labor costs are $22 per hour using regular production time and $33 using overtime. Greenville has up
to 2,400 hours of regular production time available each month and up to 1,000 additional hours of overtime available each month. If production for either cabinet exceeds demand in month 1, the cabinets can be stored at a cost of $5 per cabinet. For each product, determine the number of units that should be manufactured
each month on regular time and on overtime to minimize total production and storage costs. (Round your answers to the nearest integer. Let SaR = regular small cabinets for month 1, SbR = regular small cabinets for month 2, LaR = regular large cabinets for month 1, LbR = regular large cabinets for month 2, Sa0 = overtime
small cabinets for month 1, SbO = overtime small cabinets for month 2, LaO = overtime large cabinets for month 1, and LbO = overtime large cabinets for month 2)
(SaR, SbR, LaR, LbR, SaO, Sbo, LaO, LbO) =
Total Production Cost = $
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 7 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259667473
Author:
William J Stevenson
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259666100
Author:
F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259667473
Author:
William J Stevenson
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259666100
Author:
F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Purchasing and Supply Chain Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781285869681
Author:
Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. Patterson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781478623069
Author:
Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon Olsen
Publisher:
Waveland Press, Inc.