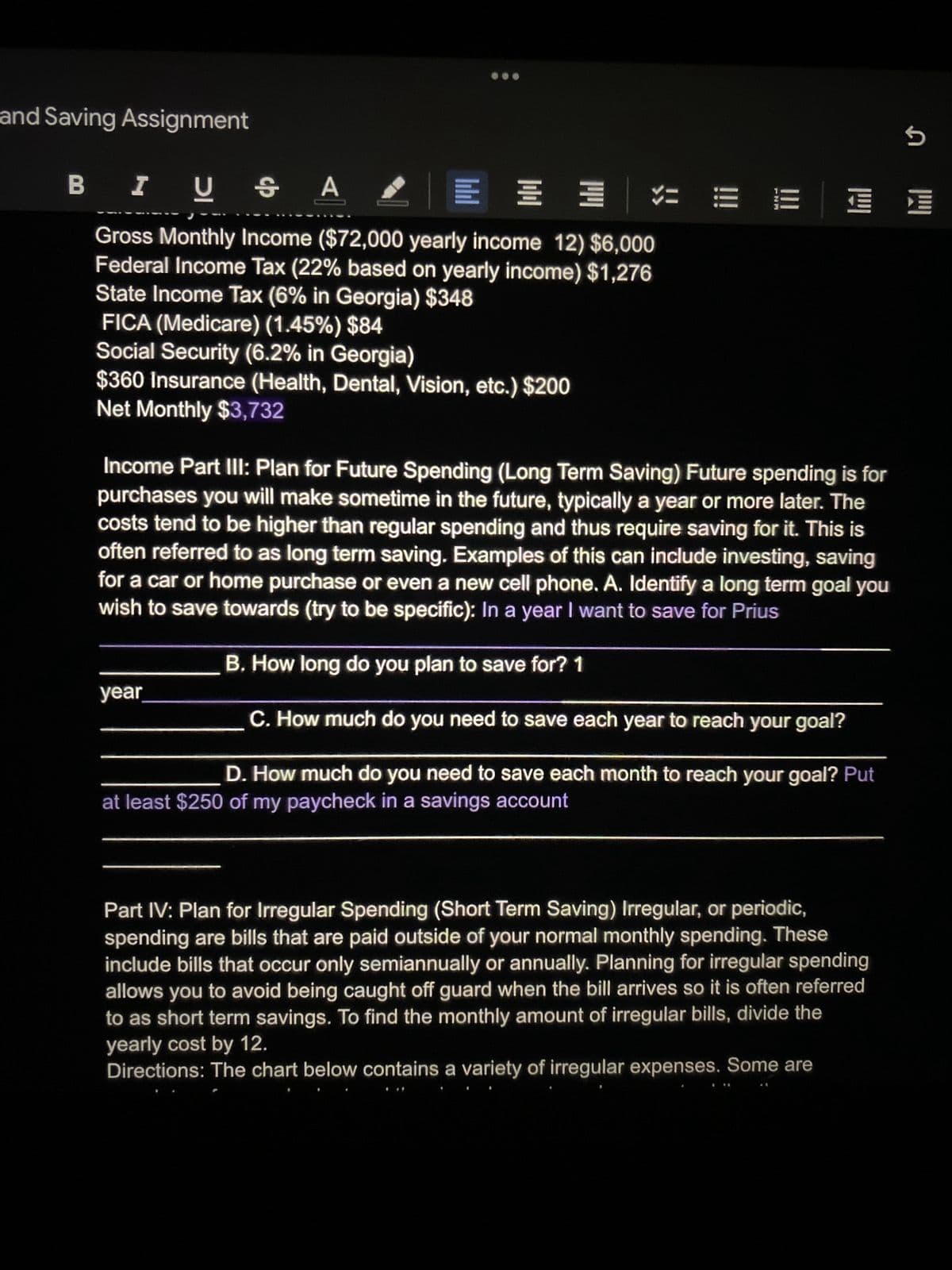
Gross Monthly Income ($72,000 yearly income 12) $6,000 Federal Income Tax (22% based on yearly income) $1,276 State Income Tax (6% in Georgia) $348 FICA (Medicare) (1.45%) $84 Social Security (6.2% in Georgia) $360 Insurance (Health, Dental, Vision, etc.) $200 Net Monthly $3,732 Income Part III: Plan for Future Spending (Long Term Saving) Future spending is for purchases you will make sometime in the future, typically a year or more later. The costs tend to be higher than regular spending and thus require saving for it. This is often referred to as long term saving. Examples of this can include investing, saving for a car or home purchase or even a new cell phone. A. Identify a long term goal you wish to save towards (try to be specific): In a year I want to save for Prius B. How long do you plan to save for? 1 C. How much do you need to save each year to reach your goal? D. How much do you need to save each month to reach your goal? Put at least $250 of my paycheck in a savings account year
Gross Monthly Income ($72,000 yearly income 12) $6,000 Federal Income Tax (22% based on yearly income) $1,276 State Income Tax (6% in Georgia) $348 FICA (Medicare) (1.45%) $84 Social Security (6.2% in Georgia) $360 Insurance (Health, Dental, Vision, etc.) $200 Net Monthly $3,732 Income Part III: Plan for Future Spending (Long Term Saving) Future spending is for purchases you will make sometime in the future, typically a year or more later. The costs tend to be higher than regular spending and thus require saving for it. This is often referred to as long term saving. Examples of this can include investing, saving for a car or home purchase or even a new cell phone. A. Identify a long term goal you wish to save towards (try to be specific): In a year I want to save for Prius B. How long do you plan to save for? 1 C. How much do you need to save each year to reach your goal? D. How much do you need to save each month to reach your goal? Put at least $250 of my paycheck in a savings account year
Chapter4: Operating Activities: Sales And Cash Receipts
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4.9C
Related questions
Question
NOT A GRADE THIS IS A STUDY GUIDE.
Only need help on Part III
Goal is to save for a Prius
Gross monthly income and net monthly income provided
Transcribed Image Text:and Saving Assignment
BIUS A
Gross Monthly Income ($72,000 yearly income 12) $6,000
Federal Income Tax (22% based on yearly income) $1,276
State Income Tax (6% in Georgia) $348
FICA (Medicare) (1.45%) $84
Social Security (6.2% in Georgia)
$360 Insurance (Health, Dental, Vision, etc.) $200
Net Monthly $3,732
Income Part III: Plan for Future Spending (Long Term Saving) Future spending is for
purchases you will make sometime in the future, typically a year or more later. The
costs tend to be higher than regular spending and thus require saving for it. This is
often referred to as long term saving. Examples of this can include investing, saving
for a car or home purchase or even a new cell phone. A. Identify a long term goal you
wish to save towards (try to be specific): In a year I want to save for Prius
B. How long do you plan to save for? 1
C. How much do you need to save each year to reach your goal?
D. How much do you need to save each month to reach your goal? Put
at least $250 of my paycheck in a savings account
year
Part IV: Plan for Irregular Spending (Short Term Saving) Irregular, or periodic,
spending are bills that are paid outside of your normal monthly spending. These
include bills that occur only semiannually or annually. Planning for irregular spending
allows you to avoid being caught off guard when the bill arrives so it is often referred
to as short term savings. To find the monthly amount of irregular bills, divide the
yearly cost by 12.
Directions: The chart below contains a variety of irregular expenses. Some are
lil
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

