g(x) = = ax + C, where a ER Power: is continuous on [a, b], differentiable on (a, b) and g'(x) = f(x). +C, where r + – 1 r +1 FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS II If fis continuous on [a,b] and F is any antiderivative of f, then Edx = In|x|+C Exponential: Sndx = F(b) – F(a). b +C, where b e (0,00) In(b) Trigonometric: NET CHANGE THEOREM cos(x)d x = sin(x) +C If F' is continuous on [a, b], then sin(x) = - cos(x) +C F'(x)dx = F(b) – F(a). Jsec"wnd x = tan(x) + C VARIABLE SUBSTITUTION sec(x)tan(x)d x = sec(x) +C If u = g(x) is differentiable whose range contains [a, b] and fis continuous on [a, b), then Jescundx = - cot(2) + C csctr)cot(x)dx = - esc(x) + C VARIABLE SUBSTITUTION FOR DEFINITE INTEGRALS If u = g(x) is differentiable whose range contains [a, b] and fis continuous on [a, b], then tan(x)dx = - In|cos(x)| +C Janterds cot(x)dx = In|sin(x)| +C f(u)du. v)dx = In|sec{x) + tan(x)|+ C ela) csc(x)dx = In|csc(x) - cot(x)| +C VOLUMES OF SOLIDS OF REVOLUTION Inverse Trigonometric: Revolving about x Revolving about y- axis dx aresin(x) + C, where x #± 1 -ахis Disks/Washers Integrate x variable Integrate y variable dx = arctan(x) + C Cylindrical Shells Integrate y variable Integrate x variable Нуpertbolic AVERAGE VALUE OF A FUNCTION cosh(x)d x = sinh(x) +C Iffis continuous on (a, b), then sinh(x) + C = cosh(x) +c favg f(x)d x.
g(x) = = ax + C, where a ER Power: is continuous on [a, b], differentiable on (a, b) and g'(x) = f(x). +C, where r + – 1 r +1 FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS II If fis continuous on [a,b] and F is any antiderivative of f, then Edx = In|x|+C Exponential: Sndx = F(b) – F(a). b +C, where b e (0,00) In(b) Trigonometric: NET CHANGE THEOREM cos(x)d x = sin(x) +C If F' is continuous on [a, b], then sin(x) = - cos(x) +C F'(x)dx = F(b) – F(a). Jsec"wnd x = tan(x) + C VARIABLE SUBSTITUTION sec(x)tan(x)d x = sec(x) +C If u = g(x) is differentiable whose range contains [a, b] and fis continuous on [a, b), then Jescundx = - cot(2) + C csctr)cot(x)dx = - esc(x) + C VARIABLE SUBSTITUTION FOR DEFINITE INTEGRALS If u = g(x) is differentiable whose range contains [a, b] and fis continuous on [a, b], then tan(x)dx = - In|cos(x)| +C Janterds cot(x)dx = In|sin(x)| +C f(u)du. v)dx = In|sec{x) + tan(x)|+ C ela) csc(x)dx = In|csc(x) - cot(x)| +C VOLUMES OF SOLIDS OF REVOLUTION Inverse Trigonometric: Revolving about x Revolving about y- axis dx aresin(x) + C, where x #± 1 -ахis Disks/Washers Integrate x variable Integrate y variable dx = arctan(x) + C Cylindrical Shells Integrate y variable Integrate x variable Нуpertbolic AVERAGE VALUE OF A FUNCTION cosh(x)d x = sinh(x) +C Iffis continuous on (a, b), then sinh(x) + C = cosh(x) +c favg f(x)d x.
Chapter3: Functions
Section3.3: Rates Of Change And Behavior Of Graphs
Problem 2SE: If a functionfis increasing on (a,b) and decreasing on (b,c) , then what can be said about the local...
Related questions
Question
Not graded. Please only solve using the given formulas. Thank you
(p10)
![FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS I
If fis continuous on [a,b] then the function
BASIC ANTIDERIVATIVES
Constant
= ax +C, where a ER
%3D
Power:
is continuous on [a, b], dfferentiable on (a, b) and gʻ'(x) = f(x).
(rds =
+C, where r + - 1
r +1
FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS II
If fis continuous on [a,b] and F is any antiderivative of f, then
= In |x|+C
Exponential:
f(x)dx = F(b) – F(a).
b
+C, where b E (0,00)
In(b)
Trigonometric:
NET CHANGE THEOREM
cos(x)dx = sin(x) +C
If F' is continuous on [a, b), then
Jamer-
sec-(endx = tan(x) + C
= - cos(x) +C
F(x)dx = F(b) – F(a).
VARIABLE SUBSTITUTION
sec(x)tan(x)d x = sec(x) + C
If u = g(x) is differentiable whose range contains [a, b] and fis
continuous on [a, b), then
Joscondx = - cot(2) + C
r)cot(x)dx = - csc(x) +C
VARIABLE SUBSTITUTION FOR DEFINITE INTEGRALS
tan(x)dx = - In|cos(x)|+C_
If u = g(x) is differentiable whose range contains [a, b] and fis
continuous on [a, b), then
Jcot(o)d x = In |sin(<)| + c
f(u)du.
sec(x)dx = In|sec(x) + tan(x)| + C
gla)
x)dx = In[cse(x) – cot(x)| +C
VOLUMES OF SOLIDS OF REVOLUTION
Inverse Trigonometric:
Revolving about x Revolving about y-
xp
= arcsin(x) + C, where x *±1
-ахis
axis
Disks/Washers Integrate x variable Integrate y variable
dx
= arctan(x) + C
1+x2
Cylindrical Shells Integrate y variable Integrate x variable
Нурerbolic
AVERAGE VALUE OF A FUNCTION
cosh(x)d x = sinh(x) +C
Iffis continuous on [a, b], then
sinh(x) +C = cosh(x) + C
Savg =
f(x)dx.
b- a](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F73b00b2a-4fa8-4b66-93aa-a27c1d9b51ff%2F5dd0af14-9a45-4b5e-87c7-de12aaa72bc1%2Fv96d9ca_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS I
If fis continuous on [a,b] then the function
BASIC ANTIDERIVATIVES
Constant
= ax +C, where a ER
%3D
Power:
is continuous on [a, b], dfferentiable on (a, b) and gʻ'(x) = f(x).
(rds =
+C, where r + - 1
r +1
FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS II
If fis continuous on [a,b] and F is any antiderivative of f, then
= In |x|+C
Exponential:
f(x)dx = F(b) – F(a).
b
+C, where b E (0,00)
In(b)
Trigonometric:
NET CHANGE THEOREM
cos(x)dx = sin(x) +C
If F' is continuous on [a, b), then
Jamer-
sec-(endx = tan(x) + C
= - cos(x) +C
F(x)dx = F(b) – F(a).
VARIABLE SUBSTITUTION
sec(x)tan(x)d x = sec(x) + C
If u = g(x) is differentiable whose range contains [a, b] and fis
continuous on [a, b), then
Joscondx = - cot(2) + C
r)cot(x)dx = - csc(x) +C
VARIABLE SUBSTITUTION FOR DEFINITE INTEGRALS
tan(x)dx = - In|cos(x)|+C_
If u = g(x) is differentiable whose range contains [a, b] and fis
continuous on [a, b), then
Jcot(o)d x = In |sin(<)| + c
f(u)du.
sec(x)dx = In|sec(x) + tan(x)| + C
gla)
x)dx = In[cse(x) – cot(x)| +C
VOLUMES OF SOLIDS OF REVOLUTION
Inverse Trigonometric:
Revolving about x Revolving about y-
xp
= arcsin(x) + C, where x *±1
-ахis
axis
Disks/Washers Integrate x variable Integrate y variable
dx
= arctan(x) + C
1+x2
Cylindrical Shells Integrate y variable Integrate x variable
Нурerbolic
AVERAGE VALUE OF A FUNCTION
cosh(x)d x = sinh(x) +C
Iffis continuous on [a, b], then
sinh(x) +C = cosh(x) + C
Savg =
f(x)dx.
b- a
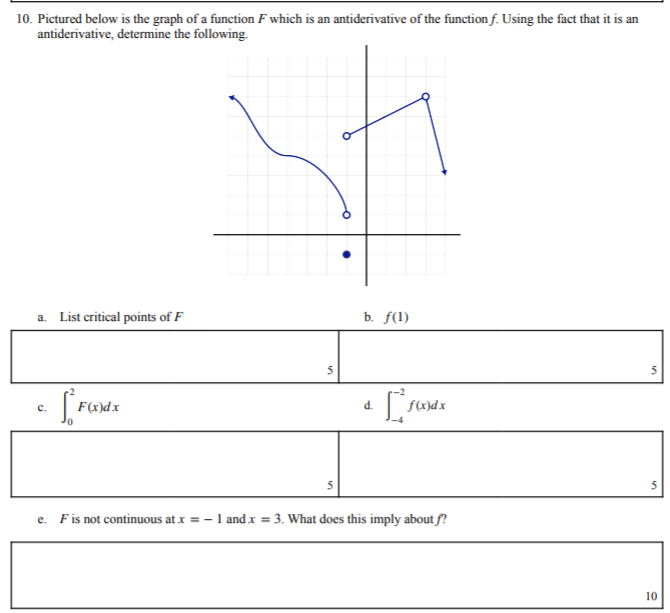
Transcribed Image Text:10. Pictured below is the graph of a function F which is an antiderivative of the function f. Using the fact that it is an
antiderivative, determine the following.
a. List critical points of F
b. f(1)
с.
F(x)dx
d.
f(x)dx
e. Fis not continuous at x = - 1 and x = 3. What does this imply about f?
10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

