he production rate per day = units. (Enter your response as a whole number.) l in the table below. (Enter your responses as whole numbers.) Month 1 January Deman 900 2 February 3 March 4 April 5 May 6 June 700 800 1,200 1,500 1,100 he total regular production cost = S (Enter your response as a whole number.) he total subcontracting cost = $(Enter your response as a whole number.) otal cost with plan 5 = S (Enter your response as a whole number.) Juarez has yet a sixth plan. A constant workforce of 7 is selected, with the remainder of demand filled by subcontracting. Evaluate this plan. be production rate ner day =llunite (Enter vOur reenonse ee a hole nunber
he production rate per day = units. (Enter your response as a whole number.) l in the table below. (Enter your responses as whole numbers.) Month 1 January Deman 900 2 February 3 March 4 April 5 May 6 June 700 800 1,200 1,500 1,100 he total regular production cost = S (Enter your response as a whole number.) he total subcontracting cost = $(Enter your response as a whole number.) otal cost with plan 5 = S (Enter your response as a whole number.) Juarez has yet a sixth plan. A constant workforce of 7 is selected, with the remainder of demand filled by subcontracting. Evaluate this plan. be production rate ner day =llunite (Enter vOur reenonse ee a hole nunber
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter9: Decision Making Under Uncertainty
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 30P
Related questions
Question
please answer within 30 minutes. its urgent.
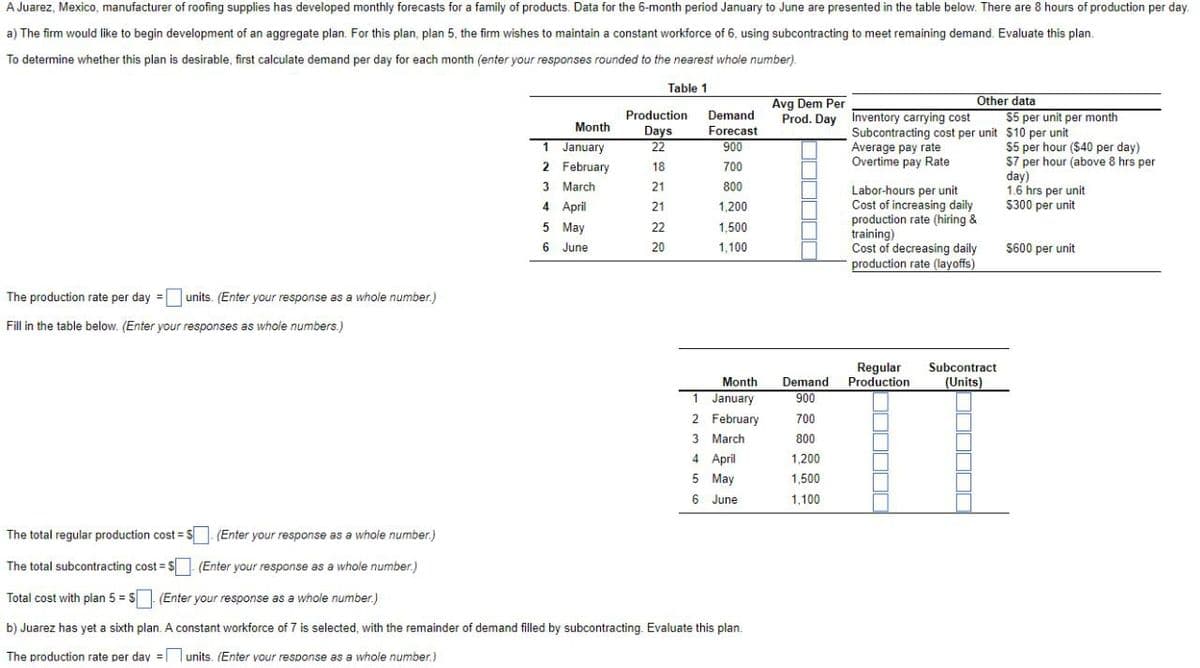
Transcribed Image Text:A Juarez, Mexico, manufacturer of roofing supplies has developed monthly forecasts for a family of products. Data for the 6-month period January to June are presented in the table below. There are 8 hours of production per day.
a) The firm would like to begin development of an aggregate plan. For this plan, plan 5, the firm wishes to maintain a constant workforce of 6, using subcontracting to meet remaining demand. Evaluate this plan.
To determine whether this plan is desirable, first calculate demand per day for each month (enter your responses rounded to the nearest whole number).
Table 1
Avg Dem Per
Prod. Day Inventory carrying cost
Other data
$5 per unit per month
Production
Demand
Month
Days
22
Forecast
Subcontracting cost per unit $10 per unit
Average pay rate
Overtime pay Rate
$5 per hour ($40 per day)
$7 per hour (above 8 hrs per
day)
1.6 hrs per unit
$300 per unit
1 January
2 February
900
18
700
3 March
21
800
Labor-hours per unit
Cost of increasing daily
production rate (hiring &
training)
Cost of decreasing daily
production rate (layoffs)
4 April
21
1,200
5 May
22
1,500
6 June
20
1,100
S600 per unit
The production rate per day = units. (Enter your response as a whole number.)
Fill in the table below. (Enter your responses as whole numbers.)
Regular
Production
Subcontract
Month
Demand
(Units)
1 January
2 February
900
700
3 March
800
4 April
1,200
5 May
1,500
6 June
1,100
The total regular production cost = S (Enter your response as a whole number.)
The total subcontracting cost = $ (Enter your response as a whole number.)
Total cost with plan 5 = S (Enter your response as a whole number.)
b) Juarez has yet a sixth plan. A constant workforce of 7 is selected, with the remainder of demand filled by subcontracting. Evaluate this plan.
The production rate per day =| Tunits. (Enter vour response as a whole number.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Purchasing and Supply Chain Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781285869681
Author:
Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. Patterson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Marketing
Marketing
ISBN:
9780357033791
Author:
Pride, William M
Publisher:
South Western Educational Publishing

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Purchasing and Supply Chain Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781285869681
Author:
Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. Patterson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Marketing
Marketing
ISBN:
9780357033791
Author:
Pride, William M
Publisher:
South Western Educational Publishing