How do they compare? O The model appears to fit the data well. O The model appears to not fit the data well. (C) Use the model to estimate the distance traveled during impact, assuming that the passenger deceleration must not exceed 25 g's. (Round your answer to one decimal place.) (d) Do you think it is practical to lower the number of g's experienced during impact to fewer than 23? Explain your reasoning.
How do they compare? O The model appears to fit the data well. O The model appears to not fit the data well. (C) Use the model to estimate the distance traveled during impact, assuming that the passenger deceleration must not exceed 25 g's. (Round your answer to one decimal place.) (d) Do you think it is practical to lower the number of g's experienced during impact to fewer than 23? Explain your reasoning.
Chapter3: Polynomial Functions
Section3.5: Mathematical Modeling And Variation
Problem 7ECP: The kinetic energy E of an object varies jointly with the object’s mass m and the square of the...
Related questions
Question
100%
I have marked all the answers to the first page. I need help with the second page.
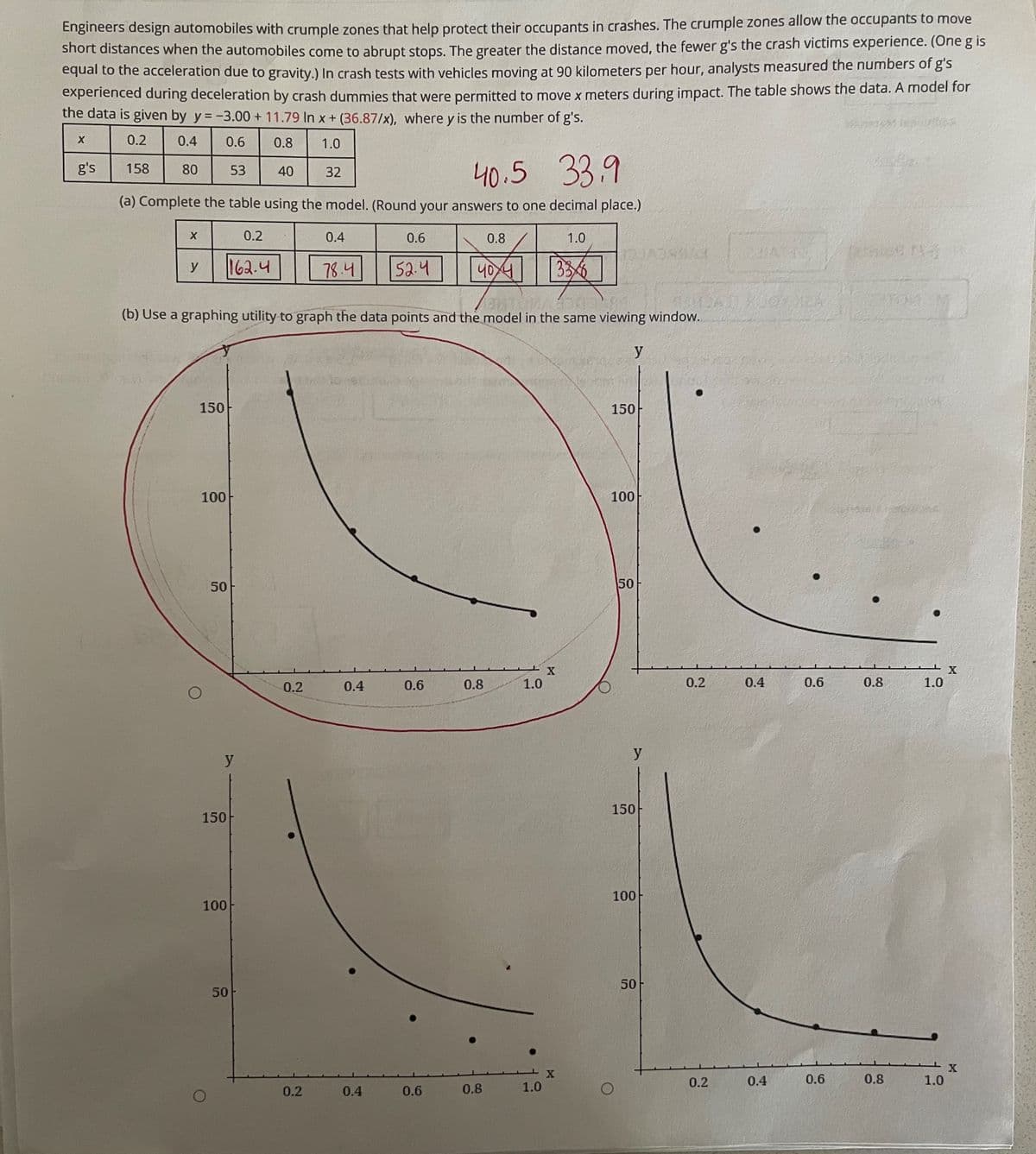
Transcribed Image Text:Engineers design automobiles with crumple zones that help protect their occupants in crashes. The crumple zones allow the occupants to move
short distances when the automobiles come to abrupt stops. The greater the distance moved, the fewer g's the crash victims experience. (Oneg is
equal to the acceleration due to gravity.) In crash tests with vehicles moving at 90 kilometers per hour, analysts measured the numbers of g's
experienced during deceleration by crash dummies that were permitted to move x meters during impact. The table shows the data. A model for
the data is given by y = -3.00 + 11.79 In x + (36.87/x), where y is the number of g's.
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
40.5 33.9
g's
158
80
53
40
32
(a) Complete the table using the model. (Round your answers to one decimal place.)
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
162.4
78.4
52.4
336
y
(b) Use a graphing utility to graph the data points and the model in the same viewing window.
y
150
150
100
100
50
50
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
y
150
150
100
100
50
50
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0

Transcribed Image Text:How do they compare?
O The model appears to fit the data welI.
O The model appears to not fit the data well.
(C) Use the model to estimate the distance traveled during impact, assuming that the passenger deceleration must not exceed 25 g's.
(Round your answer to one decimal place.)
(d) Do you think it is practical to lower the number of g's experienced during impact to fewer than 23? Explain your reasoning.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 10 images

Recommended textbooks for you


Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell


Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill