I am trying to model a simple RC circuit with one resistor and one capacitor using Simulink. I was given this equation G(jw)=1/(1+jw*tau), tau=RC, and need to convert it to this form in the image: v_dot_o = 1/RC(Vi-Vo). I have also attached a longer image with more detailed steps of how to get to the final equation, but I don't get how a derivative of Vo has appeared out of nowhere somewhere in the middle of the procedure. Please show as many steps as possible and explain the steps if necessary. I'm purely intending to learn from the process, so it'd be really nice if you could explain how each step was done!
I am trying to model a simple RC circuit with one resistor and one capacitor using Simulink. I was given this equation G(jw)=1/(1+jw*tau), tau=RC, and need to convert it to this form in the image: v_dot_o = 1/RC(Vi-Vo). I have also attached a longer image with more detailed steps of how to get to the final equation, but I don't get how a derivative of Vo has appeared out of nowhere somewhere in the middle of the procedure. Please show as many steps as possible and explain the steps if necessary. I'm purely intending to learn from the process, so it'd be really nice if you could explain how each step was done!
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Stephen L. Herman
Chapter19: Capacitors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1PP: Fill in all the missing values. Refer to the formulas that follow. Resistance Capacitance Time...
Related questions
Question
100%
I am trying to model a simple RC circuit with one resistor and one capacitor using Simulink.
I was given this equation G(jw)=1/(1+jw*tau), tau=RC, and need to convert it to this form in the image: v_dot_o = 1/RC(Vi-Vo).
I have also attached a longer image with more detailed steps of how to get to the final equation, but I don't get how a derivative of Vo has appeared out of nowhere somewhere in the middle of the procedure. Please show as many steps as possible and explain the steps if necessary. I'm purely intending to learn from the process, so it'd be really nice if you could explain how each step was done!

Transcribed Image Text:1
We are given the transfer function, G(j@) =
T = RC.
1+ jøt'
Simulink works in the Laplace or s-domain, so make the substitu-
tion:
G(s)
1
T = RC
1 + ST
We know by the definition of a transfer function that v,
Recall also that v, and v; vary with time in the time domain, and
G(s) * Vị-
are functions of s in the s-domain.
So we can write our relationship as
V, + sv,RC = v;
Remember that sv, in the Laplace domain is the first derivative in
the time domain. So we can think of this as:
Vo + v,RC = v;
To build a Simulink model containing derivatives, it's often a
good start to isolate the highest level derivative of the desired output.
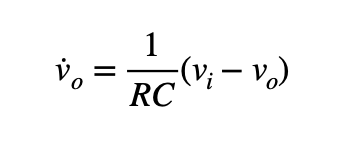
Transcribed Image Text:1
vo
(v; – v)
=
RC
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning