Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:James Stewart
Chapter1: Functions And Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:1.
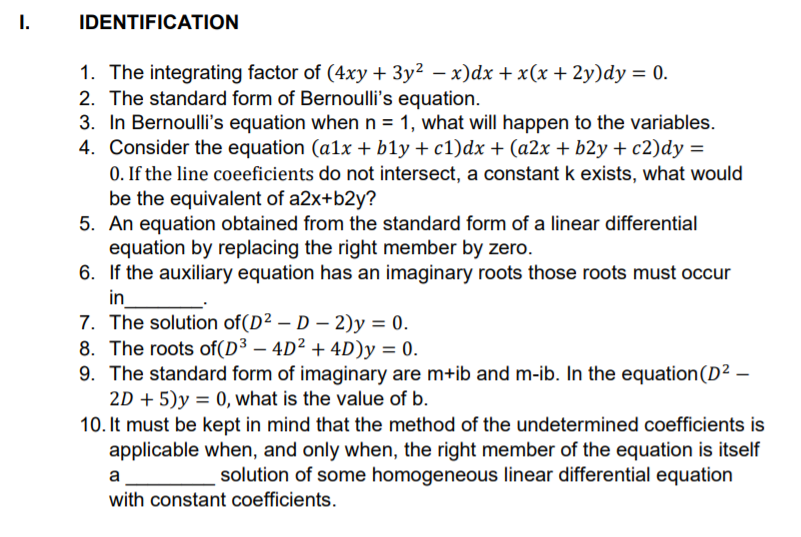
IDENTIFICATION
1. The integrating factor of (4xy + 3y² – x)dx +x(x+ 2y)dy = 0.
2. The standard form of Bernoulli's equation.
3. In Bernoulli's equation when n = 1, what will happen to the variables.
4. Consider the equation (a1x + b1y + c1)dx + (a2x + b2y + c2)dy =
0. If the line coeeficients do not intersect, a constant k exists, what would
be the equivalent of a2x+b2y?
5. An equation obtained from the standard form of a linear differential
equation by replacing the right member by zero.
6. If the auxiliary equation has an imaginary roots those roots must occur
in
7. The solution of(D² – D – 2)y = 0.
8. The roots of(D³ – 4D² + 4D)y = 0.
9. The standard form of imaginary are m+ib and m-ib. In the equation(D² –
2D + 5)y = 0, what is the value of b.
10. It must be kept in mind that the method of the undetermined coefficients is
applicable when, and only when, the right member of the equation is itself
a
solution of some homogeneous linear differential equation
with constant coefficients.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781319050740
Author:
Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:
9781337552516
Author:
Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:
Cengage Learning