If F is the vector field of this example, show that F. dr = 0 for every simple closed path that does not pass through or enclose the origin.
If F is the vector field of this example, show that F. dr = 0 for every simple closed path that does not pass through or enclose the origin.
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305658004
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Ron Larson
Chapter5: Inner Product Spaces
Section5.CM: Cumulative Review
Problem 5CM: Take this test to review the material in Chapters 4 and 5. After you are finished, check your work...
Related questions
Concept explainers
Equations and Inequations
Equations and inequalities describe the relationship between two mathematical expressions.
Linear Functions
A linear function can just be a constant, or it can be the constant multiplied with the variable like x or y. If the variables are of the form, x2, x1/2 or y2 it is not linear. The exponent over the variables should always be 1.
Question
100%
Please solve the screenshot! (Example is the other screenshot.)
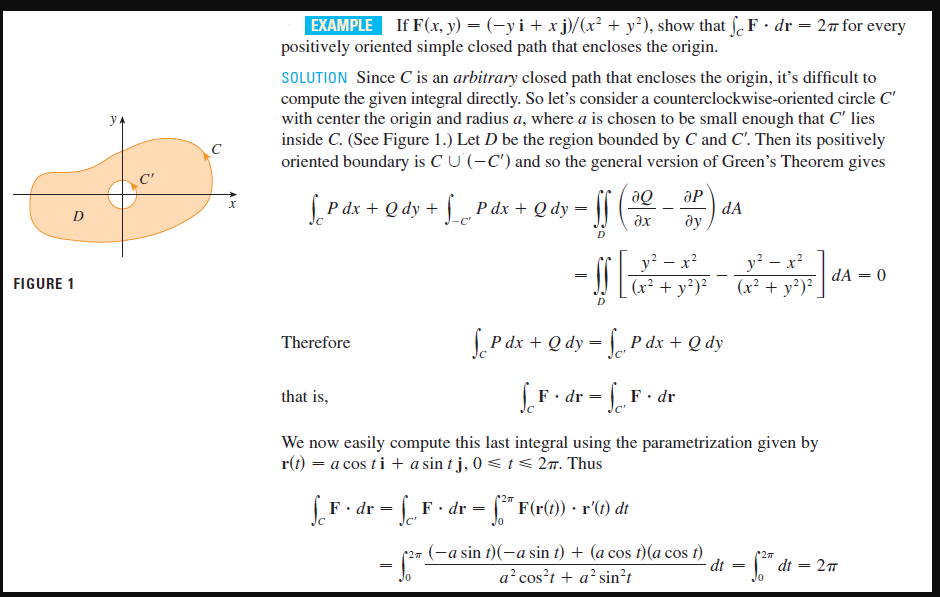
Transcribed Image Text:EXAMPLE
If F(x, y) = (-yi+ x j)/(x² + y²), show that f. F· dr = 2n for every
positively oriented simple closed path that encloses the origin.
SOLUTION Since Cis an arbitrary closed path that encloses the origin, it's difficult to
compute the given integral directly. So let's consider a counterclockwise-oriented circle C'
with center the origin and radius a, where a is chosen to be small enough that C' lies
inside C. (See Figure 1.) Let D be the region bounded by C and C'. Then its positively
oriented boundary is C U (-C') and so the general version of Green's Theorem gives
y
C'
P dx + Q dy + P dx + Q dy = ||
õe
ӘР
dA
ду
D
-C'
y? – x?
(x² + y²)²
y? – x?
(x² + y²)².
dA = 0
FIGURE 1
Therefore
Рӑх + Q dy 3D | Pӑх + Qdy
S. F • dr - F• dr
that is,
We now easily compute this last integral using the parametrization given by
r(t) = a cos ti + a sin t j, 0 < t < 27. Thus
F· dr = F· dr = " F(r(t)) · r(t) dt
Jc'
(27 (-a sin t)(-a sin t) + (a cos t)(a cos t)
a cos?t + a²sin?t
dt =
" = 27
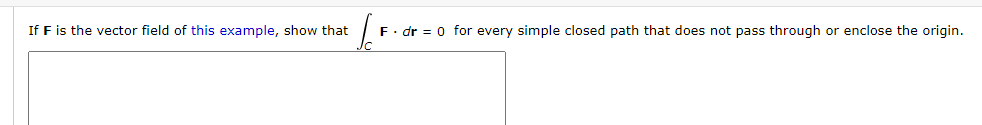
Transcribed Image Text:If F is the vector field of this example, show that
F. dr = 0 for every simple closed path that does not pass through or enclose the origin.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,