If f(1) and g(1) are arbitrary polynomials of degree at most 2, then the mapping (f,g) = f(-1)g(-1)+ f(0)g(0) + f(3)g(3) defines an inner product in P2. Use this inner product to find (f, 9), ||f|l, Ilg|l, and the angle af.g between f(z) and g(1) for f(x) = 2x² + 3x + 4 and g(x) = 3z2 - 5z - 9. (f, g) = ||f|| = l9|| %3D afg =
If f(1) and g(1) are arbitrary polynomials of degree at most 2, then the mapping (f,g) = f(-1)g(-1)+ f(0)g(0) + f(3)g(3) defines an inner product in P2. Use this inner product to find (f, 9), ||f|l, Ilg|l, and the angle af.g between f(z) and g(1) for f(x) = 2x² + 3x + 4 and g(x) = 3z2 - 5z - 9. (f, g) = ||f|| = l9|| %3D afg =
Elements Of Modern Algebra
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285463230
Author:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Chapter8: Polynomials
Section8.2: Divisibility And Greatest Common Divisor
Problem 18E
Related questions
Question
3
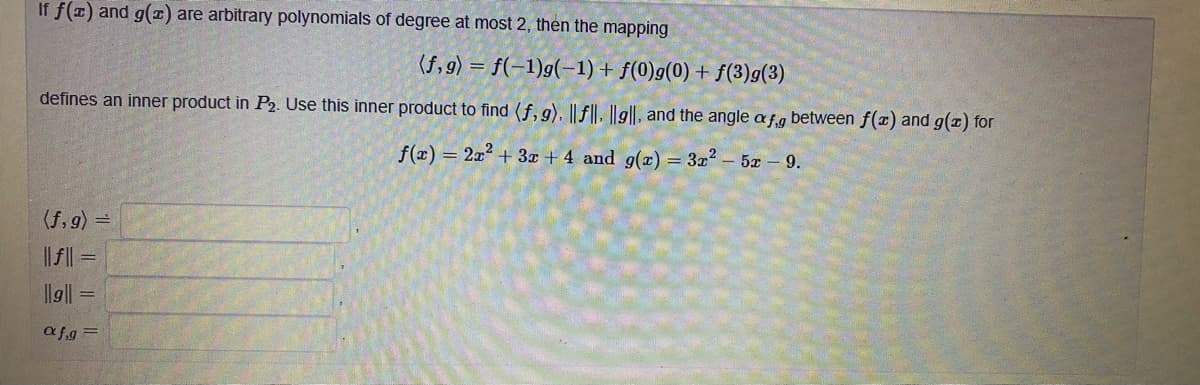
Transcribed Image Text:If f(1) and g(1) are arbitrary polynomials of degree at most 2, then the mapping
(f, 9) = f(-1)g(-1)+ f(0)g(0) + f(3)g(3)
defines an inner product in P2. Use this inner product to find (f, 9). ||f||, ||g||, and the angle af.g between f(x) and g(x) for
f(z) = 2x2 + 3x + 4 and g(x) = 3z2 – 5z - 9.
(f, g) =
|| || =
llg||
afg =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning