If m and n are any positive integers and mn is a perfect square, then m and n are perfect squares. Is the statement true or false? Find values of m and n that can be used to answer this question and enter them below. (m, n) = When you substitute the values you filled in for m and n, which of the choices below answers the question? O The statement is true. Proof: Let m and n be the numbers in the ordered pair above. Then mn is a perfect square and m and n are perfect squares. O The statement is false. Counterexample: Let m and n be the numbers in the ordered pair above. Then mn is a perfect square and at least one of m and n is not a perfect square. O The statement is false. Counterexample: Let m and n be the numbers in the ordered pair above. Then mn is not a perfect square and at least one of m and n is not a perfect square. O The statement is false. Counterexample: Let m and n be the numbers in the ordered pair above. Then mn is not a perfect square but m andn are perfect squares. Need Help? Read It
If m and n are any positive integers and mn is a perfect square, then m and n are perfect squares. Is the statement true or false? Find values of m and n that can be used to answer this question and enter them below. (m, n) = When you substitute the values you filled in for m and n, which of the choices below answers the question? O The statement is true. Proof: Let m and n be the numbers in the ordered pair above. Then mn is a perfect square and m and n are perfect squares. O The statement is false. Counterexample: Let m and n be the numbers in the ordered pair above. Then mn is a perfect square and at least one of m and n is not a perfect square. O The statement is false. Counterexample: Let m and n be the numbers in the ordered pair above. Then mn is not a perfect square and at least one of m and n is not a perfect square. O The statement is false. Counterexample: Let m and n be the numbers in the ordered pair above. Then mn is not a perfect square but m andn are perfect squares. Need Help? Read It
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter1: Fundamental Concepts Of Algebra
Section1.1: Real Numbers
Problem 35E
Related questions
Question
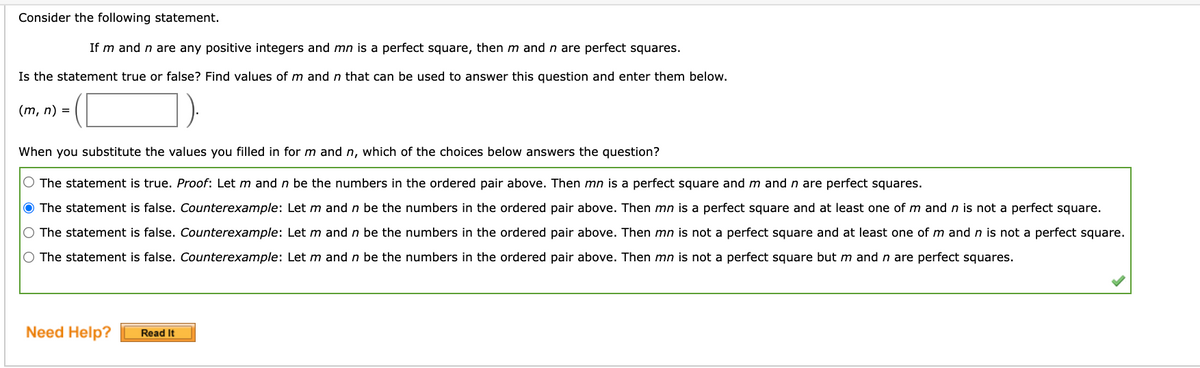
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following statement.
If m and n are any positive integers and mn is a perfect square, then m and n are perfect squares.
Is the statement true or false? Find values of m and n that can be used to answer this question and enter them below.
(m, n) = |
When you substitute the values you filled in for m and n, which of the choices below answers the question?
O The statement is true. Proof: Let m and n be the numbers in the ordered pair above. Then mn is a perfect square and m and n are perfect squares.
O The statement is false. Counterexample: Let m and n be the numbers in the ordered pair above. Then mn is a perfect square and at least one of m and n is not a perfect square.
O The statement is false. Counterexample: Let m and n be the numbers in the ordered pair above. Then mn is not a perfect square and at least one of m and n is not a perfect square.
O The statement is false. Counterexample: Let m and n be the numbers in the ordered pair above. Then mn is not a perfect square but m and n are perfect squares.
Need Help?
Read It
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell