If the current position of the object at time t is s (t), then the position at time h later is s (t + h). The average velocity (speed) during that additional tir (s(t+h)-s(t)) h is If we want to analyze the instantaneous velocity at time t, this can be made into a mathematical model by taking the limit as h h i.e. the derivative s' (t). Use this function in the model below for the velocity function v (t). The acceleration is the rate of change of velocity, so using the same logic, the acceleration function a (t) can be modeled with the derivative of the vele function, or the second derivative of the position function a (t) = v' (t) = s" (t). Problem Set question: A particle moves according to the position function s (t) = e2t sin (5t). Enclose arguments of functions in parentheses. For example, sin (2t). (a) Find the velocity function. a |a| sin (a)
If the current position of the object at time t is s (t), then the position at time h later is s (t + h). The average velocity (speed) during that additional tir (s(t+h)-s(t)) h is If we want to analyze the instantaneous velocity at time t, this can be made into a mathematical model by taking the limit as h h i.e. the derivative s' (t). Use this function in the model below for the velocity function v (t). The acceleration is the rate of change of velocity, so using the same logic, the acceleration function a (t) can be modeled with the derivative of the vele function, or the second derivative of the position function a (t) = v' (t) = s" (t). Problem Set question: A particle moves according to the position function s (t) = e2t sin (5t). Enclose arguments of functions in parentheses. For example, sin (2t). (a) Find the velocity function. a |a| sin (a)
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Chapter2: Graphical And Tabular Analysis
Section2.1: Tables And Trends
Problem 1TU: If a coffee filter is dropped, its velocity after t seconds is given by v(t)=4(10.0003t) feet per...
Related questions
Question
Find the velocity function v(t) and the acceleration function a(t) based on the information in the problem below. thank you!
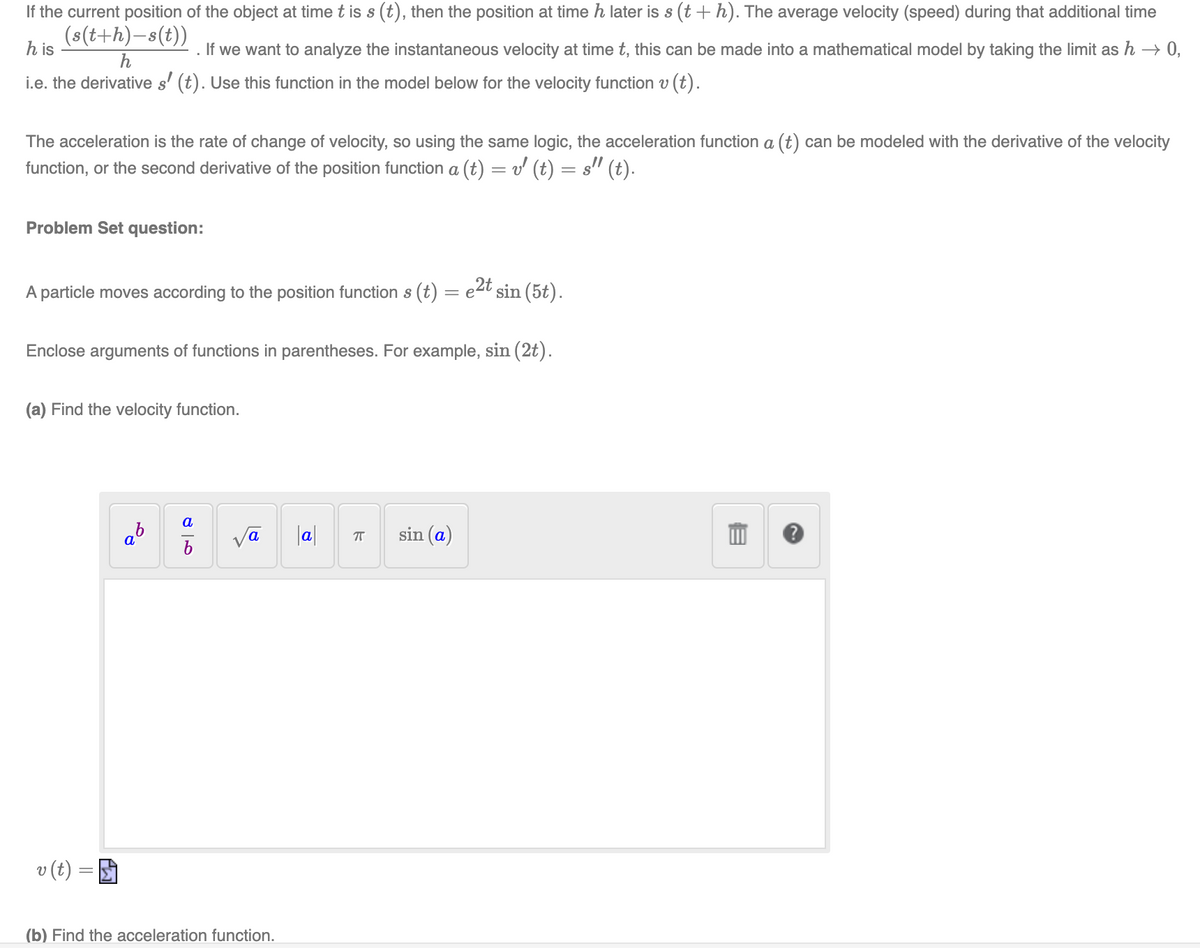
Transcribed Image Text:If the current position of the object at time t is s (t), then the position at time h later is s (t +h). The average velocity (speed) during that additional time
(s(t+h)-s(t))
h is
If we want to analyze the instantaneous velocity at time t, this can be made into a mathematical model by taking the limit as h → 0,
h
i.e. the derivative s' (t). Use this function in the model below for the velocity function v (t).
The acceleration is the rate of change of velocity, so using the same logic, the acceleration function a (t) can be modeled with the derivative of the velocity
function, or the second derivative of the position function a (t) = v' (t) = s" (t).
|3D
Problem Set question:
A particle moves according to the position function s (t) = e4t sin (5t).
Enclose arguments of functions in parentheses. For example, sin (2t).
(a) Find the velocity function.
a
|a|
sin (a)
a
v (t)
(b) Find the acceleration function.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning