If Two Entire Functions Agree On A Segment Of The Real Axis, Must They Agree On C? Jse
If Two Entire Functions Agree On A Segment Of The Real Axis, Must They Agree On C? Jse
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter4: Polynomial And Rational Functions
Section4.5: Rational Functions
Problem 51E
Related questions
Question
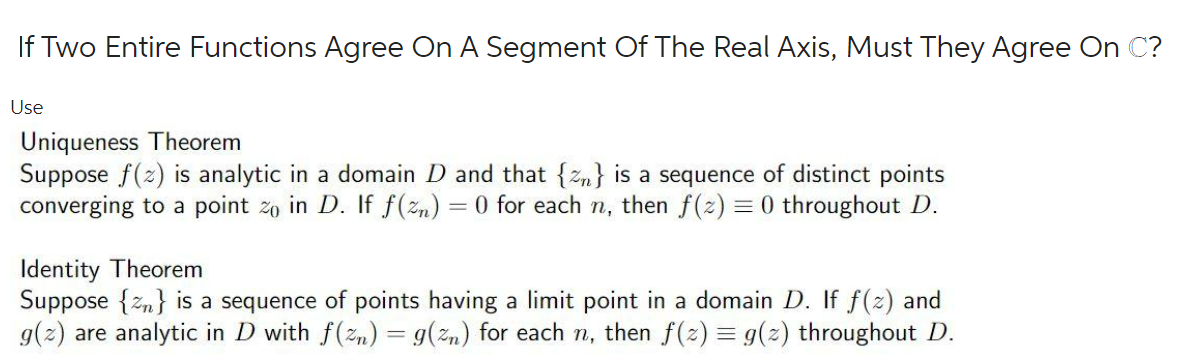
Transcribed Image Text:If Two Entire Functions Agree On A Segment Of The Real Axis, Must They Agree On C?
Use
Uniqueness Theorem
Suppose f(z) is analytic in a domain D and that {zn} is a sequence of distinct points
converging to a point zo in D. If f(zn) = 0 for each n, then f(z) = 0 throughout D.
Identity Theorem
Suppose {zn} is a sequence of points having a limit point in a domain D. If f(2) and
g(2) are analytic in D with f(zn) = g(zn) for each n, then f(2) = g(2) throughout D.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage
