If two objects travel through space along two different curves, it is always important to know whether they are going to collide. Curves can intersect, but we need to know if the objects will be in the same position at the same time. Suppose the paths of two particles are given by the following vector functions (image 1 and 2). If the particles collide, say the coordinates of the point.
If two objects travel through space along two different curves, it is always important to know whether they are going to collide. Curves can intersect, but we need to know if the objects will be in the same position at the same time. Suppose the paths of two particles are given by the following vector functions (image 1 and 2). If the particles collide, say the coordinates of the point.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter4: Polynomial And Rational Functions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5T
Related questions
Question
If two objects travel through space along two different curves, it is always important to know whether they are going to collide. Curves can intersect, but we need to know if the objects will be in the same position at the same time. Suppose the paths of two particles are given by the following vector functions (image 1 and 2). If the particles collide, say the coordinates of the point.

Transcribed Image Text:71(t) = (t², 7t – 12, t²)
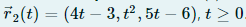
Transcribed Image Text:T2(t) = (4t – 3, ť², 5t – 6), t > 0.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage
