In a classic carnival ride patrons stand against the wall in a cylindrically shaped room. Once the room gets spinning fast enough, the floor drops from the bottom of the room! Friction between the walls of the room and the people on the ride make them the "stick" to the wall so they do not slide down. In one ride, the radius of the cylindrical room is 9 m and the room spins with a frequency f of 22.5 revolutions per minute.
In a classic carnival ride patrons stand against the wall in a cylindrically shaped room. Once the room gets spinning fast enough, the floor drops from the bottom of the room! Friction between the walls of the room and the people on the ride make them the "stick" to the wall so they do not slide down. In one ride, the radius of the cylindrical room is 9 m and the room spins with a frequency f of 22.5 revolutions per minute.
Related questions
Question
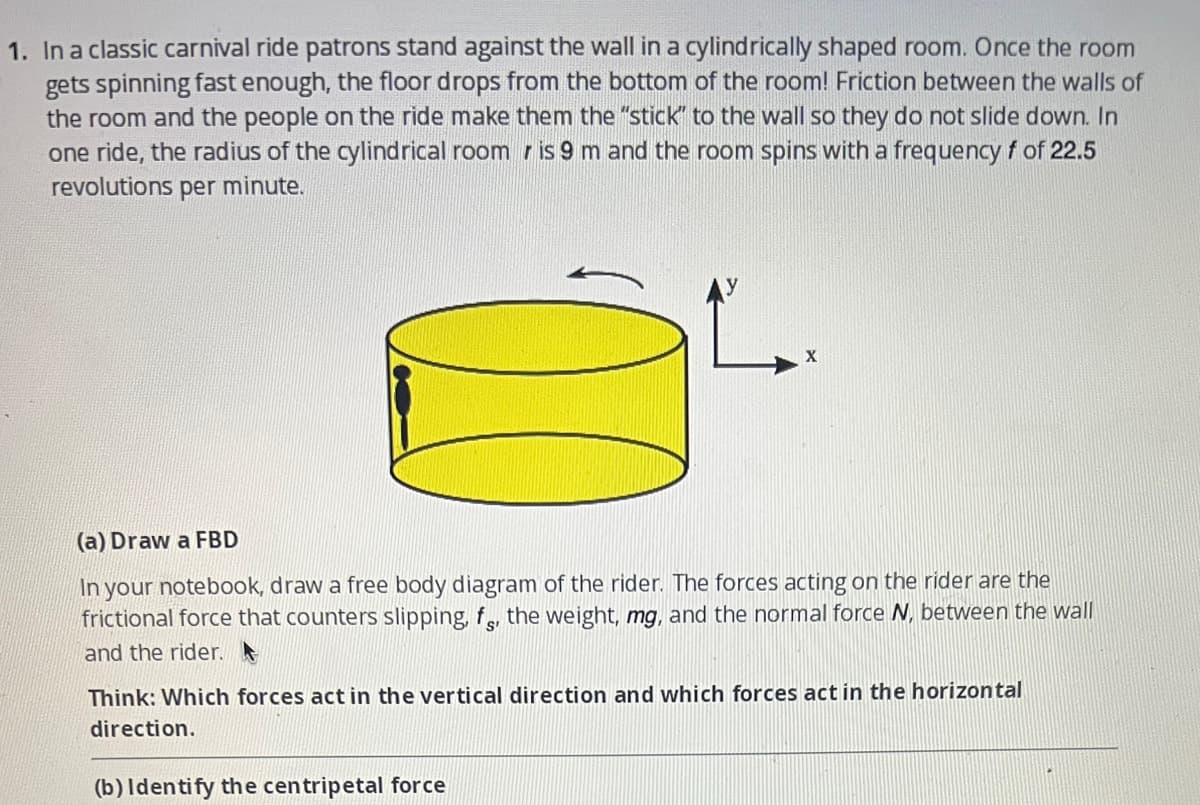
Transcribed Image Text:1. In a classic carnival ride patrons stand against the wall in a cylindrically shaped room. Once the room
gets spinning fast enough, the floor drops from the bottom of the room! Friction between the walls of
the room and the people on the ride make them the "stick" to the wall so they do not slide down. In
one ride, the radius of the cylindrical room is 9 m and the room spins with a frequency f of 22.5
revolutions per minute.
(a) Draw a FBD
In your notebook, draw a free body diagram of the rider. The forces acting on the rider are the
frictional force that counters slipping, f, the weight, mg, and the normal force N, between the wall
and the rider.
Think: Which forces act in the vertical direction and which forces act in the horizontal
direction.
(b) Identify the centripetal force
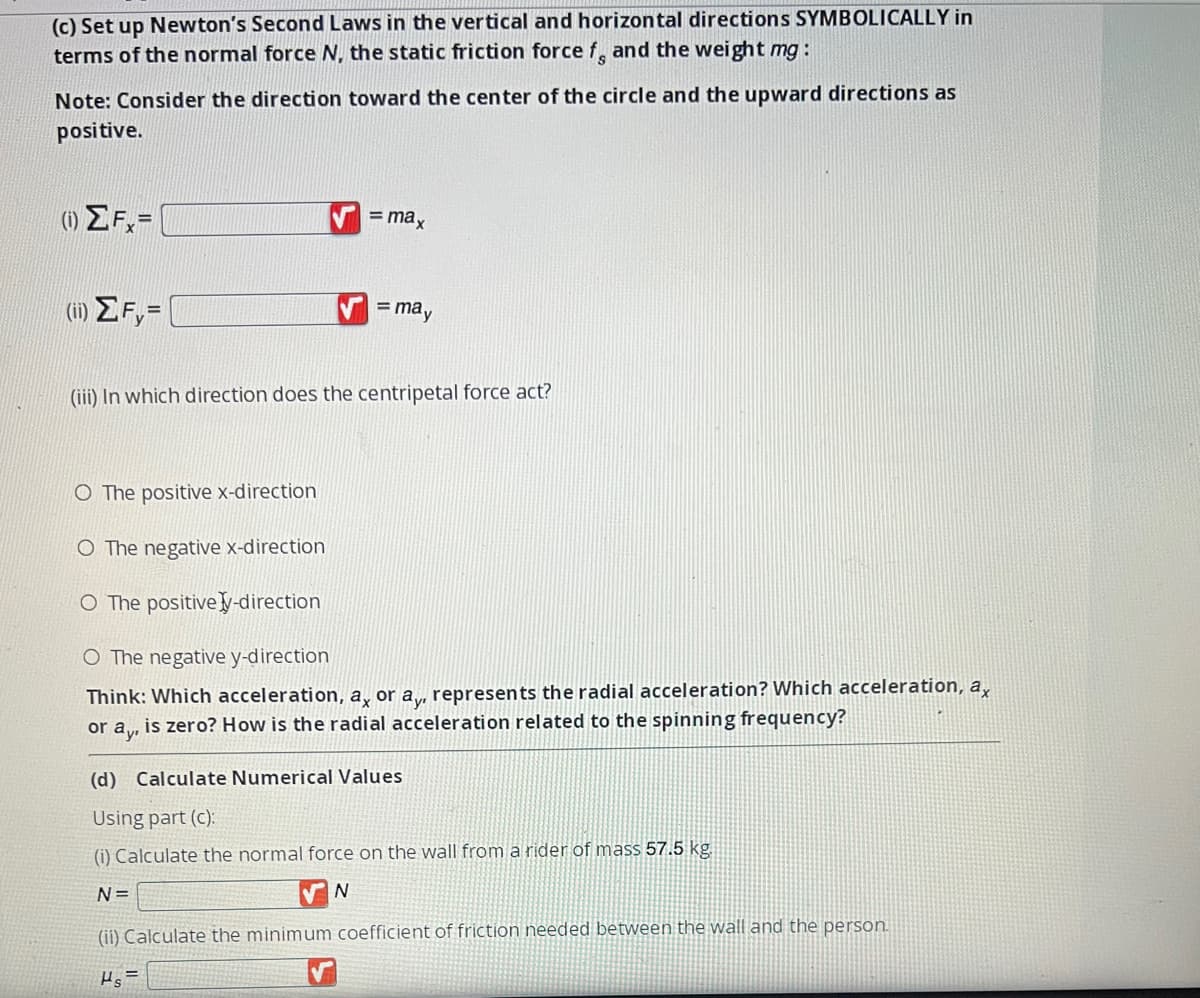
Transcribed Image Text:(c) Set up Newton's Second Laws in the vertical and horizontal directions SYMBOLICALLY in
terms of the normal force N, the static friction force f, and the weight mg:
Note: Consider the direction toward the center of the circle and the upward directions as
positive.
(0) ΣF=
(ii) ΣF=
= max
= may
(iii) In which direction does the centripetal force act?
O The positive x-direction
O The negative x-direction
O The positive y-direction
O The negative y-direction
Think: Which acceleration, a¸ or a,, represents the radial acceleration? Which acceleration, ax
or ay,
is zero? How is the radial acceleration related to the spinning frequency?
(d) Calculate Numerical Values
Using part (c):
(i) Calculate the normal force on the wall from a rider of mass 57.5 kg.
N=
N
(ii) Calculate the minimum coefficient of friction needed between the wall and the person.
Hs=
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images
