In cylindrical coordinates, a vector function of position is given by f = r² zer +4r²e + 2zęz Consider the region of space bounded by a cylinder of radius 2 centered around the z-axis, and having faces at z = -1 and z=1. a) Compute the value of ſf (f.n) dA by direct computation of the surface integral. b) Explain on physical grounds why the component of ƒ in the direction does not contribute to the surface integral. c) Determine the value of ſſf (V.ƒ)dV by direct computation of the volume integral.
In cylindrical coordinates, a vector function of position is given by f = r² zer +4r²e + 2zęz Consider the region of space bounded by a cylinder of radius 2 centered around the z-axis, and having faces at z = -1 and z=1. a) Compute the value of ſf (f.n) dA by direct computation of the surface integral. b) Explain on physical grounds why the component of ƒ in the direction does not contribute to the surface integral. c) Determine the value of ſſf (V.ƒ)dV by direct computation of the volume integral.
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:In cylindrical coordinates, a vector function of position is given by
f = r²zer + 4r²e + 2zęz
Consider the region of space bounded by a cylinder of radius 2 centered around the z-axis, and
having faces at z = -1 and z=1.
a) Compute the value of ff (f.n) dA by direct computation of the surface integral.
A
b) Explain on physical grounds why the component of f in the direction does not
contribute to the surface integral.
c) Determine the value of fff (V. f)dV by direct computation of the volume integral.
Expert Solution
Step 1
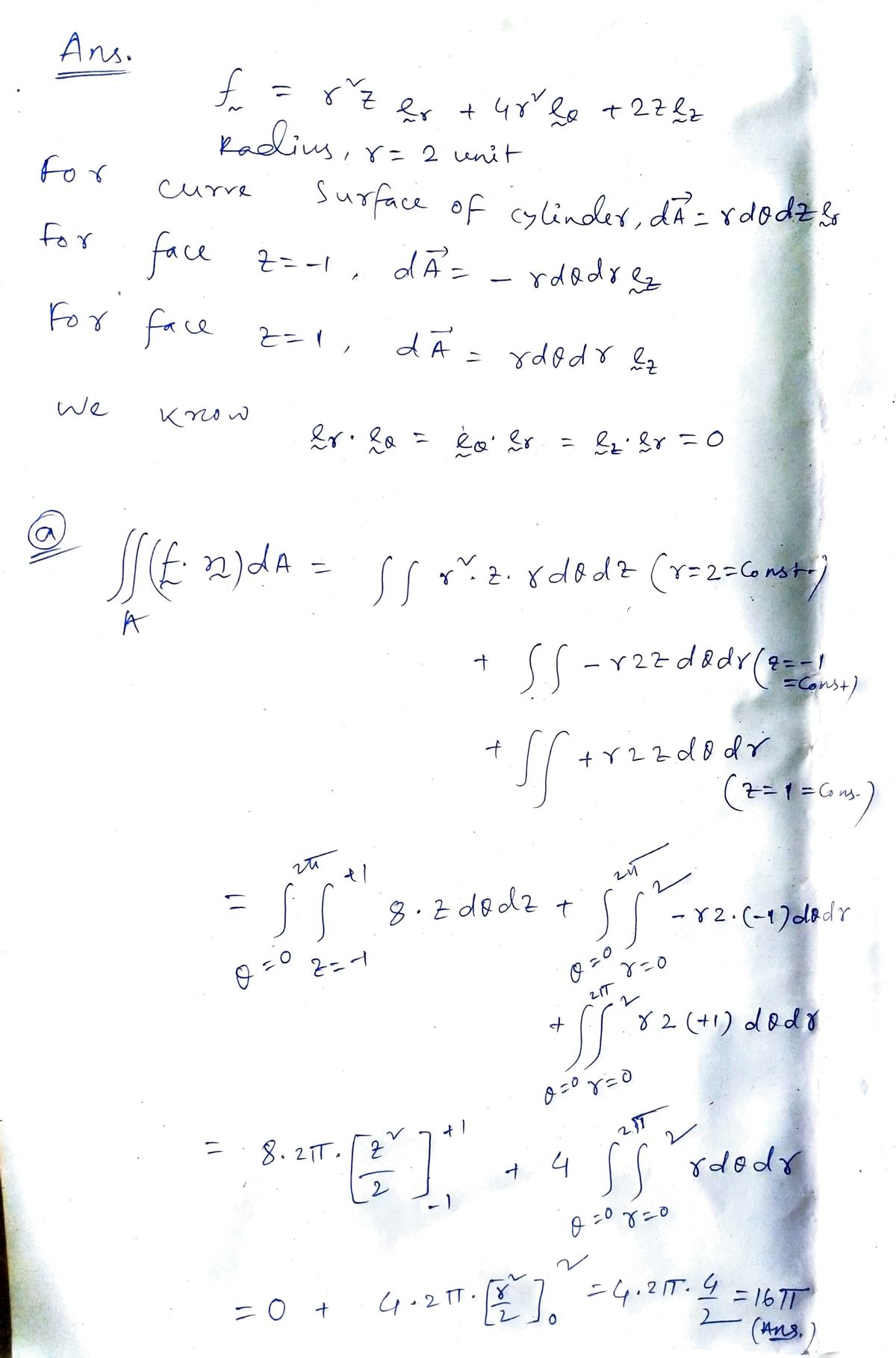
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images
