In the arrangement shown below, an object can be hung from a string (with linear mass density u = 0.00200 kg/m) that passes over a light pulley. The string is connected to a vibrator (of constant frequency f), and the length of the string between point P and the pulley is L = 1.70 m. When the mass m of the object is either 36.0 kg or 49.0 kg, standing waves are observed; no standing waves are observed with any mass between these values, however. Vibrator - L. m (a) What is the frequency of the vibrator (in Hz)? (Note: The greater the tension in the string, the smaller the number of nodes in the standing wave.) 862.4 Hz (b) What is the largest object mass (in kg) for which standing waves could be observed? 1754.6 V kg (c) What If? What would the linear mass density of the string have to be (in kg/m) if 49.0 kg is the largest mass for which standing waves are observed? 0.0000552 V kg/m (d) For what values of m (in kg) would standing waves with the next four higher numbers of nodes be observed in this case? m2 = kg m3 kg = m4 kg kg
In the arrangement shown below, an object can be hung from a string (with linear mass density u = 0.00200 kg/m) that passes over a light pulley. The string is connected to a vibrator (of constant frequency f), and the length of the string between point P and the pulley is L = 1.70 m. When the mass m of the object is either 36.0 kg or 49.0 kg, standing waves are observed; no standing waves are observed with any mass between these values, however. Vibrator - L. m (a) What is the frequency of the vibrator (in Hz)? (Note: The greater the tension in the string, the smaller the number of nodes in the standing wave.) 862.4 Hz (b) What is the largest object mass (in kg) for which standing waves could be observed? 1754.6 V kg (c) What If? What would the linear mass density of the string have to be (in kg/m) if 49.0 kg is the largest mass for which standing waves are observed? 0.0000552 V kg/m (d) For what values of m (in kg) would standing waves with the next four higher numbers of nodes be observed in this case? m2 = kg m3 kg = m4 kg kg
Related questions
Question
Help with part d only thanks
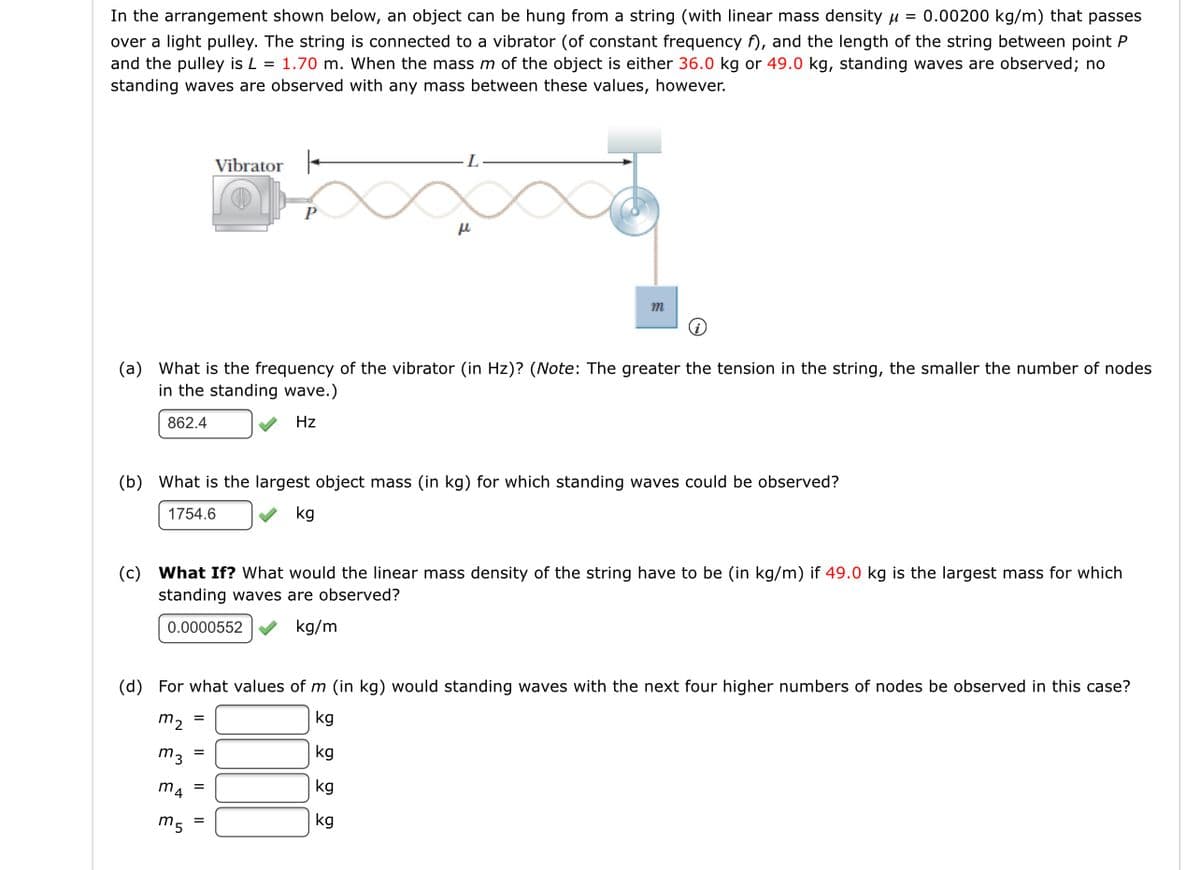
Transcribed Image Text:In the arrangement shown below, an object can be hung from a string (with linear mass density u = 0.00200 kg/m) that passes
over a light pulley. The string is connected to a vibrator (of constant frequency f), and the length of the string between point P
and the pulley is L = 1.70 m. When the mass m of the object is either 36.0 kg or 49.0 kg, standing waves are observed; no
standing waves are observed with any mass between these values, however.
Vibrator -
P
m
(a) What is the frequency of the vibrator (in Hz)? (Note: The greater the tension in the string, the smaller the number of nodes
in the standing wave.)
862.4
Hz
(b) What is the largest object mass (in kg) for which standing waves could be observed?
1754.6
kg
(c) What If? What would the linear mass density of the string have to be (in kg/m) if 49.0 kg is the largest mass for which
standing waves are observed?
0.0000552
kg/m
(d) For what values of m (in kg) would standing waves with the next four higher numbers of nodes be observed in this case?
m, =
kg
m3 =
kg
m4
kg
m5
kg
=
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps
