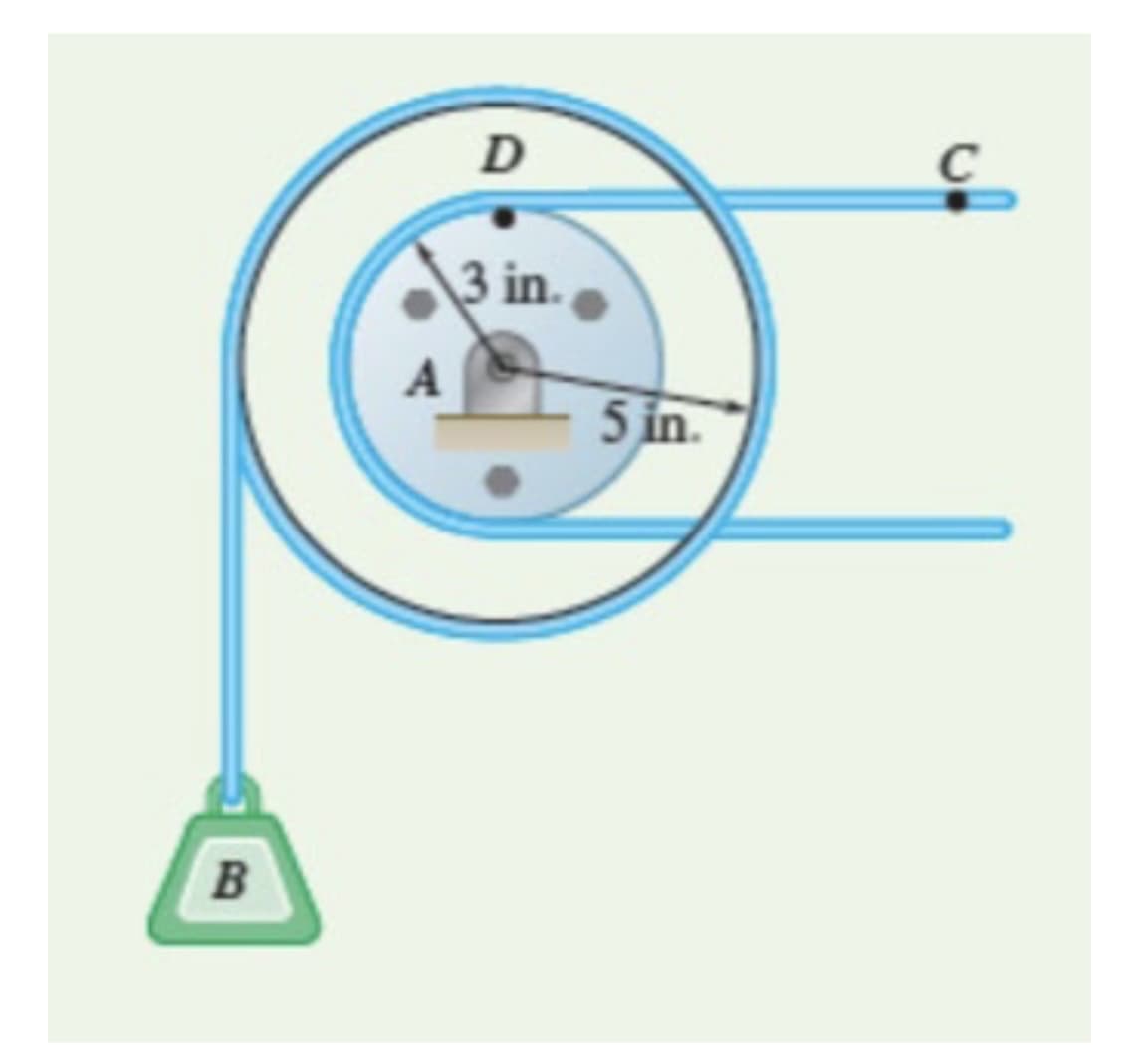
In the figure, the load at B is connected to a cable on the larger pulley. That pulley is controlled by the rotation of the smaller pulley, which is pulled by the cable at C. If the cable at C has a constant acceleration of 9 in./s2, and starts moving to the right at 12 in./s, determine: a. how many revolutions the larger pulley will complete in 2 seconds b. The velocity and rise (∆y) in the load after 2 seconds c. The angular acceleration of the pulley at D
In the figure, the load at B is connected to a cable on the larger pulley. That pulley is controlled by the rotation of the smaller pulley, which is pulled by the cable at C. If the cable at C has a constant acceleration of 9 in./s2, and starts moving to the right at 12 in./s, determine: a. how many revolutions the larger pulley will complete in 2 seconds b. The velocity and rise (∆y) in the load after 2 seconds c. The angular acceleration of the pulley at D
Related questions
Question
In the figure, the load at B is connected to a cable on the larger pulley. That pulley is controlled by the rotation of the smaller pulley, which is pulled by the cable at C. If the cable at C has a constant acceleration of 9 in./s2, and starts moving to the right at 12 in./s, determine:
a. how many revolutions the larger pulley will complete in 2 seconds
b. The velocity and rise (∆y) in the load after 2 seconds
c. The angular acceleration of the pulley at D
Transcribed Image Text:B
A
D
3 in.
5 in.
C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images
