In Version 4 of the Internet Protocol (IPV4), an IP address is a string of 32 bits. It begins with a networl number (netid followed by a host number (hostid), which identifies a computer as a member of a particular network. Class A net id (7 bit) host id (24 bit) Class B 10 net id (14 bit) host id (16 bit) Class C 110 net id (21 bit) host id (8 kit) Three forms of addresses are used, with different numbers of bits used for netids and hostids. Class A addresses, used for the largest networks, consist of 0, followed by a 7-bit netid and a 24-bit hostid. Cls B addresses, used for medium-sized networks, consist of 10, followed by a 14-bit netid and a 16-bit hostid. Class C addresses, used for the smallest networks, consist of 110, followed by a 21-bit netid and an 8-bit hostid. There are several restrictions on addresses because of special uses: 1111111 is not available as the netid of a Class A network, and the hostids consisting of all Os and all 1s are not availal for use in any network. A computer on the Internet has either a Class A, a Class B, or a Class C address How many different IPv4 addresses are available for computers on the Internet?
In Version 4 of the Internet Protocol (IPV4), an IP address is a string of 32 bits. It begins with a networl number (netid followed by a host number (hostid), which identifies a computer as a member of a particular network. Class A net id (7 bit) host id (24 bit) Class B 10 net id (14 bit) host id (16 bit) Class C 110 net id (21 bit) host id (8 kit) Three forms of addresses are used, with different numbers of bits used for netids and hostids. Class A addresses, used for the largest networks, consist of 0, followed by a 7-bit netid and a 24-bit hostid. Cls B addresses, used for medium-sized networks, consist of 10, followed by a 14-bit netid and a 16-bit hostid. Class C addresses, used for the smallest networks, consist of 110, followed by a 21-bit netid and an 8-bit hostid. There are several restrictions on addresses because of special uses: 1111111 is not available as the netid of a Class A network, and the hostids consisting of all Os and all 1s are not availal for use in any network. A computer on the Internet has either a Class A, a Class B, or a Class C address How many different IPv4 addresses are available for computers on the Internet?
Chapter12: Network Configuration
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13RQ
Related questions
Question
Discrete Structures or Discrete Mathematics
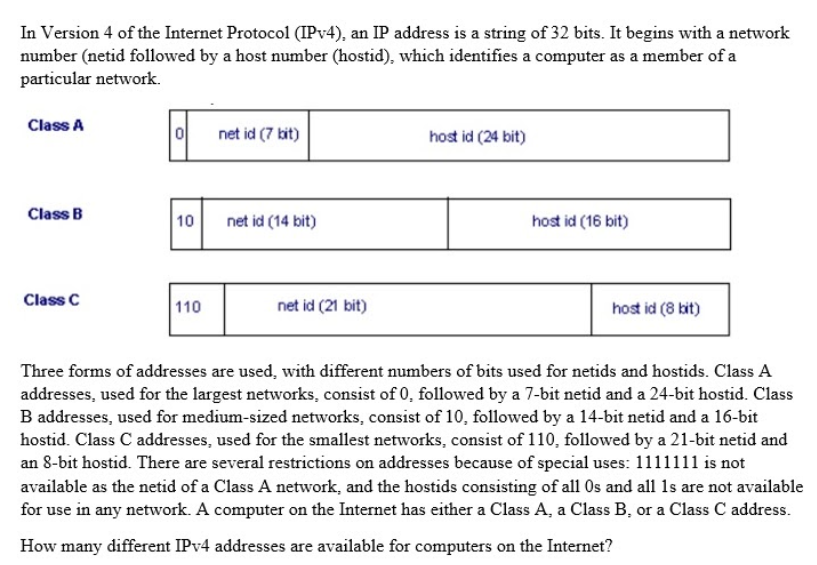
Transcribed Image Text:In Version 4 of the Internet Protocol (IPV4), an IP address is a string of 32 bits. It begins with a network
number (netid followed by a host number (hostid), which identifies a computer as a member of a
particular network.
Class A
net id (7 kit)
host id (24 bit)
Class B
10
net id (14 bit)
host id (16 bit)
Class C
110
net id (21 bit)
host id (8 kit)
Three forms of addresses are used, with different numbers of bits used for netids and hostids. Class A
addresses, used for the largest networks, consist of 0, followed by a 7-bit netid and a 24-bit hostid. Class
B addresses, used for medium-sized networks, consist of 10, followed by a 14-bit netid and a 16-bit
hostid. Class C addresses, used for the smallest networks, consist of 110, followed by a 21-bit netid and
an 8-bit hostid. There are several restrictions on addresses because of special uses: 1111111 is not
available as the netid of a Class A network, and the hostids consisting of all Os and all 1s are not available
for use in any network. A computer on the Internet has either a Class A, a Class B, or a Class C address.
How many different IPV4 addresses are available for computers on the Internet?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

LINUX+ AND LPIC-1 GDE.TO LINUX CERTIF.
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781337569798
Author:
ECKERT
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

Systems Architecture
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781305080195
Author:
Stephen D. Burd
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

LINUX+ AND LPIC-1 GDE.TO LINUX CERTIF.
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781337569798
Author:
ECKERT
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

Systems Architecture
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781305080195
Author:
Stephen D. Burd
Publisher:
Cengage Learning