Instructions for forms of answers in differential equation problems: For second order DEs, the roots of the characteristic equation may be real or complex. If the roots are real, the complementary solution is the weighted sum of real exponentials. Use C1 and C2 for the weights, where C1 is associated with the root with smaller magnitude. If the roots are complex, the complementary solution is the weighted sum of complex conjugate exponentials, which can be written as a constant times a decaying exponential times a cosine with phase. Use C1 for the constant and Phi for the phase. (Note: Some equations in the text give the constant multiplying the decaying exponential as 2C1. This was done for the derivation. The constant for this problem should be C1 alone.) All numerical angles(phases) should be given in radian angles (not degrees). Given the differential equation y" + 10y + 26y = 9cos(5t + 1.5708)u(t). a. Write the functional form of the complementary solution, y.(t), Ye(t) = help (formulas) b. Find the particular solution, y,(t). Yp(t) = help (formulas) c. Find the total solution, y(t) for the initial condition v(0) - 11 and v (O) - 2
Instructions for forms of answers in differential equation problems: For second order DEs, the roots of the characteristic equation may be real or complex. If the roots are real, the complementary solution is the weighted sum of real exponentials. Use C1 and C2 for the weights, where C1 is associated with the root with smaller magnitude. If the roots are complex, the complementary solution is the weighted sum of complex conjugate exponentials, which can be written as a constant times a decaying exponential times a cosine with phase. Use C1 for the constant and Phi for the phase. (Note: Some equations in the text give the constant multiplying the decaying exponential as 2C1. This was done for the derivation. The constant for this problem should be C1 alone.) All numerical angles(phases) should be given in radian angles (not degrees). Given the differential equation y" + 10y + 26y = 9cos(5t + 1.5708)u(t). a. Write the functional form of the complementary solution, y.(t), Ye(t) = help (formulas) b. Find the particular solution, y,(t). Yp(t) = help (formulas) c. Find the total solution, y(t) for the initial condition v(0) - 11 and v (O) - 2
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:James Stewart
Chapter1: Functions And Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Question
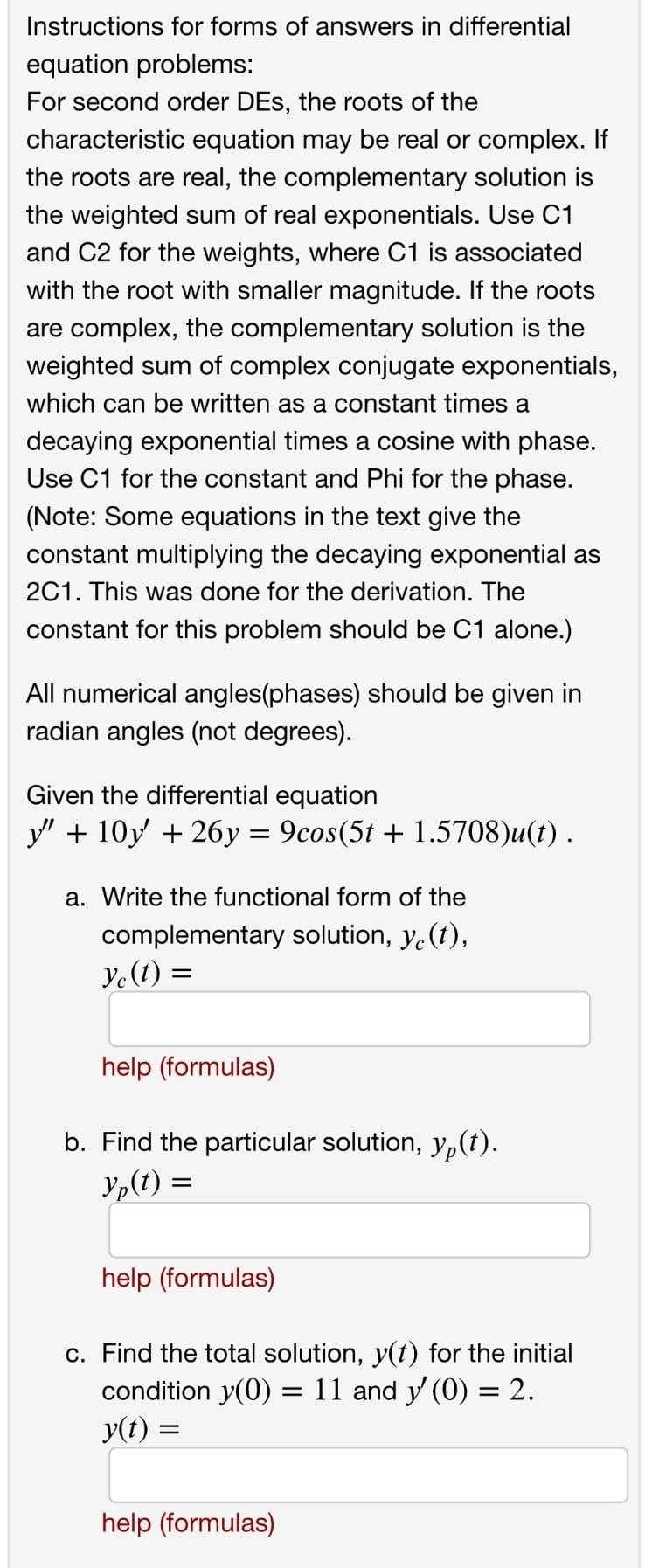
Transcribed Image Text:Instructions for forms of answers in differential
equation problems:
For second order DEs, the roots of the
characteristic equation may be real or complex. If
the roots are real, the complementary solution is
the weighted sum of real exponentials. Use C1
and C2 for the weights, where C1 is associated
with the root with smaller magnitude. If the roots
are complex, the complementary solution is the
weighted sum of complex conjugate exponentials,
which can be written as a constant times a
decaying exponential times a cosine with phase.
Use C1 for the constant and Phi for the phase.
(Note: Some equations in the text give the
constant multiplying the decaying exponential as
2C1. This was done for the derivation. The
constant for this problem should be C1 alone.)
All numerical angles(phases) should be given in
radian angles (not degrees).
Given the differential equation
y" + 10y + 26y = 9cos(5t + 1.5708)u(t).
a. Write the functional form of the
complementary solution, y.(t),
Ye(t) =
help (formulas)
b. Find the particular solution, y,(t).
Yp(t) =
help (formulas)
c. Find the total solution, y(t) for the initial
condition y(0)
y(t) :
= 11 and y (0) = 2.
%3D
help (formulas)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781319050740
Author:
Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:
9781337552516
Author:
Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:
Cengage Learning