km, k=1 m = 0, 1, 2 or 3 (these identities were discussed in class and also appear in the textbook), to evaluate the following sum: (k-9)(1-(k-10)²) Use the properties of sigma notation and the identities for 100 k=9 n where Explicitly state all identities that you are using and note that you do not need to
km, k=1 m = 0, 1, 2 or 3 (these identities were discussed in class and also appear in the textbook), to evaluate the following sum: (k-9)(1-(k-10)²) Use the properties of sigma notation and the identities for 100 k=9 n where Explicitly state all identities that you are using and note that you do not need to
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section10.4: Mathematical Induction
Problem 39E
Related questions
Question
Make sure to use the properties and identities stated in the question.
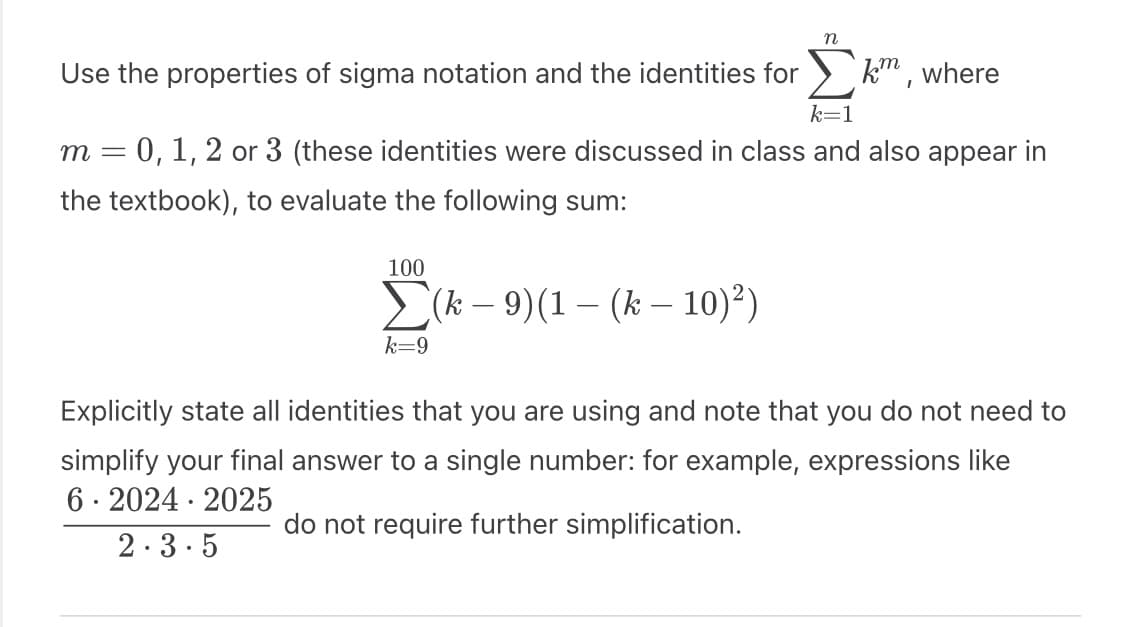
Transcribed Image Text:km,
k=1
m = 0, 1, 2 or 3 (these identities were discussed in class and also appear in
the textbook), to evaluate the following sum:
(k-9)(1-(k-10)²)
Use the properties of sigma notation and the identities for
100
k=9
n
where
Explicitly state all identities that you are using and note that you do not need to
simplify your final answer to a single number: for xample, expressions like
6 2024 2025
do not require further simplification.
2.3.5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage