Let A and B be vectors in R" and let c be a real number. Then (1) ||A|| 2 0, and || A|| = 0 if and only if A = 0 (2) ||cA|| = |c| ||A|| (3) ||A + B|| < || || + ||B||
Let A and B be vectors in R" and let c be a real number. Then (1) ||A|| 2 0, and || A|| = 0 if and only if A = 0 (2) ||cA|| = |c| ||A|| (3) ||A + B|| < || || + ||B||
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter8: Applications Of Trigonometry
Section8.4: The Dot Product
Problem 37E
Related questions
Question
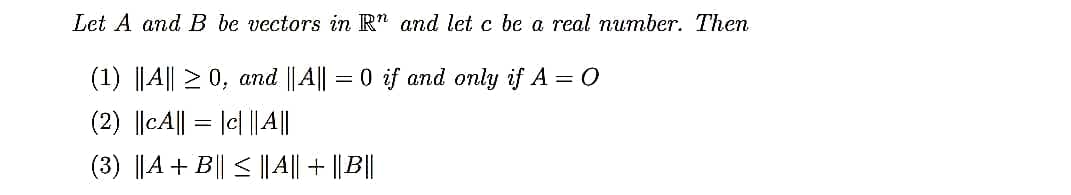
Transcribed Image Text:Let A and B be vectors in R" and let c be a real number. Then
(1) ||A|| 2 0, and ||A|| = 0 if and only if A = 0
(2) ||cA|| = |c| |||
(3) ||A + B|| < ||A|| + || B||
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning