Let & denote the convolution operator. If f (t) = et and g (t) = sin (6t), calculate (f®g)(t). Note: Use exact arithmetic. That means no calculator values. For example is exact, 0.33333 is not.
Let & denote the convolution operator. If f (t) = et and g (t) = sin (6t), calculate (f®g)(t). Note: Use exact arithmetic. That means no calculator values. For example is exact, 0.33333 is not.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter7: Analytic Trigonometry
Section7.4: Multiple-angle Formulas
Problem 54E
Related questions
Question
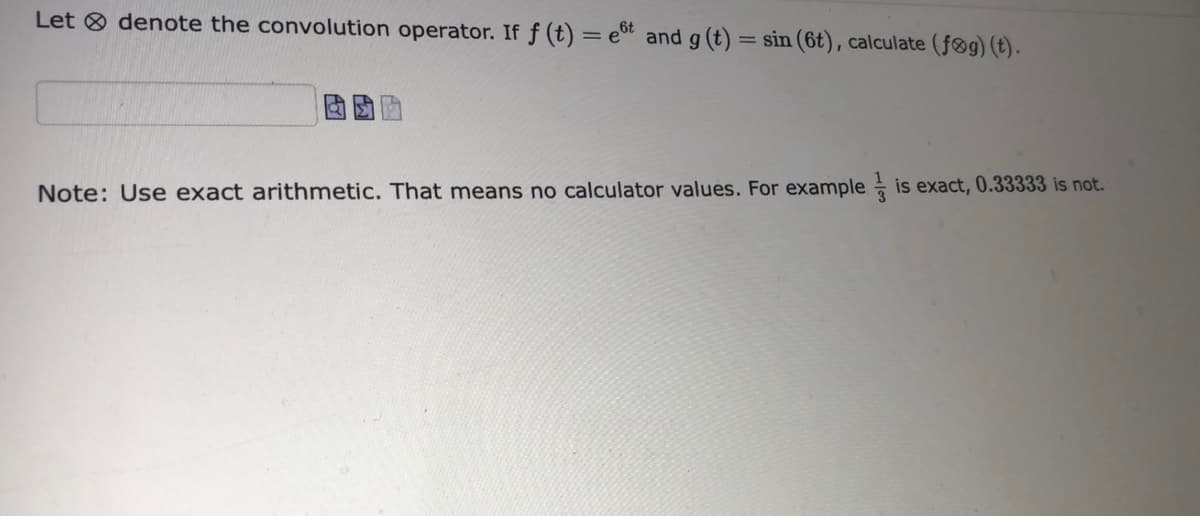
Transcribed Image Text:Let O denote the convolution operator. If f (t) = e" and g (t) = sin (6t), calculate (føg) (t).
Note: Use exact arithmetic. That means no calculator values. For example is exact, 0.33333 is not.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning