Let h(x) = f(g(x)) and p(x) = g(f(x)). Use the table below to compute the following derivatives. a. h'(1) b. p'(4) 1 2 3 3 2 f(x) f'(x) 1 - 3 4 - 4 - 2 - 9 g(x) 3 2 1 7 5 3 gʻ(x) 8 8
Let h(x) = f(g(x)) and p(x) = g(f(x)). Use the table below to compute the following derivatives. a. h'(1) b. p'(4) 1 2 3 3 2 f(x) f'(x) 1 - 3 4 - 4 - 2 - 9 g(x) 3 2 1 7 5 3 gʻ(x) 8 8
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337278461
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Ron Larson
ChapterP: Prerequisites
SectionP.6: Analyzing Graphs Of Functions
Problem 6ECP: Find the average rates of change of f(x)=x2+2x (a) from x1=3 to x2=2 and (b) from x1=2 to x2=0.
Related questions
Question
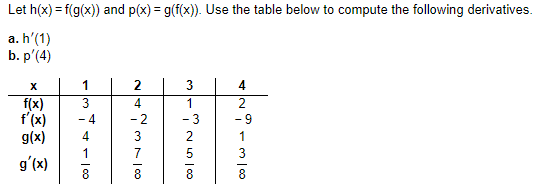
Transcribed Image Text:Let h(x) = f(g(x)) and p(x) = g(f(x)). Use the table below to compute the following derivatives.
a. h'(1)
b. p'(4)
1
2
3
f(x)
f'(x)
g(x)
3
4
2
- 2
- 3
- 9
- 4
4
3
1
7
5
3
gʻ(x)
8.
8.
8
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning