Let P(n) be the statement fi + f2 + ... + fn = fn fn+1, where for is the nth Fibonacci number. Click and drag expressions to show in algebraic detail that K(P(K) → P(k + 1)) is true. Vk (f+f+.... +f/+f/²+1 = (fk−1 + fk)(fk + fk+1) IH = (f² + f fkfk+1+f+1 = (f² + ƒ²+.. + ··· + f/²) + (fk−1 + fk)² ) fk+1(fk+fk+1) (f² + ƒ² + ··· + ƒ² ²) + (fk−1 + fk)² fkfk+1+f+1 fk+1f(k+1)+1 (fk-1+fk)(fk+fk+1)
Let P(n) be the statement fi + f2 + ... + fn = fn fn+1, where for is the nth Fibonacci number. Click and drag expressions to show in algebraic detail that K(P(K) → P(k + 1)) is true. Vk (f+f+.... +f/+f/²+1 = (fk−1 + fk)(fk + fk+1) IH = (f² + f fkfk+1+f+1 = (f² + ƒ²+.. + ··· + f/²) + (fk−1 + fk)² ) fk+1(fk+fk+1) (f² + ƒ² + ··· + ƒ² ²) + (fk−1 + fk)² fkfk+1+f+1 fk+1f(k+1)+1 (fk-1+fk)(fk+fk+1)
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305658004
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Ron Larson
Chapter4: Vector Spaces
Section4.2: Vector Spaces
Problem 48E: Let R be the set of all infinite sequences of real numbers, with the operations...
Related questions
Question
Please help me with this question. I am having trouble understanding what to do.
Thank you

Transcribed Image Text:Let P(n) be the statement ƒ + ƒ₂ + ... + ƒn
fn fn+1, where for is the nth Fibonacci number.
Click and drag expressions to show in algebraic detail that V K(P(k) → P(k + 1)) is true.
Vk (f² + f²² +
· + f / + f/²+1
=
IH
H=
II
(fk-1+fk) (fk + fk+1)
(ƒ² + ƒ²² +
fkfk+1+f²+1
=
(ƒ² + ƒ√ √² + ·
+ ƒ² ²) + (fk−1 + fk) 2
)
fk+1(fk+fk+1)
(f² + ƒ² +
· + ƒ² ²) + (fk−1 + fk)²
+ f²²) + f/²+1
fkfk+1+f/+1
fk+1f(k+1)+1
(fk-1+fk) (fk+fk+1)
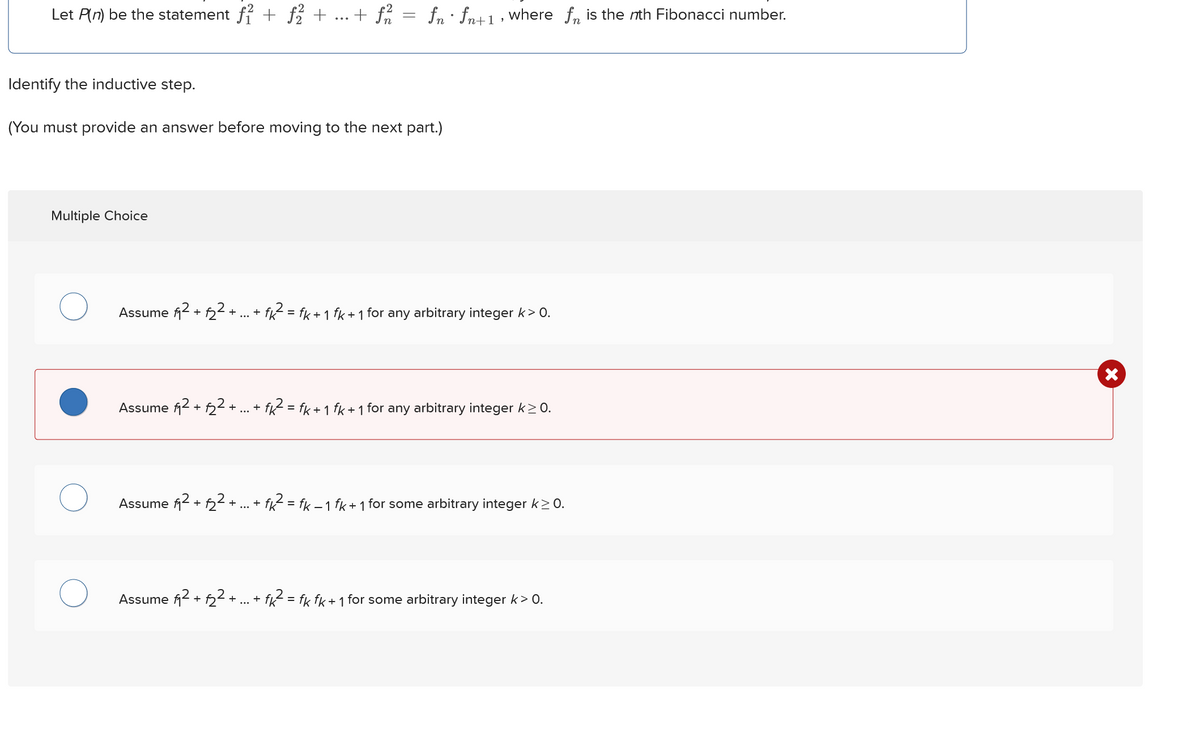
Transcribed Image Text:Let P(n) be the statement ƒ² + ƒ¾ +
...
+ f
=
fn fn+1, where for is the nth Fibonacci number.
.
Identify the inductive step.
(You must provide an answer before moving to the next part.)
Multiple Choice
Assume ƒ² + ½² + ... + fk² = fk + 1 fk + 1 for any arbitrary integer k> 0.
Assume ² + 122+.
+
- fk²² = fk + 1 fk + 1 for any arbitrary integer k≥0.
Assume f² +22+.
+1
+
Assume 2 + 22+
- fk² = fk − 1 fk + 1 for some arbitrary integer k≥0.
-
+
• fk² = fk fk + 1 for some arbitrary integer k> 0.
×
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,