Let R be a ring with identity, and let x e R be an element with a multiplicative inverse. Then the equation (-x) -(x¹) = 1 is true in R. Fill in the white boxes to make a proof of this fact. For each step in the proof, fill in the grey box to indicate which ring axiom or other fact is used to derive that step. Proof: . By ● By . By . By . By we have we have , we have we have we have (-x) -(x¹) = 1.
Let R be a ring with identity, and let x e R be an element with a multiplicative inverse. Then the equation (-x) -(x¹) = 1 is true in R. Fill in the white boxes to make a proof of this fact. For each step in the proof, fill in the grey box to indicate which ring axiom or other fact is used to derive that step. Proof: . By ● By . By . By . By we have we have , we have we have we have (-x) -(x¹) = 1.
Elements Of Modern Algebra
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285463230
Author:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Chapter5: Rings, Integral Domains, And Fields
Section5.2: Integral Domains And Fields
Problem 11E: Let R be the set of all matrices of the form [abba], where a and b are real numbers. Assume that R...
Related questions
Question
i need all blanks answers
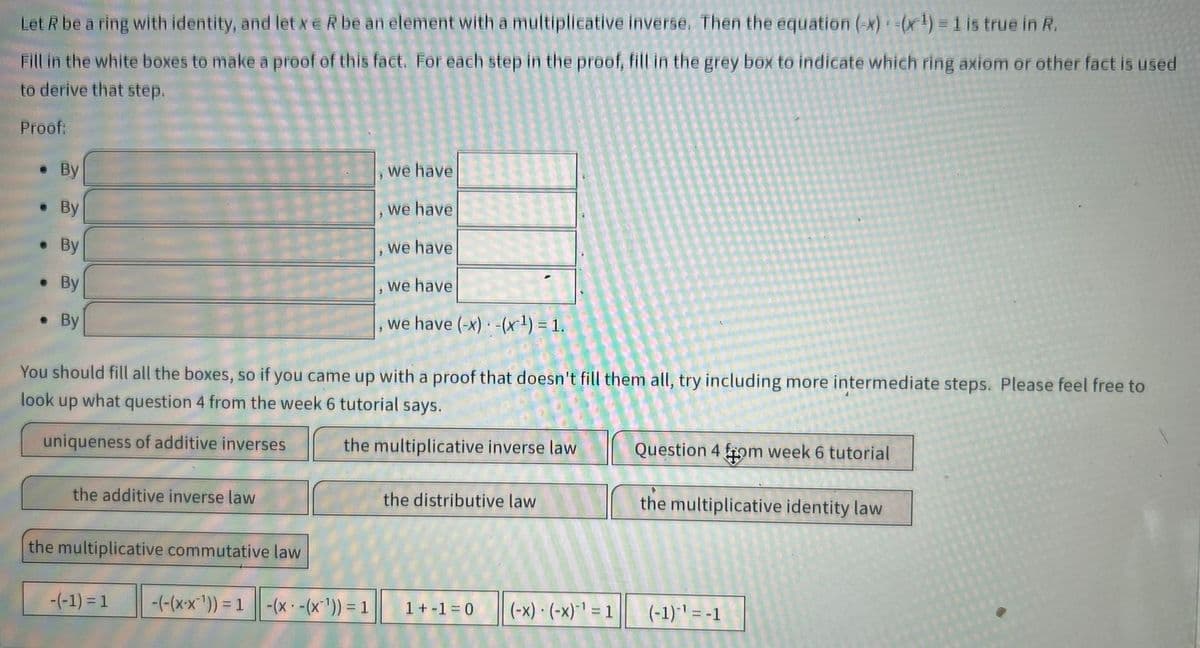
Transcribed Image Text:Let R be a ring with identity, and let xe R be an element with a multiplicative inverse. Then the equation (-x) =(x¹) = 1 is true in R.
Fill in the white boxes to make a proof of this fact. For each step in the proof, fill in the grey box to indicate which ring axiom or other fact is used
to derive that step.
Proof:
. By
By
●
By
. By
. By
●
the additive inverse law
You should fill all the boxes, so if you came up with a proof that doesn't fill them all, try including more intermediate steps. Please feel free to
look up what question 4 from the week 6 tutorial says.
uniqueness of additive inverses
the multiplicative inverse law
the multiplicative commutative law
-(-1) = 1
we have
we have
we have
we have
we have (-x) -(x¹) = 1.
-(-(x-x¹)) = 1 -(x -(x¹)) = 1
3
the distributive law
1+-1=0 (-x) - (-x)-¹ = 1
Question 4 from week 6 tutorial
the multiplicative identity law
(-1)-¹ = -1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,