Let the null space of matrix G and the null space of matrix H be orthogonal complements. Then only one of the following statement can be true: N(G) = N(H) 6. N(G")=N(H") N(G)=C(H") d. N(G)= C(H) %3D a. If the column space of a 3x3 matrix consists of all vectors b=|b2 | such that b, +b, = 3b, then b3 one of the following set of vectors forms a basis for the left null space of that matrix: (9)* N 3 3 (b. 3 and 3 d. 3 с. a. 1 and 3 -3 -3
Let the null space of matrix G and the null space of matrix H be orthogonal complements. Then only one of the following statement can be true: N(G) = N(H) 6. N(G")=N(H") N(G)=C(H") d. N(G)= C(H) %3D a. If the column space of a 3x3 matrix consists of all vectors b=|b2 | such that b, +b, = 3b, then b3 one of the following set of vectors forms a basis for the left null space of that matrix: (9)* N 3 3 (b. 3 and 3 d. 3 с. a. 1 and 3 -3 -3
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter6: Vector Spaces
Section6.2: Linear Independence, Basis, And Dimension
Problem 3AEXP
Related questions
Question
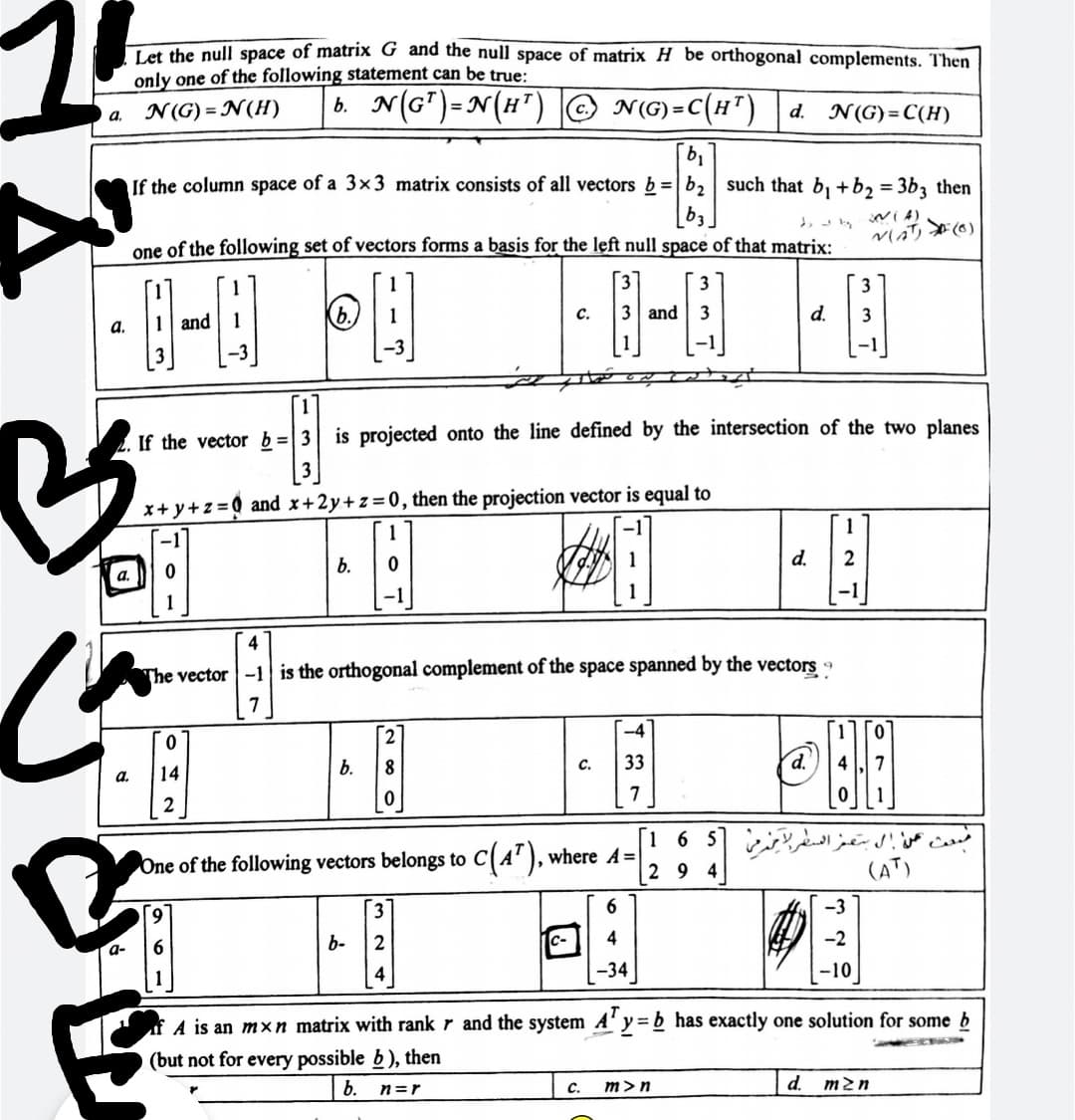
Transcribed Image Text:1.
Let the null space of matrix G and the null space of matrix H_be orthogonal complements. Then
only one of the following statement can be true:
N(G) = N(H)
b. N(G")=N(H") |© N()=C(H")
a.
d.
N(G)= C(H)
If the column space of a 3×3 matrix consists of all vectors b=|b2 such that b, +b2 = 3b3 then
one of the following set of vectors forms a basis for the left null space of that matrix:
Vaリ(6)
3
3
b.)
and
3
d.
3
с.
а.
and
3
If the vector b=|3| is projected onto the line defined by the intersection of the two planes
x+ y+z =Q and x+2y+z=0, then the projection vector is equal to
1
1
d.
b.
a.
-1
4
The vector-1 is the orthogonal complement of the space spanned by the vectors
7
[2
-4
0.
14
b.
C.
33
d.'
a.
7
C(A"), where A=
2 9
16 5 c
(AT)
One of the following vectors belongs to
-3
b-
2
4
-2
a-
-34
-10
A is an mxn matrix with rank r and the system A'y= b has exactly one solution for some b
(but not for every possible b ), then
b.
C.
m>n
d.
m2n
n=r
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning