Listen 10 76 KEY TERMS: Did You Get It? | 1. Match each term to its definition, as identified by its preceding letter code. A A partially permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of all cells. B Movement of substances across a biological membrane without energy expenditure. active transport carier protein C The passive movement of molecules from high to low concentration. concentration gradient D A type of passive transport facilitated by transport proteins. E A membrane-bound protein involved in the transport of a specific molecule across the membrane either by active transport or facilitated diffusion. diffusion F The energy-requiring movement of substances across a biological membrane against a concentration gradient. endocytosis facilitated diffusion ...... G Chemical used to enhance the contrast or highlight specific parts be viewed under a microscope. a cell or tissue to ion pump H A transmembrane protein that moves ions across a plasma membrane against their concentration gradient. osmosis I Passive movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane down a concentration gradient. passive transport J The gradual difference in the concentration of solutes in a solution between two regions. In biology, this usually results from unequal distribution of ions across a membrane. plasma membrane K Active transport in which molecules are engulfed by the plasma membrane, forming a phagosome or food vacuole within the cell. stain 2. The diagrams below depict what happens when a red blood cell is placed into three solutions with differing concentrations of solutes. Describe the tonicity of the solution (in relation to the cell) and describe what is happening: 3. Consider the two diagrams below. For each, draw in the appropriate box what you would expect to see after one hour. Particle with diameter of 5 nm Particle with After one hour: diameter of 20 nm Scluble particles placed in at high concentration Container of water at 20° C Partially permeable membrane with pores of 10 nm.
Listen 10 76 KEY TERMS: Did You Get It? | 1. Match each term to its definition, as identified by its preceding letter code. A A partially permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of all cells. B Movement of substances across a biological membrane without energy expenditure. active transport carier protein C The passive movement of molecules from high to low concentration. concentration gradient D A type of passive transport facilitated by transport proteins. E A membrane-bound protein involved in the transport of a specific molecule across the membrane either by active transport or facilitated diffusion. diffusion F The energy-requiring movement of substances across a biological membrane against a concentration gradient. endocytosis facilitated diffusion ...... G Chemical used to enhance the contrast or highlight specific parts be viewed under a microscope. a cell or tissue to ion pump H A transmembrane protein that moves ions across a plasma membrane against their concentration gradient. osmosis I Passive movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane down a concentration gradient. passive transport J The gradual difference in the concentration of solutes in a solution between two regions. In biology, this usually results from unequal distribution of ions across a membrane. plasma membrane K Active transport in which molecules are engulfed by the plasma membrane, forming a phagosome or food vacuole within the cell. stain 2. The diagrams below depict what happens when a red blood cell is placed into three solutions with differing concentrations of solutes. Describe the tonicity of the solution (in relation to the cell) and describe what is happening: 3. Consider the two diagrams below. For each, draw in the appropriate box what you would expect to see after one hour. Particle with diameter of 5 nm Particle with After one hour: diameter of 20 nm Scluble particles placed in at high concentration Container of water at 20° C Partially permeable membrane with pores of 10 nm.
Biology (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Chapter5: Biological Membranes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7TYU: Test Your Understanding 7.In cotransport (indirect active transport) (a) a uniporter moves a solute...
Related questions
Question
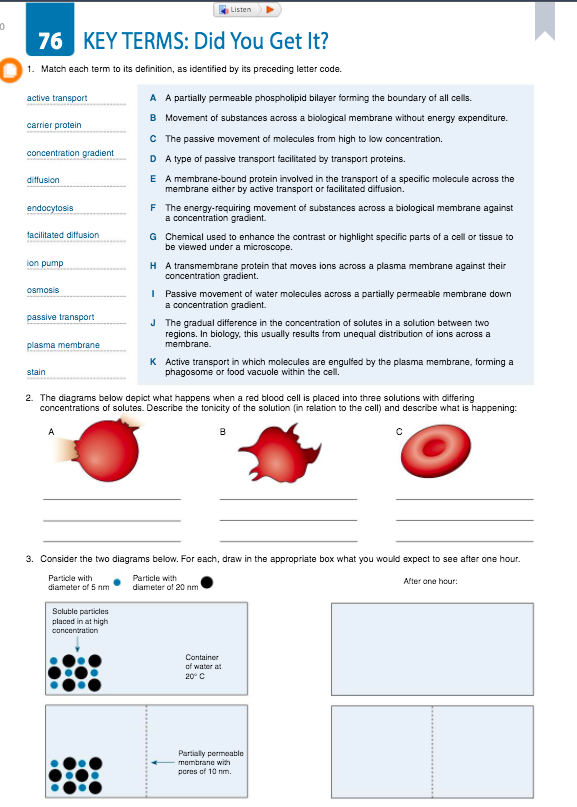
Transcribed Image Text:Listen
10
76 KEY TERMS: Did You Get It?
| 1. Match each term to its definition, as identified by its preceding letter code.
A A partially permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of all cells.
B Movement of substances across a biological membrane without energy expenditure.
active transport
carier protein
C The passive movement of molecules from high to low concentration.
concentration gradient
D A type of passive transport facilitated by transport proteins.
E A membrane-bound protein involved in the transport of a specific molecule across the
membrane either by active transport or facilitated diffusion.
diffusion
F The energy-requiring movement of substances across a biological membrane against
a concentration gradient.
endocytosis
facilitated diffusion
......
G Chemical used to enhance the contrast or highlight specific parts
be viewed under a microscope.
a cell or tissue to
ion pump
H A transmembrane protein that moves ions across a plasma membrane against their
concentration gradient.
osmosis
I Passive movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane down
a concentration gradient.
passive transport
J The gradual difference in the concentration of solutes in a solution between two
regions. In biology, this usually results from unequal distribution of ions across a
membrane.
plasma membrane
K Active transport in which molecules are engulfed by the plasma membrane, forming a
phagosome or food vacuole within the cell.
stain
2. The diagrams below depict what happens when a red blood cell is placed into three solutions with differing
concentrations of solutes. Describe the tonicity of the solution (in relation to the cell) and describe what is happening:
3. Consider the two diagrams below. For each, draw in the appropriate box what you would expect to see after one hour.
Particle with
diameter of 5 nm
Particle with
After one hour:
diameter of 20 nm
Scluble particles
placed in at high
concentration
Container
of water at
20° C
Partially permeable
membrane with
pores of 10 nm.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781337392938
Author:
Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781337392938
Author:
Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168116
Author:
Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:
OpenStax College