Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
15th Edition
ISBN:9781337408332
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Chapter16: Evidence Of Evolution
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8SQ
Related questions
Question
100%
Make a concept map involving the structure and thinking about biology (characteristics of living things)
Transcribed Image Text:1
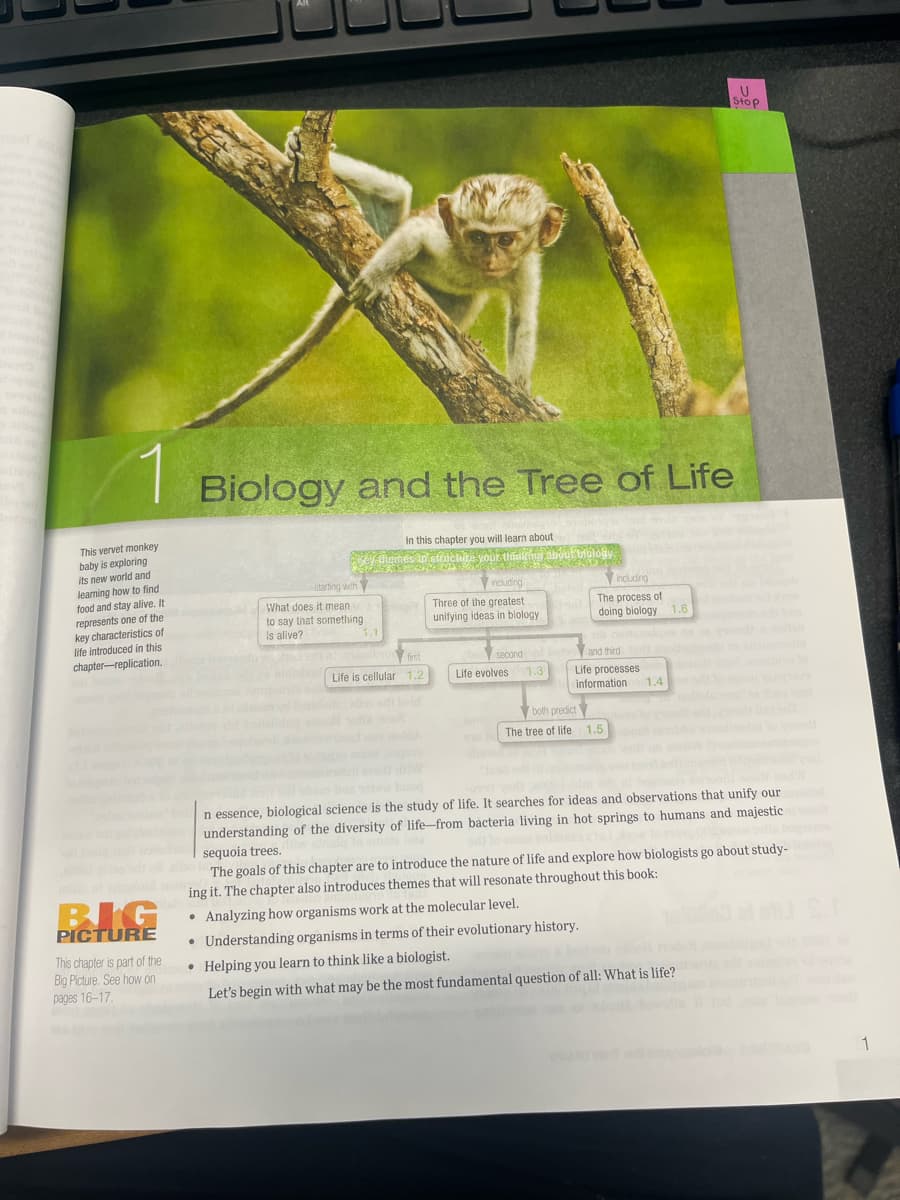
This vervet monkey
baby is exploring
its new world and
learning how to find
food and stay alive. It
represents one of the
key characteristics of
life introduced in this
chapter-replication.
BIG
PICTURE
000
This chapter is part of the
Big Picture. See how on
pages 16-17.
Biology and the Tree of Life
In this chapter you will learn about
Sey themes to structure your thinking about biology
AARON On
starting with
What does it mean
to say that something
is alive?
1.1
first
Life is cellular 1.2
including
Three of the greatest
unifying ideas in biology
second
bo
Life evolves 1.3
including
The process of
doing biology 1.6
and third tat
Life processes
information
both predict
The tree of life 1.5
U
Stop
1.4
the Ro
bobula sequoia trees.
The goals of this chapter are to introduce the nature of life and explore how biologists go about study-
ing it. The chapter also introduces themes that will resonate throughout this book:
• Analyzing how organisms work at the molecular level.
• Understanding organisms in terms of their evolutionary history.
• Helping you learn to think like a biologist.
Let's begin with what may be the most fundamental question of all: What is life?
broq
n essence, biological science is the study of life. It searches for ideas and observations that unify our
understanding of the diversity of life-from bacteria living in hot springs to humans and majestic
1
Transcribed Image Text:ngBiology
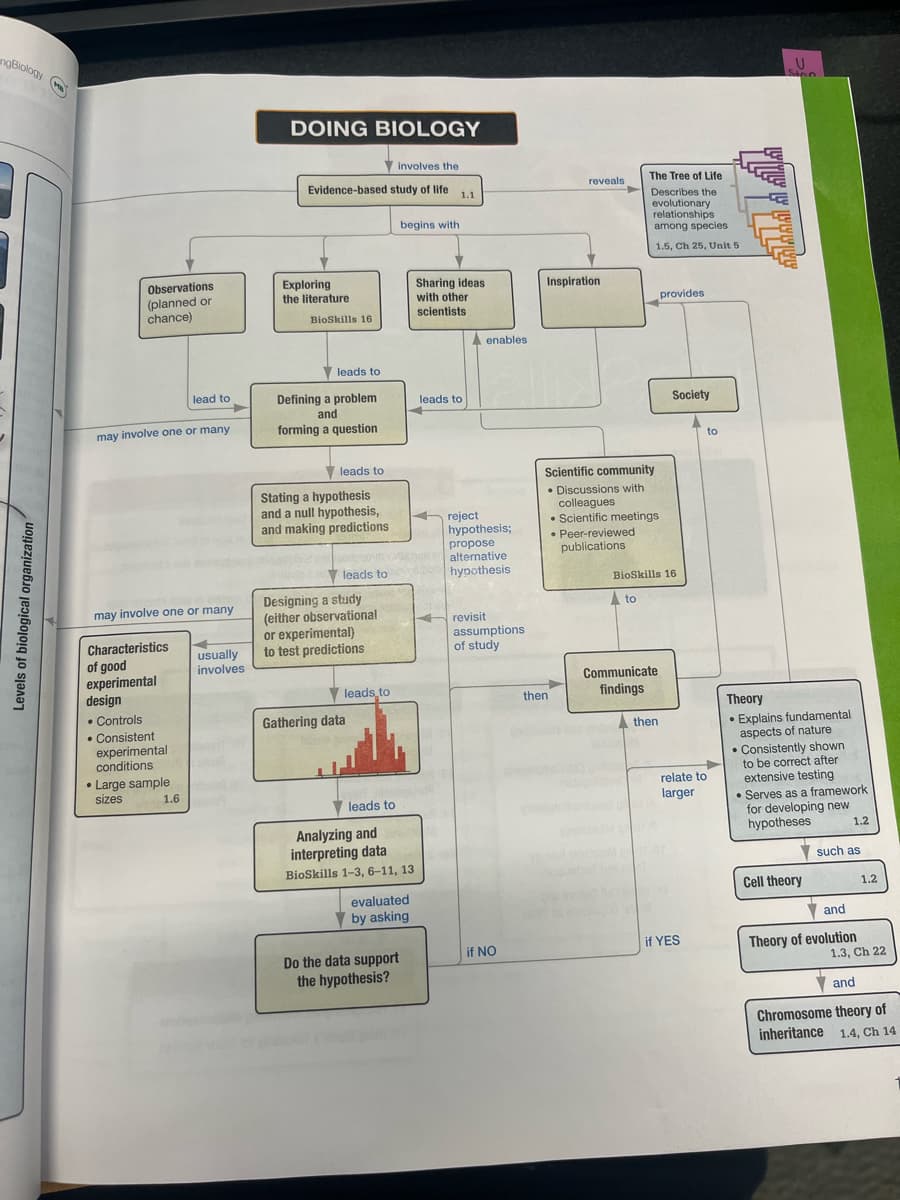
Levels of biological organization
MB
Observations
(planned or
chance)
may involve one or many
may involve one or many
Characteristics
of good
experimental
design
• Controls
• Consistent
experimental
conditions
lead to
• Large sample
sizes
1.6
usually
involves
DOING BIOLOGY
involves the
Evidence-based study of life
Exploring
the literature
BioSkills 16
leads to
Defining a problem
and
forming a question
leads to
Stating a hypothesis
and a null hypothesis,
and making predictions
leads to
Designing a study
(either observational
or experimental)
to test predictions
leads to
Gathering data
leads to
Analyzing and
interpreting data
Skills 1-3, 6-11, 13
begins with
evaluated
by asking
Do the data support
the hypothesis?
life 1.1
Sharing ideas
with other
scientists
leads to
enables
reject
hypothesis;
propose
alternative
bol hypothesis
revisit
assumptions
of study
if NO
reveals
Inspiration
then
Scientific community
• Discussions with
colleagues
The Tree of Life
Describes the
evolutionary
relationships
among species
1.5, Ch 25, Unit 5
Scientific meetings
• Peer-reviewed
publications
to
BioSkills 16
Communicate
findings
provides
then
Society
relate to
larger
if YES
to
+
U
Ston
Theory
Explains fundamental
aspects of nature
.
.
• Consistently shown
to be correct after
extensive testing
Serves as a framework.
for developing new
hypotheses
Cell theory
1.2
such as
and
Theory of evolution
1.2
1.3, Ch 22
and
Chromosome theory of
inheritance 1.4, Ch 14
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781337408332
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305073951
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781337408332
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305073951
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning