Multiple steps in signaling pathways allow for signal amplification. Each step can be magnified (a) Signaling pathway RECEPTION Binding of epinephrine to G protein-linked receptor TRANSDUCTION Inactive G protein Inactive adenylyl cyclase RESPONSE Active G protein 3012 Bearson Education Active adenylyl cyclase ATP Cyclic AMP Inactive protein kinase A Active protein kinase A Inactive phosphorylase kinase Active phosphorylase kinase Inactive glycogen phosphorylase (b) Number of molecules activated Glycogen 1 molecule 10² molecules 10² molecules 104 molecules 104 molecules 105 molecules Active glycogen phosphorylase 106 molecules Glucose-1-phosphate 108 molecules 3
Multiple steps in signaling pathways allow for signal amplification. Each step can be magnified (a) Signaling pathway RECEPTION Binding of epinephrine to G protein-linked receptor TRANSDUCTION Inactive G protein Inactive adenylyl cyclase RESPONSE Active G protein 3012 Bearson Education Active adenylyl cyclase ATP Cyclic AMP Inactive protein kinase A Active protein kinase A Inactive phosphorylase kinase Active phosphorylase kinase Inactive glycogen phosphorylase (b) Number of molecules activated Glycogen 1 molecule 10² molecules 10² molecules 104 molecules 104 molecules 105 molecules Active glycogen phosphorylase 106 molecules Glucose-1-phosphate 108 molecules 3
Biology 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Chapter9: Cell Communication
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12RQ: Histamine binds to the H1 G-protein-linked receptor to initiate the itchiness and airway...
Related questions
Question
Explain what is meant by ‘Multiple steps in signaling pathways allow for signal amplification.’
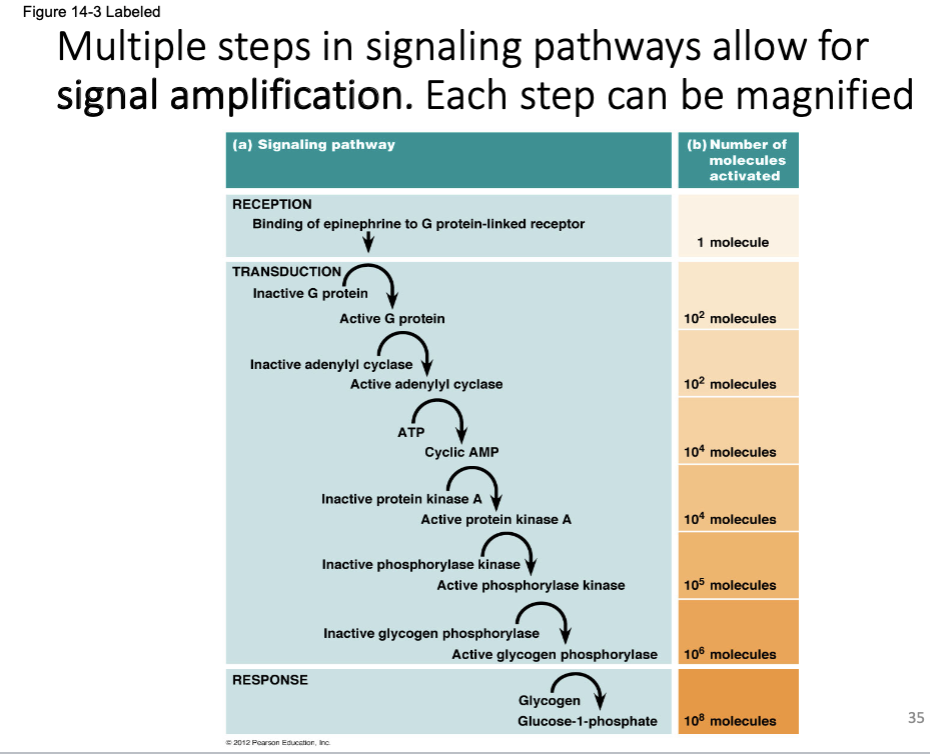
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 14-3 Labeled
Multiple steps in signaling pathways allow for
signal amplification. Each step can be magnified
(a) Signaling pathway
RECEPTION
Binding of epinephrine to G protein-linked receptor
TRANSDUCTION
Inactive G protein
Inactive adenylyl cyclase
RESPONSE
Active G protein
Active adenylyl cyclase
ATP
©2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Cyclic AMP
Inactive protein kinase A
Active protein kinase A
Inactive phosphorylase kinase
Active phosphorylase kinase
Inactive glycogen phosphorylase
Glycogen
(b) Number of
molecules
activated
Glucose-1-phosphate
1 molecule
10² molecules
10² molecules
104 molecules
104 molecules
Active glycogen phosphorylase 106 molecules
105 molecules
108 molecules
35
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning