no0 Dond nas a 6.5 percent even years rcurrent interest rates are 10 price bond pays interest annually. Use Appendix B and Appendix D to answer the question. Round your answer to the nearest dollar. b. If after four years interest rates are still 10 percent, what should be the price of the bond? Use Appendix B and Appendix D to answer the question. Assume that the bond pays interest annually. Round your answer to the nearest dollar. c. Even though interest rates did not change in a and b, why did the price of the bond change? The price of the bond with the longer term is -Select- v than the price of the bond with the shorter term as the investors will collect the -Select- v interest payments and receive the principal within a longer period of time. d. Change the interest rate in a and b to 4 percent and rework your answers. Assume that the bond pays interest annually. Round your answers to the nearest dollar. Price of the bond (eleven years to maturity): $ Price of the bond (seven years to maturity): $ Even though the interest rate is 4 percent in both calculations, why are the bond prices different? The price of the bond with the longer term is -Select- v than the price of the bond with the shorter term as the investors will collect the -Select- interest payments for a longer period of time.
no0 Dond nas a 6.5 percent even years rcurrent interest rates are 10 price bond pays interest annually. Use Appendix B and Appendix D to answer the question. Round your answer to the nearest dollar. b. If after four years interest rates are still 10 percent, what should be the price of the bond? Use Appendix B and Appendix D to answer the question. Assume that the bond pays interest annually. Round your answer to the nearest dollar. c. Even though interest rates did not change in a and b, why did the price of the bond change? The price of the bond with the longer term is -Select- v than the price of the bond with the shorter term as the investors will collect the -Select- v interest payments and receive the principal within a longer period of time. d. Change the interest rate in a and b to 4 percent and rework your answers. Assume that the bond pays interest annually. Round your answers to the nearest dollar. Price of the bond (eleven years to maturity): $ Price of the bond (seven years to maturity): $ Even though the interest rate is 4 percent in both calculations, why are the bond prices different? The price of the bond with the longer term is -Select- v than the price of the bond with the shorter term as the investors will collect the -Select- interest payments for a longer period of time.
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Makers
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305654174
Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Chapter10: Long-term Liabilities
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10.2E
Related questions
Question
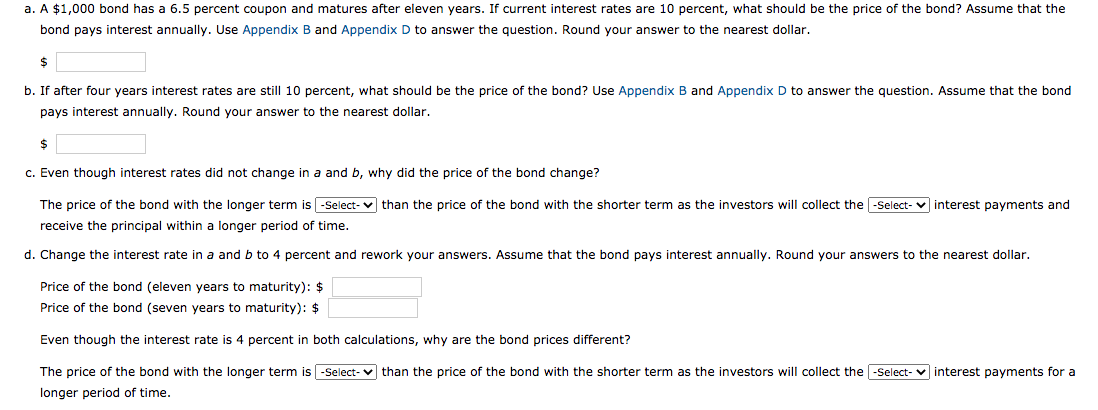
Transcribed Image Text:no0 Dond nas a 6.5 percent
even years
rcurrent interest rates are 10
price
bond pays interest annually. Use Appendix B and Appendix D to answer the question. Round your answer to the nearest dollar.
b. If after four years interest rates are still 10 percent, what should be the price of the bond? Use Appendix B and Appendix D to answer the question. Assume that the bond
pays interest annually. Round your answer to the nearest dollar.
c. Even though interest rates did not change in a and b, why did the price of the bond change?
The price of the bond with the longer term is -Select- v than the price of the bond with the shorter term as the investors will collect the -Select- v interest payments and
receive the principal within a longer period of time.
d. Change the interest rate in a and b to 4 percent and rework your answers. Assume that the bond pays interest annually. Round your answers to the nearest dollar.
Price of the bond (eleven years to maturity): $
Price of the bond (seven years to maturity): $
Even though the interest rate is 4 percent in both calculations, why are the bond prices different?
The price of the bond with the longer term is -Select- v than the price of the bond with the shorter term as the investors will collect the -Select-
interest payments for a
longer period of time.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Since you have posted a question with multiple sub-parts, we will solve first three sub-parts for you. To get remaining sub-part solved please repost the complete question and mention the sub-parts to be solved.
Step 2
a.
Calculate value of Bond as below:
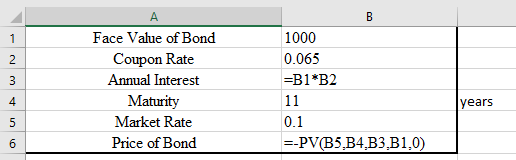
Resultant table:
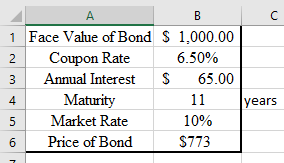
Hence, price is $773.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (…
Finance
ISBN:
9780357033609
Author:
Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. Joehnk
Publisher:
Cengage Learning