Note: You should leave any answers in surd form, instead of using decimals. To input inverse trig functions use asin() instead of arcsin, for sin 0. Similarly for the cosine and tangent functions. You can input square roots eg. 5 as sqrt(5). Calculate by using integration by substitution, 5 x dx Į xt +3 What was your substitution? u = What was your new integral in terms of u? In particular if the new integral was of the form A g(u)du where A E R then A = g(u) =
Note: You should leave any answers in surd form, instead of using decimals. To input inverse trig functions use asin() instead of arcsin, for sin 0. Similarly for the cosine and tangent functions. You can input square roots eg. 5 as sqrt(5). Calculate by using integration by substitution, 5 x dx Į xt +3 What was your substitution? u = What was your new integral in terms of u? In particular if the new integral was of the form A g(u)du where A E R then A = g(u) =
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:James Stewart
Chapter1: Functions And Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Question
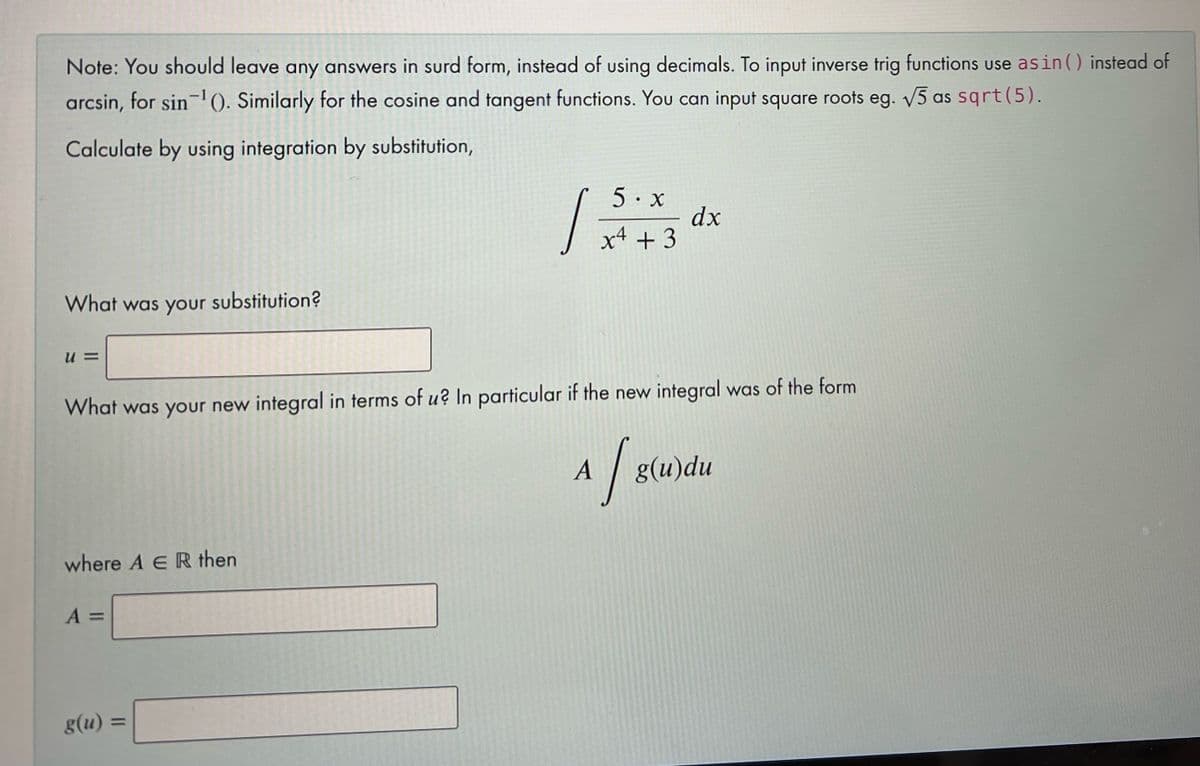
Transcribed Image Text:Note: You should leave any answers in surd form, instead of using decimals. To input inverse trig functions use asin () instead of
arcsin, for sin-'0. Similarly for the cosine and tangent functions. You can input square roots eg. V5 as sqrt(5).
Calculate by using integration by substitution,
5· x
dx
x4 + 3
What was your substitution?
What was your new integral in terms of u? In particular if the new integral was of the form
A
g(u)du
where A E R then
A =
g(u) =
%3D
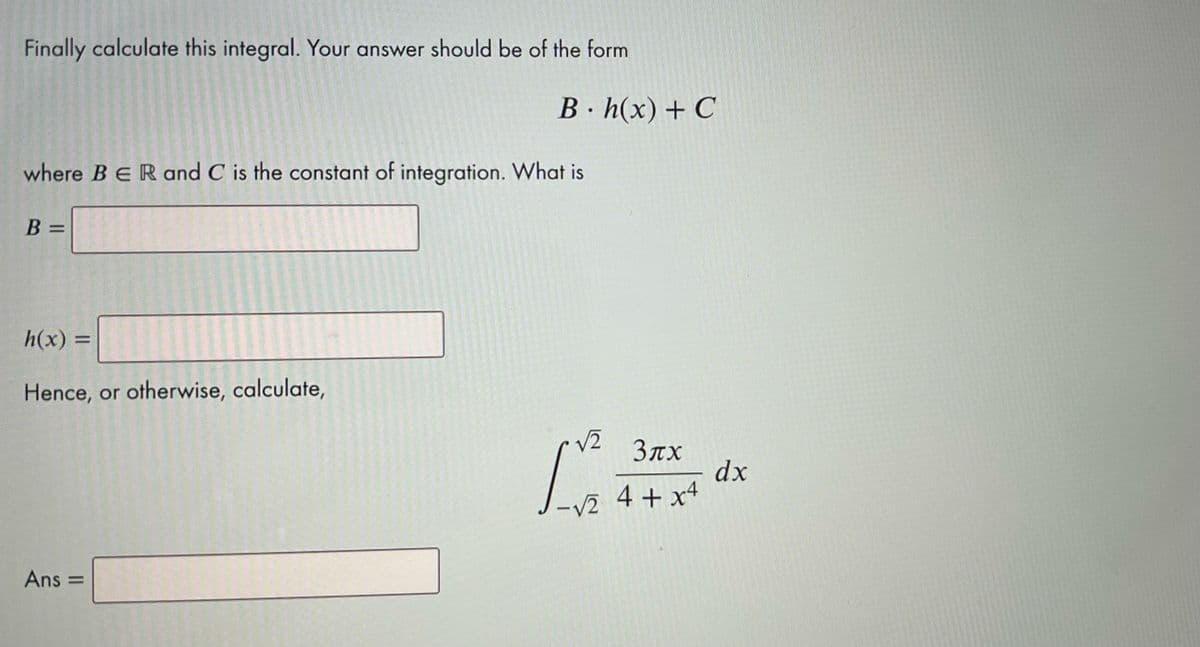
Transcribed Image Text:Finally calculate this integral. Your answer should be of the form
B·h(x) + C
where BERand C is the constant of integration. What is
B =
h(x) =
Hence, or otherwise, calculate,
/2
Злх
dx
-v2 4 + x4
Ans =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781319050740
Author:
Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:
9781337552516
Author:
Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:
Cengage Learning