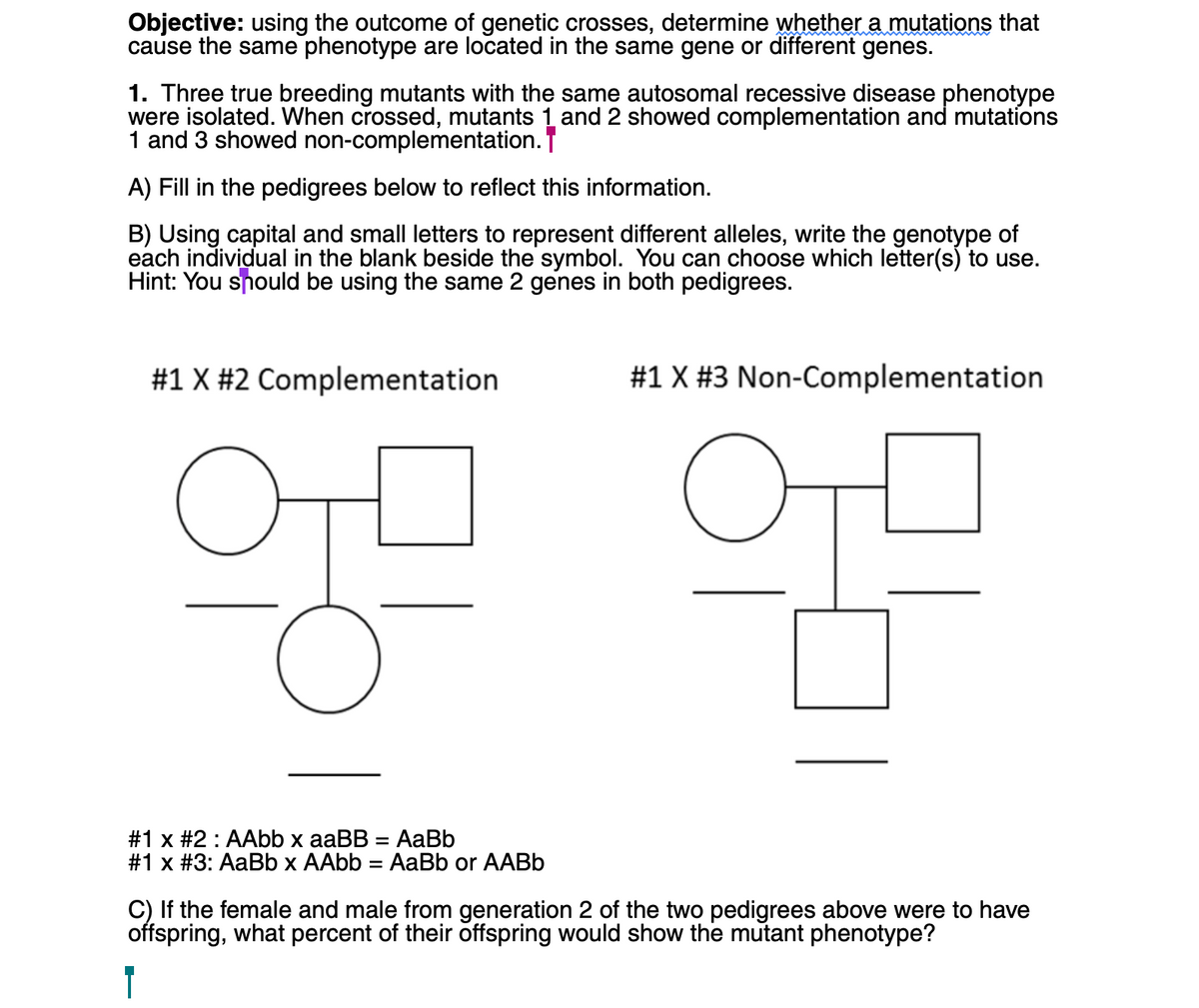
Objective: using the outcome of genetic crosses, determine whether a mutations that cause the same phenotype are located in the same gene or different genes. 1. Three true breeding mutants with the same autosomal recessive disease phenotype were isolated. When crossed, mutants 1 and 2 showed complementation and mutations 1 and 3 showed non-complementation. | A) Fill in the pedigrees below to reflect this information. B) Using capital and small letters to represent different alleles, write the genotype of each individual in the blank beside the symbol. You can choose which letter(s) to use. Hint: You should be using the same 2 genes in both pedigrees. #1 X #2 Complementation #1 X #3 Non-Complementation 무 무 O O = AaBb #1x #2: AAbb x aaBB #1x #3: AaBb x AAbb = AaBb or AABb C) If the female and male from generation 2 of the two pedigrees above were to have offspring, what percent of their offspring would show the mutant phenotype?
Genetic Recombination
Recombination is crucial to this process because it allows genes to be reassorted into diverse combinations. Genetic recombination is the process of combining genetic components from two different origins into a single unit. In prokaryotes, genetic recombination takes place by the unilateral transfer of deoxyribonucleic acid. It includes transduction, transformation, and conjugation. The genetic exchange occurring between homologous deoxyribonucleic acid sequences (DNA) from two different sources is termed general recombination. For this to happen, an identical sequence of the two recombining molecules is required. The process of genetic exchange which occurs in eukaryotes during sexual reproduction such as meiosis is an example of this type of genetic recombination.
Microbial Genetics
Genes are the functional units of heredity. They transfer characteristic information from parents to the offspring.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images


