|Consider a simple elevator design in which a 15,000 kg car A is con- nected to a 12,000kg counterweight B. Suppose that a failure of the drive system occurs (the failure does not affect the rope connecting A and B) when the car is at rest and 50 m above its buffer, causing the elevator car to fall. Model the car and the counterweight as particles and the cord as massless and inextensible, and model the action of car the emergency brakes using a Coulomb friction model with kinetic friction coefficient µk = 0.5 and a normal force equal to 35% of the car's weight. Determine the speed with which the car impacts the buffer. ca buft
|Consider a simple elevator design in which a 15,000 kg car A is con- nected to a 12,000kg counterweight B. Suppose that a failure of the drive system occurs (the failure does not affect the rope connecting A and B) when the car is at rest and 50 m above its buffer, causing the elevator car to fall. Model the car and the counterweight as particles and the cord as massless and inextensible, and model the action of car the emergency brakes using a Coulomb friction model with kinetic friction coefficient µk = 0.5 and a normal force equal to 35% of the car's weight. Determine the speed with which the car impacts the buffer. ca buft
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Chapter6: Beams And Cables
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6.66P: A uniform 80-ft pipe that weighs 960 lb is supported entirely by a cable AB of negligible weight....
Related questions
Question
100%
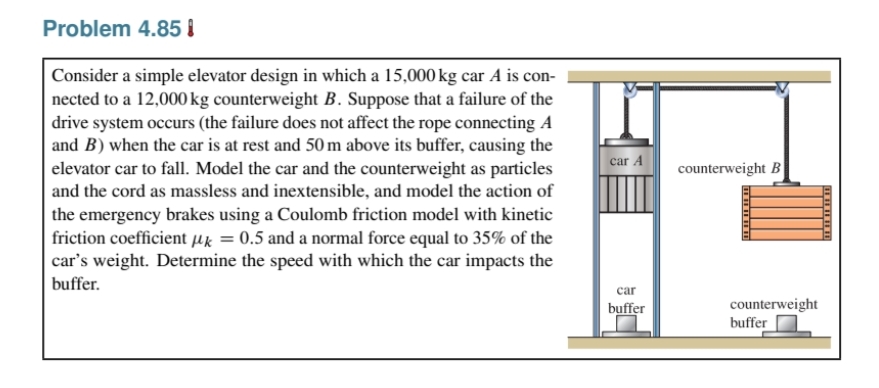
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 4.85 I
Consider a simple elevator design in which a 15,000 kg car A is con-
nected to a 12,000 kg counterweight B. Suppose that a failure of the
drive system occurs (the failure does not affect the rope connecting A
and B) when the car is at rest and 50 m above its buffer, causing the
elevator car to fall. Model the car and the counterweight as particles
car A
counterweight B
and the cord as massless and inextensible, and model the action of
the emergency brakes using a Coulomb friction model with kinetic
friction coefficient µk = 0.5 and a normal force equal to 35% of the
car's weight. Determine the speed with which the car impacts the
buffer.
car
counterweight
buffer
buffer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L