Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter6: Vector Spaces
Section6.6: The Matrix Of A Linear Transformation
Problem 30EQ
Related questions
Question
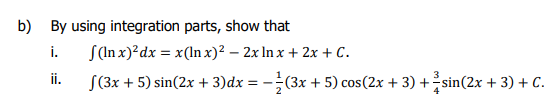
Transcribed Image Text:b) By using integration parts, show that
i.
S(In x)?dx = x(lnx)? – 2x In x + 2x + C.
ii.
S(3x + 5) sin(2x + 3)dx = -(3x + 5) cos(2x + 3) +sin(2x + 3) + C.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning