Part 2: Find each of the probabilities when a state is chosen at random: A. P(A or B) В. Р(А) С. Р(В) D. P(A and B)
Part 2: Find each of the probabilities when a state is chosen at random: A. P(A or B) В. Р(А) С. Р(В) D. P(A and B)
Chapter8: Sequences, Series,and Probability
Section8.7: Probability
Problem 6ECP: In Pennsylvania’s Cash 5 game, a player chooses five different numbers from 1 to 43. If these five...
Related questions
Question
Just need help with part 2 please!
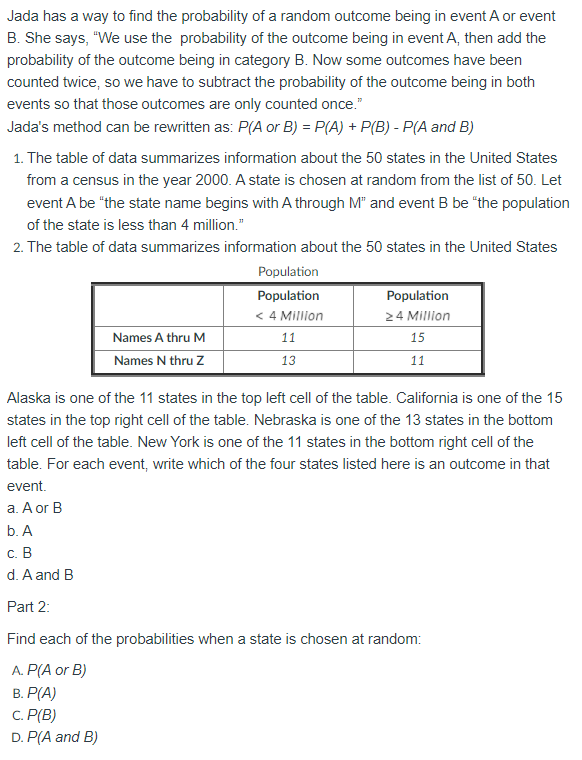
Transcribed Image Text:Jada has a way to find the probability of a random outcome being in event A or event
B. She says, "We use the probability of the outcome being in event A, then add the
probability of the outcome being in category B. Now some outcomes have been
counted twice, so we have to subtract the probability of the outcome being in both
events so that those outcomes are only counted once."
Jada's method can be rewritten as: P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B)
1. The table of data summarizes information about the 50 states in the United States
from a census in the year 2000. A state is chosen at random from the list of 50. Let
event A be "the state name begins with A through M" and event B be "the population
of the state is less than 4 million."
2. The table of data summarizes information about the 50 states in the United States
Population
Population
Population
< 4 Million
24 Million
Names A thru M
11
15
Names N thru Z
13
11
Alaska is one of the 11 states in the top left cell of the table. California is one of the 15
states in the top right cell of the table. Nebraska is one of the 13 states in the bottom
left cell of the table. New York is one of the 11 states in the bottom right cell of the
table. For each event, write which of the four states listed here is an outcome in that
event.
а. Aor B
b. A
с. В
d. A and B
Part 2:
Find each of the probabilities when a state is chosen at random:
A. P(A or B)
В. Р(А)
C. P(B)
D. P(A and B)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you


College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL


College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL