Part 3: Resistors in Parallel and Series Aim: To understand how the magnitude of the total resistance is calculated in a parallel and series circuit. Resistors in Series Procedure: 1. Create a circuit with one battery and 2 resistors in series. 2. Using the voltmeter tool, measure the voltage across each resistor, and then the whole circuit. Record results in table below. 3. Using the non-contact ammeter tool, measure the current through the wire near each resistor and the battery. Record the results. 4. Calculate the resistance for each resistor and the whole circuit using the equation R=V/I (Ohm's Law). 5. Repeat these steps, but add another resistor each time. Go up to 4 resistors.
Part 3: Resistors in Parallel and Series Aim: To understand how the magnitude of the total resistance is calculated in a parallel and series circuit. Resistors in Series Procedure: 1. Create a circuit with one battery and 2 resistors in series. 2. Using the voltmeter tool, measure the voltage across each resistor, and then the whole circuit. Record results in table below. 3. Using the non-contact ammeter tool, measure the current through the wire near each resistor and the battery. Record the results. 4. Calculate the resistance for each resistor and the whole circuit using the equation R=V/I (Ohm's Law). 5. Repeat these steps, but add another resistor each time. Go up to 4 resistors.
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Stephen L. Herman
Chapter7: Parallel Circuits
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3PP: Using the rules for parallel circuits and Ohmslaw, solve for the missing values....
Related questions
Question
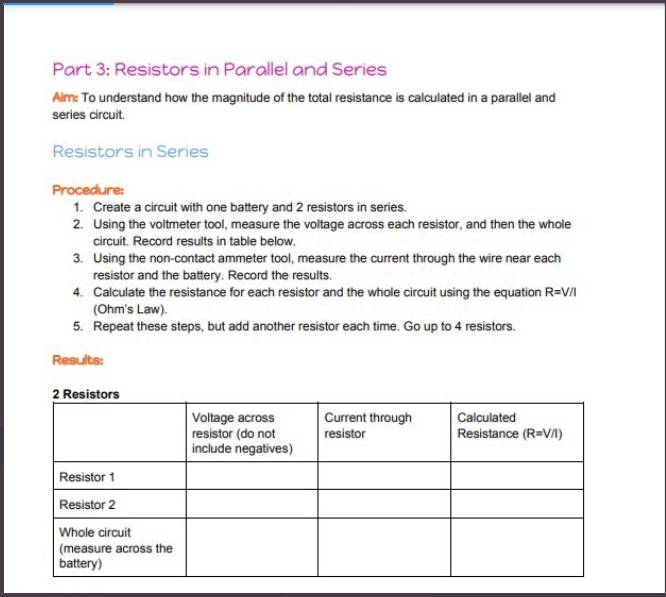
Transcribed Image Text:Part 3: Resistors in Parallel and Series
Alm: To understand how the magnitude of the total resistance is calculated in a parallel and
series circuit.
Resistors in Series
Procedure:
1. Create a circuit with one battery and 2 resistors in series.
2. Using the voltmeter tool, measure the voltage across each resistor, and then the whole
circuit. Record results in table below.
3. Using the non-contact ammeter tool, measure the current through the wire near each
resistor and the battery. Record the results.
4. Calculate the resistance for each resistor and the whole circuit using the equation R=VI
(Ohm's Law).
5. Repeat these steps, but add another resistor each time. Go up to 4 resistors.
Results:
2 Resistors
Current through
resistor
Calculated
Voltage across
resistor (do not
include negatives)
Resistance (R=V/)
Resistor 1
Resistor 2
Whole circuit
(measure across the
battery)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning