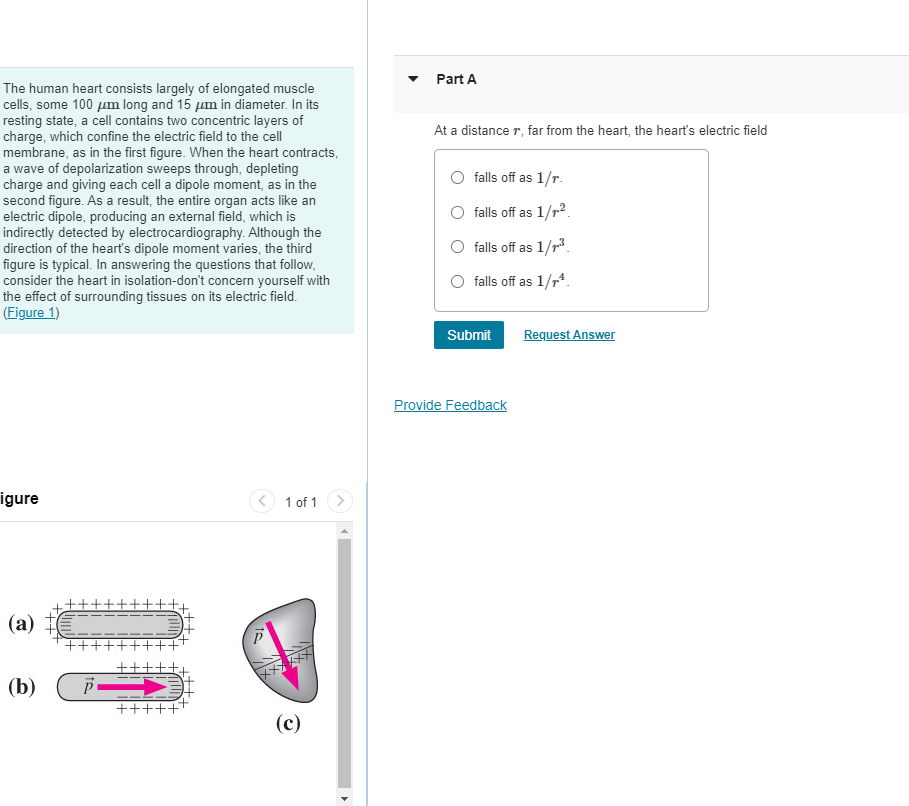
Part A The human heart consists largely of elongated muscle cells, some 100 µm long and 15 um in diameter. In its resting state, a cell contains two concentric layers of charge, which confine the electric field to the cell membrane, as in the first figure. When the heart contracts, a wave of depolarization sweeps through, depleting charge and giving each cell a dipole moment, as in the second figure. As a result, the entire organ acts like an electric dipole, producing an external field, which is indirectly detected by electrocardiography. Although the direction of the heart's dipole moment varies, the third figure is typical. In answering the questions that follow, consider the heart in isolation-don't concern yourself with the effect of surrounding tissues on its electric field. (Figure 1) At a distance r, far from the heart, the heart's electric field falls off as 1/r. falls off as 1/r?. falls off as 1/r3. falls off as 1/r*. Submit Request Answer
Part A The human heart consists largely of elongated muscle cells, some 100 µm long and 15 um in diameter. In its resting state, a cell contains two concentric layers of charge, which confine the electric field to the cell membrane, as in the first figure. When the heart contracts, a wave of depolarization sweeps through, depleting charge and giving each cell a dipole moment, as in the second figure. As a result, the entire organ acts like an electric dipole, producing an external field, which is indirectly detected by electrocardiography. Although the direction of the heart's dipole moment varies, the third figure is typical. In answering the questions that follow, consider the heart in isolation-don't concern yourself with the effect of surrounding tissues on its electric field. (Figure 1) At a distance r, far from the heart, the heart's electric field falls off as 1/r. falls off as 1/r?. falls off as 1/r3. falls off as 1/r*. Submit Request Answer
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter7: Analytic Trigonometry
Section7.2: Trigonometric Equations
Problem 97E
Related questions
Question
I am unsure about how to solve the attached calculus question.
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
The human heart consists largely of elongated muscle
cells, some 100 µm long and 15 um in diameter. In its
resting state, a cell contains two concentric layers of
charge, which confine the electric field to the cell
membrane, as in the first figure. When the heart contracts,
a wave of depolarization sweeps through, depleting
charge and giving each cell a dipole moment, as in the
second figure. As a result, the entire organ acts like an
electric dipole, producing an external field, which is
indirectly detected by electrocardiography. Although the
direction of the heart's dipole moment varies, the third
figure is typical. In answering the questions that follow,
consider the heart in isolation-don't concern yourself with
the effect of surrounding tissues on its electric field.
(Figure 1)
At a distance r, far from the heart, the heart's electric field
falls off as 1/r.
falls off as 1/r2.
falls off as 1/r3.
falls off as 1/r*.
Submit
Request Answer
Provide Feedback
igure
1 of 1
(a)
++
(b)
++++++
(c)
Expert Solution
Step 1
We need to choose correct option.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning