C. The inclined plane of line of greatest slope AD is frictionless and AD makes with the horizohlal Ul. a= 30°. Calculate the distance covered by the particle along AD before it stops. The particle reverses the motion towards A, and stops at E between AB. Calculate BE. B. The horizontal path BA-1.5m is rough and the 1or Calculate the speed of the particle at A. Exercise 6: B On an inclined plane AB =1m and of inclination 30° with the horizontal, a solid of mass mı= 600g, initially at A, is connected by means of a massless inextensible string that passes over a light pulley to another solid of mass m-400g initially at the point H (BH= 0.5m). The system is left without initial velocity at t=0. Let the reference level for the gravitational potential encrgy to be the horizontal level passing through AH. Neglect friction. mi Ya=30 H A Exerci We laune m=100g a given ir 1 m Direction of motion Ground A' B' energy EF A. Determine the mechanical energy of the system (m1, m2, pulley, ground) at any time t as a function of x and v (x is the distance covered by m on the inclined plane and v is the velocity at this instant. B. Using the principle of conservation of energy, determine the acceleration of the solid mi. C. What is the speed of m2 when it reaches the ground? D. Use Newton's Law F = Mã to determine the tension in the string connecting mi. %3D Exercise 7: A block falls, starting from rest, fron of force constant
C. The inclined plane of line of greatest slope AD is frictionless and AD makes with the horizohlal Ul. a= 30°. Calculate the distance covered by the particle along AD before it stops. The particle reverses the motion towards A, and stops at E between AB. Calculate BE. B. The horizontal path BA-1.5m is rough and the 1or Calculate the speed of the particle at A. Exercise 6: B On an inclined plane AB =1m and of inclination 30° with the horizontal, a solid of mass mı= 600g, initially at A, is connected by means of a massless inextensible string that passes over a light pulley to another solid of mass m-400g initially at the point H (BH= 0.5m). The system is left without initial velocity at t=0. Let the reference level for the gravitational potential encrgy to be the horizontal level passing through AH. Neglect friction. mi Ya=30 H A Exerci We laune m=100g a given ir 1 m Direction of motion Ground A' B' energy EF A. Determine the mechanical energy of the system (m1, m2, pulley, ground) at any time t as a function of x and v (x is the distance covered by m on the inclined plane and v is the velocity at this instant. B. Using the principle of conservation of energy, determine the acceleration of the solid mi. C. What is the speed of m2 when it reaches the ground? D. Use Newton's Law F = Mã to determine the tension in the string connecting mi. %3D Exercise 7: A block falls, starting from rest, fron of force constant
Related questions
Question
Can u solve the whole question for me
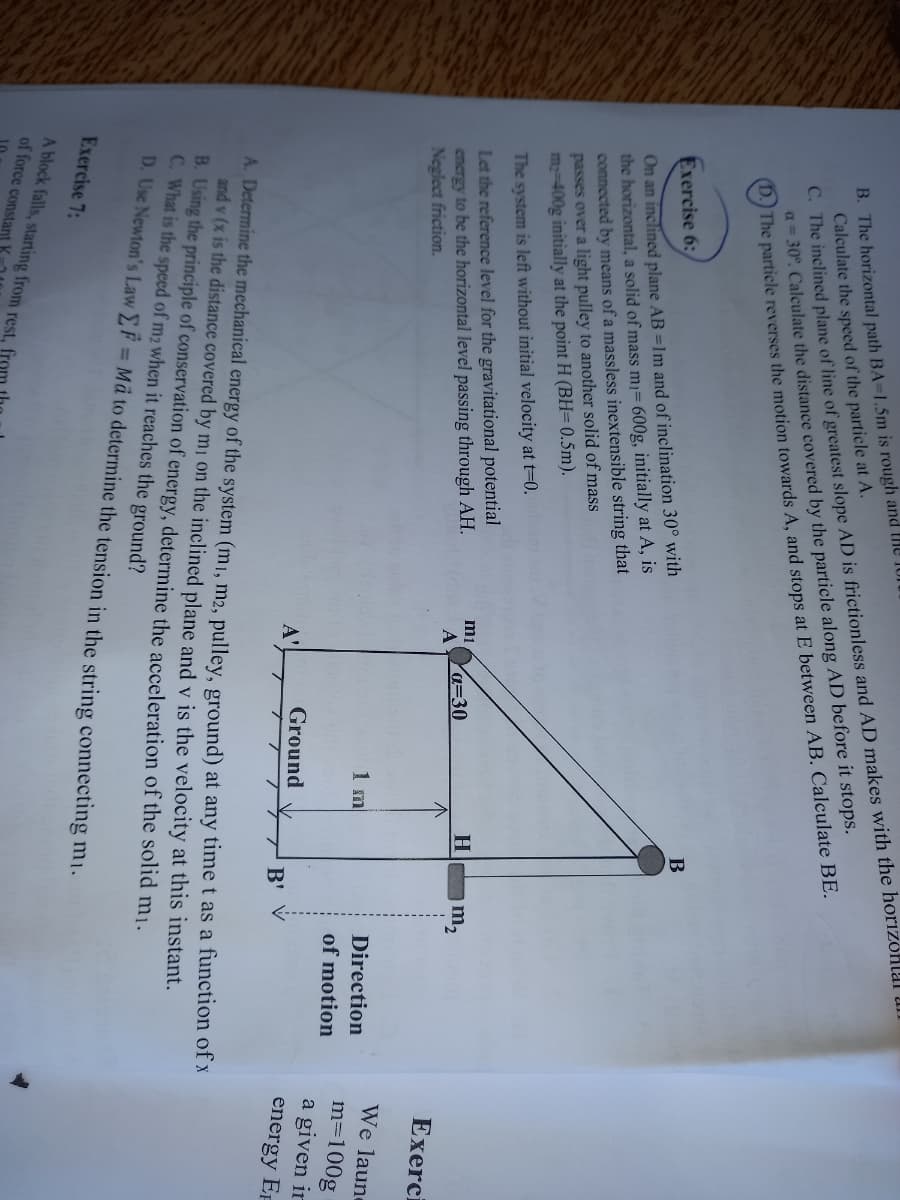
Transcribed Image Text:C. The inclined plane of line of greatest slope AD is frictionless and AD makes with the horizohlal Ul.
a= 30°. Calculate the distance covered by the particle along AD before it stops.
The particle reverses the motion towards A, and stops at E between AB. Calculate BE.
B. The horizontal path BA-1.5m is rough and the 1or
Calculate the speed of the particle at A.
Exercise 6:
B
On an inclined plane AB =1m and of inclination 30° with
the horizontal, a solid of mass mı= 600g, initially at A, is
connected by means of a massless inextensible string that
passes over a light pulley to another solid of mass
m-400g initially at the point H (BH= 0.5m).
The system is left without initial velocity at t=0.
Let the reference level for the gravitational potential
encrgy to be the horizontal level passing through AH.
Neglect friction.
mi
Ya=30
H
A
Exerci
We laune
m=100g
a given ir
1 m
Direction
of motion
Ground
A'
B'
energy EF
A. Determine the mechanical energy of the system (m1, m2, pulley, ground) at any time t as a function of x
and v (x is the distance covered by m on the inclined plane and v is the velocity at this instant.
B. Using the principle of conservation of energy, determine the acceleration of the solid mi.
C. What is the speed of m2 when it reaches the ground?
D. Use Newton's Law F = Mã to determine the tension in the string connecting mi.
%3D
Exercise 7:
A block falls, starting from rest, fron
of force constant
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps
