piecewise continuously differentiable and, absolutely integrable
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter6: The Trigonometric Functions
Section6.6: Additional Trigonometric Graphs
Problem 77E
Related questions
Question
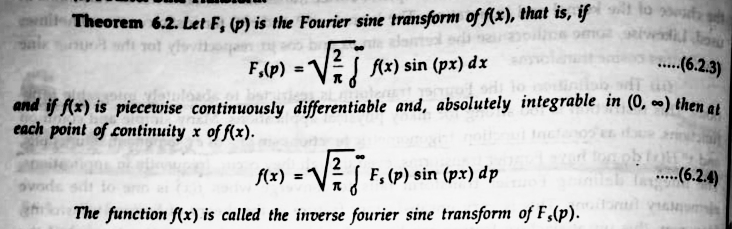
Transcribed Image Text:InTheorem 6.2. Let F, (p) is the Fourier sine transform of f(x), that is, if lo st
elatl sd
(x) sin (px) dx
F,(p)
..(6.2.3)
and if (x) is piecewise continuously differentiable and, absolutely integrable in (0, -) then at
each point of continuity x of f(x).
f(x)
F, (p) sin (px) dp
... (6.2.4)
The function f(x) is called the inverse fourier sine transform of F,(p).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage