Prince, aged 35 years, weighs approximately 185 pounds and 173 cm tall. Prince is a post-graduate student, walking approximately 2 km to university every weekdays and doing a part-time job at a supermarket that requires him lifting boxes to the shelves in the evening. (a) Calculate the estimated energy requirement (EER) by using the following Harris-Benedict equation for the calculation of basal metabolic rate (BMR) and physical activity table. (b) Determine whether Prince has energy balance at equilibrium, positive or negative energy balance if his total energy for the day comes from 320 gram (carbohydrates), 205 gram (proteins), 90 gram (fats) and 58 gram (alcohol). *1 pound = 0.453 Harris-Benedict Equation (Formula Harris-Benedict): Males : 66 + (13.7 x W) + (5 x H) - (6.8 x A) Females : 655 + (9.6 x W) + (1.7 x H) – (4.7 x A) W = actual weight (kg), H = height (cm), A = age (years) Energy cost of PA (% of BMR) Men Women Sedentary Involves sitting, driving or very low levels of activity 25-40 25-35 50-70 40-60 Lightly active Involves a lot of sitting, may involve some walking, moving around and light lifting Moderately active Involves work plus intentional exercise, such as an hour of walking /walking 4-5 days per week, may have job requiring some physical labor 65-80 50-70 come vavly active Involves great deal of physical labor such as regular heavy 90-120 80-100 lifting and digging Exceptionally active Involves a lot of physical activities for work & intentional exercise, applies to athletes who train for many hours/day 130-145 110-130
Prince, aged 35 years, weighs approximately 185 pounds and 173 cm tall. Prince is a post-graduate student, walking approximately 2 km to university every weekdays and doing a part-time job at a supermarket that requires him lifting boxes to the shelves in the evening. (a) Calculate the estimated energy requirement (EER) by using the following Harris-Benedict equation for the calculation of basal metabolic rate (BMR) and physical activity table. (b) Determine whether Prince has energy balance at equilibrium, positive or negative energy balance if his total energy for the day comes from 320 gram (carbohydrates), 205 gram (proteins), 90 gram (fats) and 58 gram (alcohol). *1 pound = 0.453 Harris-Benedict Equation (Formula Harris-Benedict): Males : 66 + (13.7 x W) + (5 x H) - (6.8 x A) Females : 655 + (9.6 x W) + (1.7 x H) – (4.7 x A) W = actual weight (kg), H = height (cm), A = age (years) Energy cost of PA (% of BMR) Men Women Sedentary Involves sitting, driving or very low levels of activity 25-40 25-35 50-70 40-60 Lightly active Involves a lot of sitting, may involve some walking, moving around and light lifting Moderately active Involves work plus intentional exercise, such as an hour of walking /walking 4-5 days per week, may have job requiring some physical labor 65-80 50-70 come vavly active Involves great deal of physical labor such as regular heavy 90-120 80-100 lifting and digging Exceptionally active Involves a lot of physical activities for work & intentional exercise, applies to athletes who train for many hours/day 130-145 110-130
Chapter21: Carbohydrate- Controlled Diets For Diabetes Mellitus
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CA
Related questions
Question
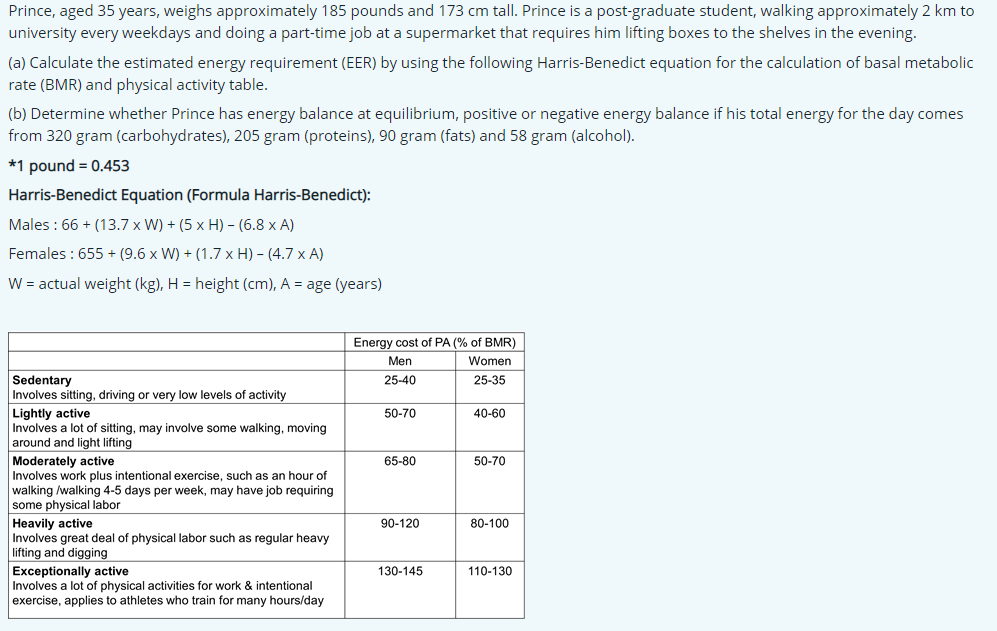
Transcribed Image Text:Prince, aged 35 years, weighs approximately 185 pounds and 173 cm tall. Prince is a post-graduate student, walking approximately 2 km to
university every weekdays and doing a part-time job at a supermarket that requires him lifting boxes to the shelves in the evening.
(a) Calculate the estimated energy requirement (EER) by using the following Harris-Benedict equation for the calculation of basal metabolic
rate (BMR) and physical activity table.
(b) Determine whether Prince has energy balance at equilibrium, positive or negative energy balance if his total energy for the day comes
from 320 gram (carbohydrates), 205 gram (proteins), 90 gram (fats) and 58 gram (alcohol).
*1 pound = 0.453
Harris-Benedict Equation (Formula Harris-Benedict):
Males : 66 + (13.7 x W) + (5 x H) - (6.8 x A)
Females : 655 + (9.6 x W) + (1.7 x H) – (4.7 x A)
W = actual weight (kg), H = height (cm), A = age (years)
Energy cost of PA (% of BMR)
Men
Women
Sedentary
Involves sitting, driving or very low levels of activity
25-40
25-35
50-70
40-60
Lightly active
Involves a lot of sitting, may involve some walking, moving
around and light lifting
Moderately active
Involves work plus intentional exercise, such as an hour of
walking /walking 4-5 days per week, may have job requiring
some physical labor
65-80
50-70
Heavily active
Involves great deal of physical labor such as regular heavy
lifting and digging
90-120
80-100
Exceptionally active
Involves a lot of physical activities for work
exercise, applies to athletes who train for many hours/day
130-145
110-130
intentional
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Nutritional Sciences: From Fundamentals to Food, …
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:
9781337486415
Author:
McGuire
Publisher:
Cengage

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Nutritional Sciences: From Fundamentals to Food, …
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:
9781337486415
Author:
McGuire
Publisher:
Cengage

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning